Passive House certification focuses on rigorous energy efficiency standards that drastically reduce a building's ecological footprint through superior insulation, airtight construction, and balanced ventilation. LEED certification encompasses a broader scope including sustainable site development, water savings, energy efficiency, and indoor environmental quality designed to promote overall green building practices. Explore the critical differences and benefits of Passive House versus LEED Certification to determine the best strategy for sustainable entrepreneurship.
Why it is important
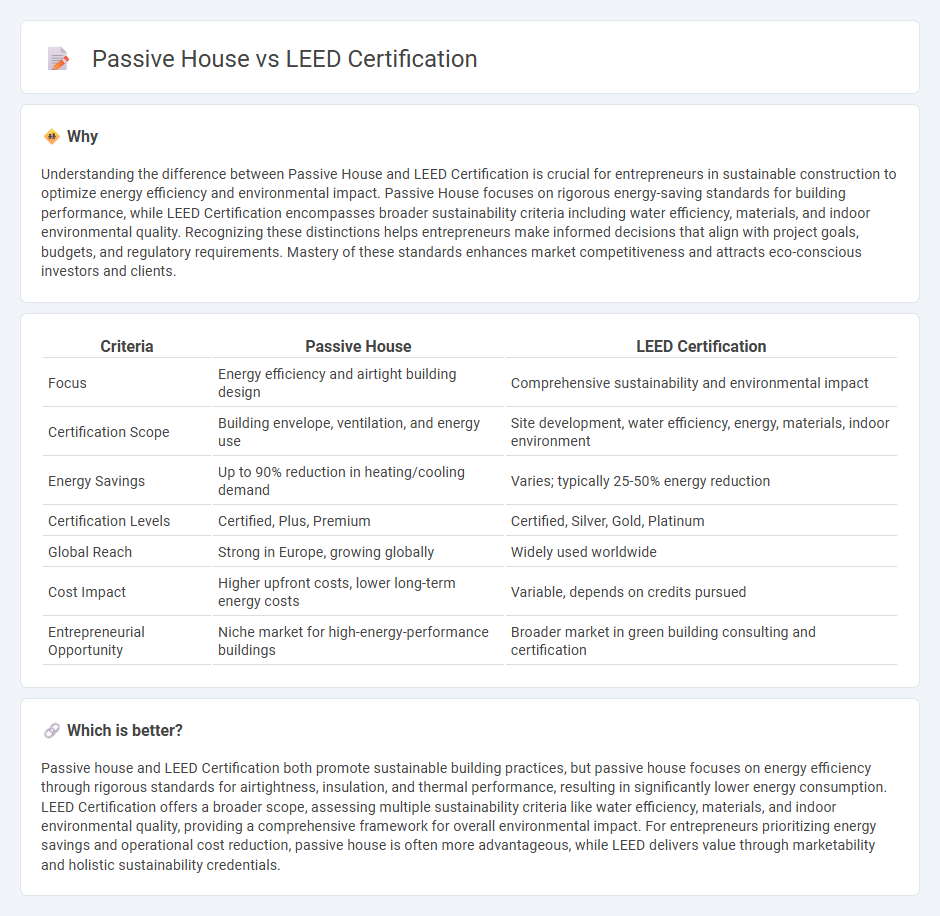
Understanding the difference between Passive House and LEED Certification is crucial for entrepreneurs in sustainable construction to optimize energy efficiency and environmental impact. Passive House focuses on rigorous energy-saving standards for building performance, while LEED Certification encompasses broader sustainability criteria including water efficiency, materials, and indoor environmental quality. Recognizing these distinctions helps entrepreneurs make informed decisions that align with project goals, budgets, and regulatory requirements. Mastery of these standards enhances market competitiveness and attracts eco-conscious investors and clients.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Passive House | LEED Certification |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Energy efficiency and airtight building design | Comprehensive sustainability and environmental impact |
| Certification Scope | Building envelope, ventilation, and energy use | Site development, water efficiency, energy, materials, indoor environment |
| Energy Savings | Up to 90% reduction in heating/cooling demand | Varies; typically 25-50% energy reduction |
| Certification Levels | Certified, Plus, Premium | Certified, Silver, Gold, Platinum |
| Global Reach | Strong in Europe, growing globally | Widely used worldwide |
| Cost Impact | Higher upfront costs, lower long-term energy costs | Variable, depends on credits pursued |
| Entrepreneurial Opportunity | Niche market for high-energy-performance buildings | Broader market in green building consulting and certification |
Which is better?
Passive house and LEED Certification both promote sustainable building practices, but passive house focuses on energy efficiency through rigorous standards for airtightness, insulation, and thermal performance, resulting in significantly lower energy consumption. LEED Certification offers a broader scope, assessing multiple sustainability criteria like water efficiency, materials, and indoor environmental quality, providing a comprehensive framework for overall environmental impact. For entrepreneurs prioritizing energy savings and operational cost reduction, passive house is often more advantageous, while LEED delivers value through marketability and holistic sustainability credentials.
Connection
Passive House and LEED Certification both emphasize sustainable building practices that enhance energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Entrepreneurs in green construction leverage Passive House's rigorous energy performance standards alongside LEED's holistic approach to sustainability, including water efficiency, indoor air quality, and material selection. Combining these certifications helps businesses meet increasing market demand for eco-friendly buildings while optimizing operational costs and regulatory compliance.
Key Terms
Energy Efficiency
LEED Certification emphasizes a comprehensive approach to energy efficiency within sustainable building practices by integrating performance metrics, renewable energy usage, and building envelope improvements. Passive House standards specifically target rigorous energy reduction through superior insulation, airtight construction, and heat recovery ventilation systems, often achieving up to 90% energy savings compared to conventional buildings. Explore detailed comparisons of these two frameworks to determine which energy efficiency strategy best suits your project goals.
Sustainability Standards
LEED Certification emphasizes a comprehensive sustainability framework covering energy efficiency, water conservation, and indoor environmental quality with a points-based system guiding green building practices. Passive House certification prioritizes rigorous energy performance, focusing on ultra-low energy use for heating and cooling through high insulation, airtightness, and advanced ventilation systems, ensuring minimal ecological impact. Explore the key differences to determine which sustainability standard best fits your building goals.
Building Performance
LEED Certification evaluates building performance through sustainability metrics such as energy efficiency, water usage, and indoor environmental quality to reduce environmental impact. Passive House standards concentrate on maximizing energy efficiency by minimizing heating and cooling demands through superior insulation, airtightness, and high-performance windows. Explore the detailed differences to understand which certification best suits your building performance goals.
Source and External Links
LEED certification: meaning and requirements - Greenly - LEED Certification is a sustainability rating system with four levels of recognition, awarded upon project compliance with green building principles that include reducing CO2 emissions and improving energy efficiency in various building types.
LEED - Wikipedia - LEED is a global green building certification program awarding Certified, Silver, Gold, and Platinum levels based on points earned for meeting prerequisites and environmental impact criteria related to energy, water, and material efficiency.
What is LEED certification, and how do you get it? - WeWork - LEED Certification uses a point system starting at 40 points for certification, covering building sustainability factors like energy, water, and environmental impact, and provides four certification tiers from Certified to Platinum based on earned points.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com