Entrepreneurship in sustainable housing explores the innovative contrast between passive houses and off-grid homes, emphasizing energy efficiency and self-sufficiency. Passive houses utilize advanced insulation and ventilation systems to minimize energy consumption within connected infrastructures. Discover deeper insights into how these eco-friendly building models drive entrepreneurial opportunities and environmental impact.
Why it is important
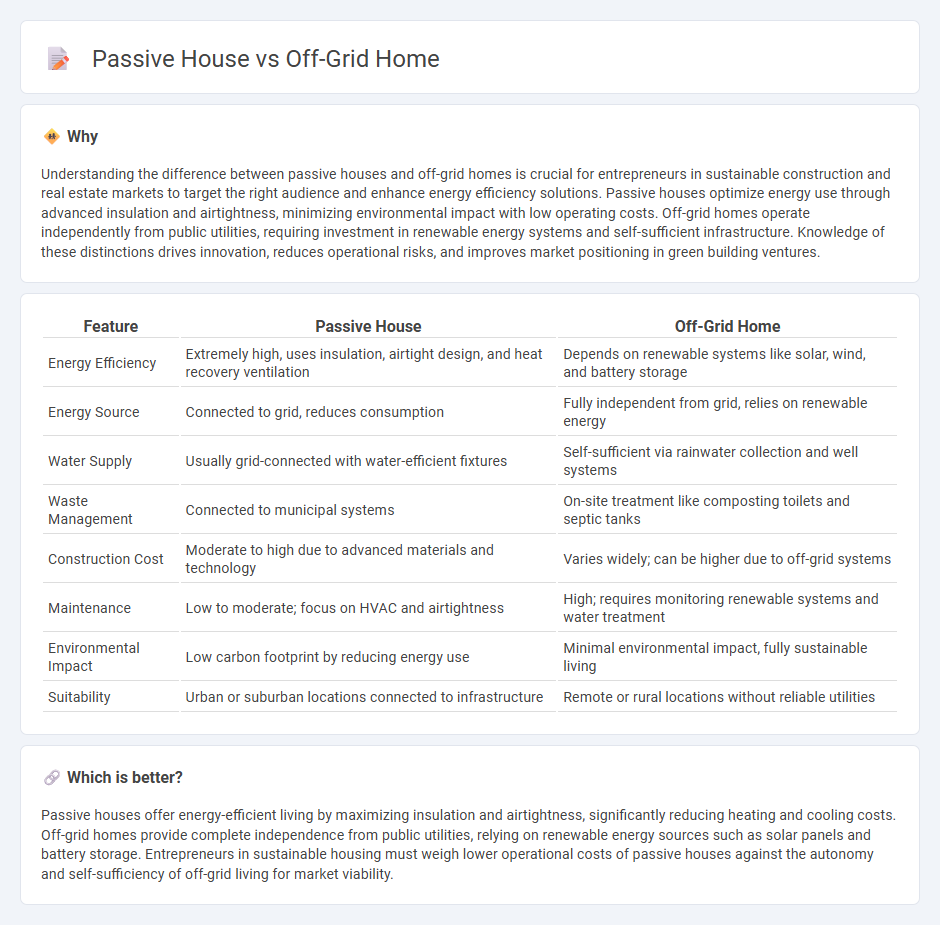
Understanding the difference between passive houses and off-grid homes is crucial for entrepreneurs in sustainable construction and real estate markets to target the right audience and enhance energy efficiency solutions. Passive houses optimize energy use through advanced insulation and airtightness, minimizing environmental impact with low operating costs. Off-grid homes operate independently from public utilities, requiring investment in renewable energy systems and self-sufficient infrastructure. Knowledge of these distinctions drives innovation, reduces operational risks, and improves market positioning in green building ventures.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Passive House | Off-Grid Home |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Extremely high, uses insulation, airtight design, and heat recovery ventilation | Depends on renewable systems like solar, wind, and battery storage |
| Energy Source | Connected to grid, reduces consumption | Fully independent from grid, relies on renewable energy |
| Water Supply | Usually grid-connected with water-efficient fixtures | Self-sufficient via rainwater collection and well systems |
| Waste Management | Connected to municipal systems | On-site treatment like composting toilets and septic tanks |
| Construction Cost | Moderate to high due to advanced materials and technology | Varies widely; can be higher due to off-grid systems |
| Maintenance | Low to moderate; focus on HVAC and airtightness | High; requires monitoring renewable systems and water treatment |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint by reducing energy use | Minimal environmental impact, fully sustainable living |
| Suitability | Urban or suburban locations connected to infrastructure | Remote or rural locations without reliable utilities |
Which is better?
Passive houses offer energy-efficient living by maximizing insulation and airtightness, significantly reducing heating and cooling costs. Off-grid homes provide complete independence from public utilities, relying on renewable energy sources such as solar panels and battery storage. Entrepreneurs in sustainable housing must weigh lower operational costs of passive houses against the autonomy and self-sufficiency of off-grid living for market viability.
Connection
Entrepreneurship in the sustainable housing sector drives innovations in Passive House and Off-Grid Home technologies by focusing on energy efficiency and self-sufficiency. Passive House standards minimize energy consumption through airtight construction and high insulation, reducing dependency on external energy sources. Off-Grid Homes complement this by integrating renewable energy systems like solar panels and rainwater harvesting, creating autonomous living solutions that attract eco-conscious consumers and investors.
Key Terms
Energy Independence
Off-grid homes achieve energy independence by generating and storing their own power through solar panels, wind turbines, and battery systems, allowing complete disconnection from utility grids. Passive houses optimize energy efficiency with superinsulation, airtight construction, and heat recovery ventilation, drastically reducing the need for external energy but often still depend on grid electricity. Explore how both approaches balance energy autonomy and sustainability to find the best solution for your eco-friendly living goals.
Building Envelope
An off-grid home prioritizes self-sufficiency with robust insulation, airtight construction, and materials that support energy independence, often incorporating solar panels and battery storage for power. Passive houses emphasize a highly optimized building envelope, featuring triple-glazed windows, continuous insulation, and advanced ventilation systems to achieve minimal energy consumption and a comfortable indoor climate. Discover the critical differences in building envelope design to enhance your sustainable living goals.
Renewable Systems
Off-grid homes rely entirely on renewable energy systems such as solar panels, wind turbines, and battery storage to maintain energy independence without connection to the utility grid. Passive houses focus primarily on energy efficiency through high-performance insulation, airtight construction, and heat recovery ventilation, significantly reducing the demand for renewable energy but often still connected to the grid. Discover how integrating renewable technologies in both off-grid and passive house designs can optimize sustainability and energy autonomy.
Source and External Links
The Ultimate Guide to Off-Grid Homes - An off-grid home is defined by its disconnection from public utilities and typically relies on solar panels, wind turbines, or other renewable sources for power, with key benefits including financial freedom and a reduced carbon footprint.
Self-Sufficient Man Built an Off-Grid Tiny House - Anders built a self-sufficient off-grid tiny house using sustainable materials, equipped with solar power, rainwater collection, wood heating, and a composting toilet while growing much of his own food.
Reality Check on Building a Family-Sized Home Off-Grid - Building a family-sized off-grid home requires careful planning around power needs, including a large enough generator and system to support property usage and renters without constant energy management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com