Entrepreneurship in sustainable construction highlights the growing interest in Passive Houses and Modular Homes, two innovative approaches that enhance energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Passive Houses focus on airtight design and superior insulation to minimize energy consumption, while Modular Homes emphasize speed and cost-effectiveness through factory-built components. Explore how these models reshape green building opportunities and investment potential.
Why it is important
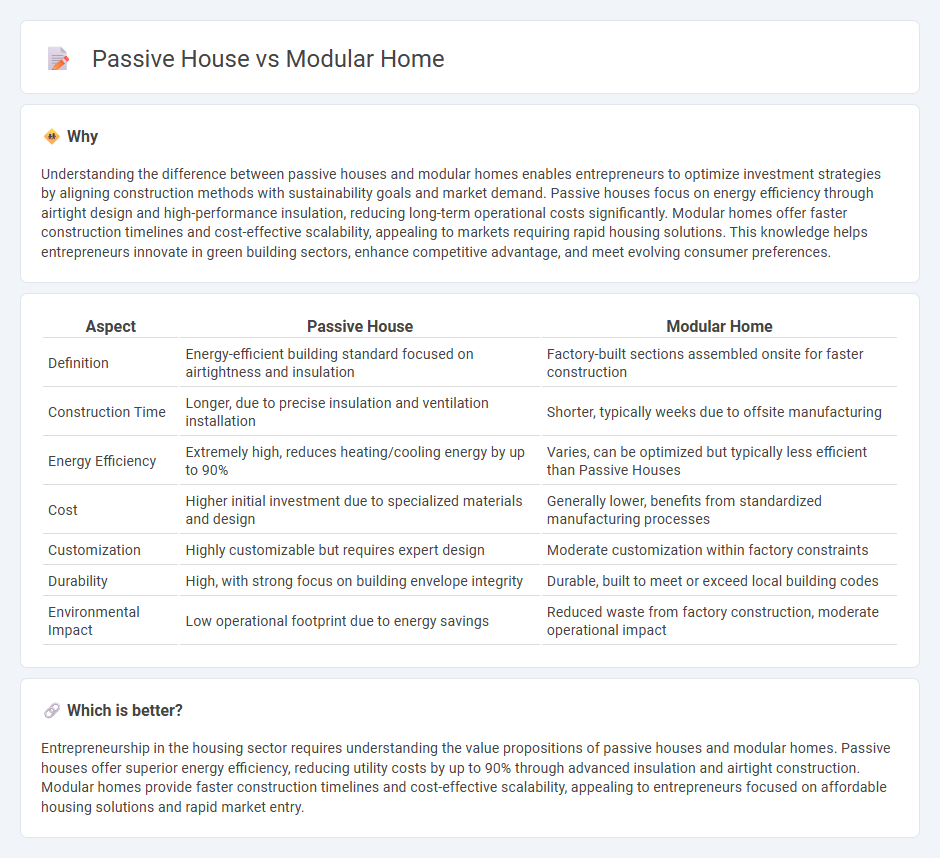
Understanding the difference between passive houses and modular homes enables entrepreneurs to optimize investment strategies by aligning construction methods with sustainability goals and market demand. Passive houses focus on energy efficiency through airtight design and high-performance insulation, reducing long-term operational costs significantly. Modular homes offer faster construction timelines and cost-effective scalability, appealing to markets requiring rapid housing solutions. This knowledge helps entrepreneurs innovate in green building sectors, enhance competitive advantage, and meet evolving consumer preferences.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Passive House | Modular Home |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Energy-efficient building standard focused on airtightness and insulation | Factory-built sections assembled onsite for faster construction |
| Construction Time | Longer, due to precise insulation and ventilation installation | Shorter, typically weeks due to offsite manufacturing |
| Energy Efficiency | Extremely high, reduces heating/cooling energy by up to 90% | Varies, can be optimized but typically less efficient than Passive Houses |
| Cost | Higher initial investment due to specialized materials and design | Generally lower, benefits from standardized manufacturing processes |
| Customization | Highly customizable but requires expert design | Moderate customization within factory constraints |
| Durability | High, with strong focus on building envelope integrity | Durable, built to meet or exceed local building codes |
| Environmental Impact | Low operational footprint due to energy savings | Reduced waste from factory construction, moderate operational impact |
Which is better?
Entrepreneurship in the housing sector requires understanding the value propositions of passive houses and modular homes. Passive houses offer superior energy efficiency, reducing utility costs by up to 90% through advanced insulation and airtight construction. Modular homes provide faster construction timelines and cost-effective scalability, appealing to entrepreneurs focused on affordable housing solutions and rapid market entry.
Connection
Entrepreneurship in the housing industry leverages Passive House and Modular Home concepts to innovate energy-efficient, sustainable living solutions. Passive House standards drastically reduce energy consumption, while Modular Homes allow for rapid, cost-effective construction, appealing to eco-conscious consumers and investors. Combining these approaches fosters scalable business models that address environmental concerns and market demand for affordable, green housing.
Key Terms
Energy Efficiency
Modular homes often incorporate energy-efficient materials and construction techniques but may not meet the rigorous performance standards of passive houses, which are designed to minimize energy consumption through superior insulation, airtightness, and heat recovery ventilation systems. Passive houses achieve up to 90% energy savings compared to traditional buildings, making them the optimal choice for sustainable living. Explore the distinct energy benefits of modular and passive homes to determine which aligns best with your eco-friendly goals.
Building Standards
Modular homes adhere to stringent building standards emphasizing factory precision, energy efficiency, and rapid construction, typically meeting or exceeding local building codes through prefabricated components. Passive houses follow rigorous international energy standards focusing on ultra-low energy consumption, airtightness, superior insulation, and mechanical ventilation with heat recovery to drastically reduce heating and cooling demands. Discover how these building standards impact cost, sustainability, and comfort by exploring further details.
Construction Method
Modular homes are built using prefabricated sections manufactured in a factory setting, allowing for faster assembly and consistent quality control compared to traditional construction. Passive houses emphasize energy efficiency with airtight construction, superior insulation, and advanced ventilation systems to minimize energy consumption. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which construction method suits your sustainable living goals.
Source and External Links
Modular Homes - Champion Homes - A modular home is a high-quality, factory-built home constructed in sections that meet the same local building codes as traditional homes, offering innovative design, energy efficiency, and affordability.
Modular Home Floorplans | Modular Home Layouts | Next Modular - Modular homes provide affordable, customizable floorplans with options like turn-key or home-only packages, enabling buyers to tailor design, finishes, and layouts to their lifestyle while enjoying a streamlined building process.
Modular Home Builders Association- Learn About Modular Homes - Modular homes are the future of housing, built quickly in factory settings with minimal material waste, offering sustainable, durable, and affordable alternatives to traditional site-built homes with over 30% faster construction times.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com