Remote-first companies prioritize flexible work from any location while maintaining a cohesive company culture through digital tools, ensuring productivity regardless of physical presence. Virtual companies operate entirely online without a centralized office, relying heavily on cloud-based platforms to manage workflows and team collaboration. Explore the key distinctions and advantages of each model to optimize your entrepreneurial strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between a remote-first company and a virtual company is crucial for entrepreneurs to design effective operational strategies and optimize team productivity. Remote-first companies prioritize remote work as the default mode of operation, maintaining a centralized digital infrastructure and often retaining physical offices. Virtual companies operate entirely online without any physical office space, relying exclusively on digital tools for communication and collaboration. This distinction impacts talent acquisition, company culture, technology investment, and scalability approaches.
Comparison Table
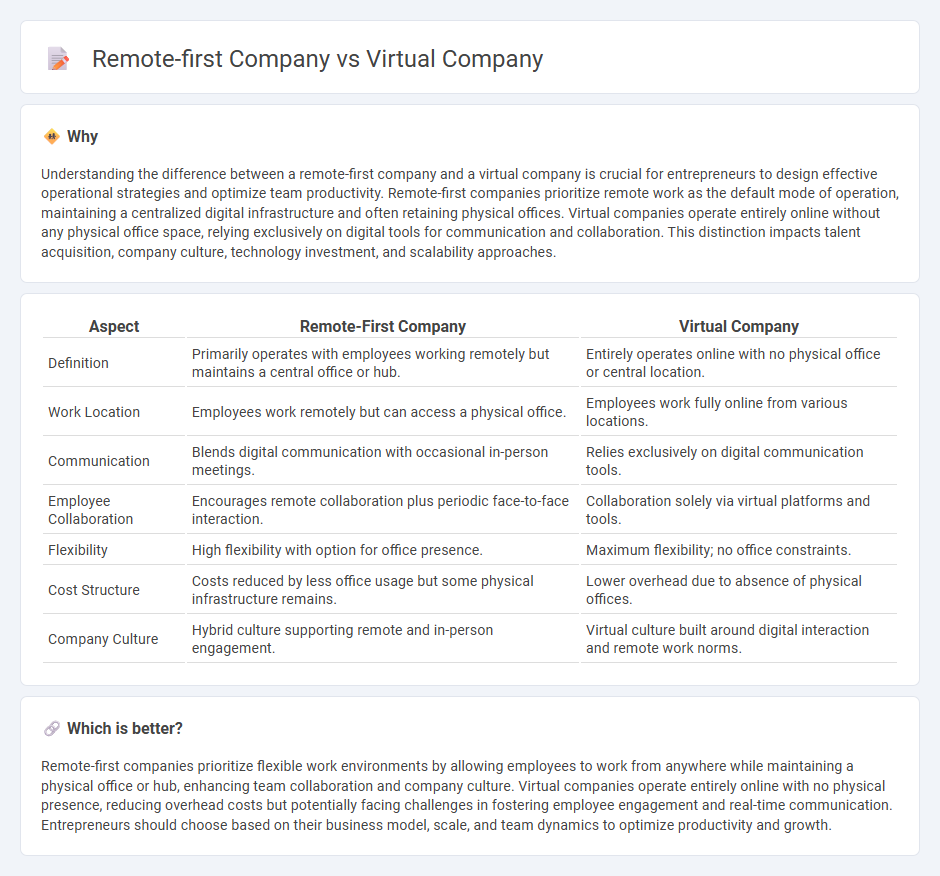
| Aspect | Remote-First Company | Virtual Company |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Primarily operates with employees working remotely but maintains a central office or hub. | Entirely operates online with no physical office or central location. |
| Work Location | Employees work remotely but can access a physical office. | Employees work fully online from various locations. |
| Communication | Blends digital communication with occasional in-person meetings. | Relies exclusively on digital communication tools. |
| Employee Collaboration | Encourages remote collaboration plus periodic face-to-face interaction. | Collaboration solely via virtual platforms and tools. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility with option for office presence. | Maximum flexibility; no office constraints. |
| Cost Structure | Costs reduced by less office usage but some physical infrastructure remains. | Lower overhead due to absence of physical offices. |
| Company Culture | Hybrid culture supporting remote and in-person engagement. | Virtual culture built around digital interaction and remote work norms. |
Which is better?
Remote-first companies prioritize flexible work environments by allowing employees to work from anywhere while maintaining a physical office or hub, enhancing team collaboration and company culture. Virtual companies operate entirely online with no physical presence, reducing overhead costs but potentially facing challenges in fostering employee engagement and real-time communication. Entrepreneurs should choose based on their business model, scale, and team dynamics to optimize productivity and growth.
Connection
Remote-first companies prioritize flexible, location-independent work environments, enabling employees to operate from any location while maintaining cohesive collaboration and productivity. Virtual companies extend this concept by functioning entirely online, leveraging digital tools to manage operations without a physical office, thus embodying the remote-first philosophy at its core. Both models drive entrepreneurial innovation by reducing overhead costs, attracting diverse talent, and accelerating scalability in the evolving digital economy.
Key Terms
Physical Presence
A virtual company operates entirely online without a fixed physical office, relying on digital tools for communication and collaboration across distributed teams. A remote-first company prioritizes remote work but may maintain physical office spaces for occasional in-person meetings or coworking, emphasizing flexibility in work environments. Discover more about the strategic impacts of physical presence on company culture and productivity.
Organizational Structure
A virtual company operates entirely online without a physical headquarters, leveraging digital tools to manage distributed teams across various locations, whereas a remote-first company maintains a physical office but prioritizes remote work as the default mode of operation, fostering flexibility and inclusivity. Virtual companies often rely on asynchronous communication and cloud-based collaboration platforms to ensure seamless organizational workflows, while remote-first firms balance synchronous interactions with occasional in-person meetings for team cohesion. Explore detailed insights on how these organizational structures impact productivity, culture, and scalability.
Communication Workflow
Virtual companies rely heavily on digital communication tools such as Slack, Zoom, and Asana to maintain seamless workflow and collaboration among dispersed teams. Remote-first companies prioritize asynchronous communication, leveraging platforms like Trello and Microsoft Teams to support flexible work schedules across different time zones. Explore how these communication strategies impact productivity and employee engagement in evolving workplace models.
Source and External Links
Virtual business - A virtual company operates primarily online without physical offices, using electronic means to conduct business including virtual worlds and virtual enterprises that connect independent companies through technology.
What is a Virtual Company? The Definite Guide - Virtual companies are businesses that operate fully or partially remotely, often without a physical office, with models ranging from fully remote to hybrid setups blending remote and occasional office work.
Virtual Business: Definition and How It Works - A virtual business runs mostly online, minimizing overhead costs and often using remote employees to adapt to modern technology trends, which is becoming standard for many industries.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com