Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) leverage blockchain technology to enable transparent, member-driven governance without centralized control, whereas limited liability companies (LLCs) provide a traditional legal structure with defined liability protections and established regulatory frameworks. DAOs offer dynamic decision-making through smart contracts and token-based voting, contrasting with LLCs' formal management roles and legal compliance requirements. Explore the distinct advantages and challenges of DAOs versus LLCs to determine the best fit for your entrepreneurial venture.
Why it is important
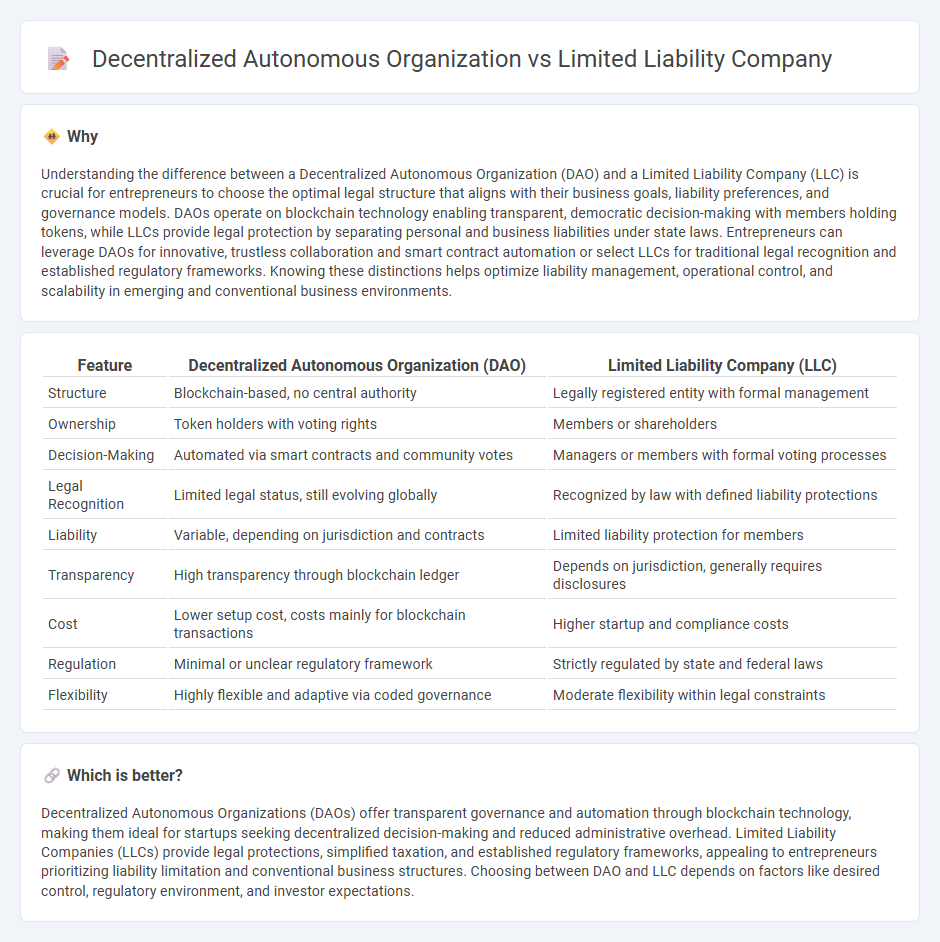
Understanding the difference between a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) and a Limited Liability Company (LLC) is crucial for entrepreneurs to choose the optimal legal structure that aligns with their business goals, liability preferences, and governance models. DAOs operate on blockchain technology enabling transparent, democratic decision-making with members holding tokens, while LLCs provide legal protection by separating personal and business liabilities under state laws. Entrepreneurs can leverage DAOs for innovative, trustless collaboration and smart contract automation or select LLCs for traditional legal recognition and established regulatory frameworks. Knowing these distinctions helps optimize liability management, operational control, and scalability in emerging and conventional business environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) | Limited Liability Company (LLC) |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Blockchain-based, no central authority | Legally registered entity with formal management |
| Ownership | Token holders with voting rights | Members or shareholders |
| Decision-Making | Automated via smart contracts and community votes | Managers or members with formal voting processes |
| Legal Recognition | Limited legal status, still evolving globally | Recognized by law with defined liability protections |
| Liability | Variable, depending on jurisdiction and contracts | Limited liability protection for members |
| Transparency | High transparency through blockchain ledger | Depends on jurisdiction, generally requires disclosures |
| Cost | Lower setup cost, costs mainly for blockchain transactions | Higher startup and compliance costs |
| Regulation | Minimal or unclear regulatory framework | Strictly regulated by state and federal laws |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and adaptive via coded governance | Moderate flexibility within legal constraints |
Which is better?
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) offer transparent governance and automation through blockchain technology, making them ideal for startups seeking decentralized decision-making and reduced administrative overhead. Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) provide legal protections, simplified taxation, and established regulatory frameworks, appealing to entrepreneurs prioritizing liability limitation and conventional business structures. Choosing between DAO and LLC depends on factors like desired control, regulatory environment, and investor expectations.
Connection
A Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) and a Limited Liability Company (LLC) are connected through hybrid legal frameworks that combine blockchain governance with traditional corporate structures. DAOs leverage smart contracts for decentralized decision-making, while LLCs provide legal recognition and liability protection, enabling DAOs to operate within existing regulatory environments. This integration allows entrepreneurs to innovate in organizational management while ensuring compliance and investor confidence.
Key Terms
Legal structure
A limited liability company (LLC) is a legally recognized business entity that combines the liability protection of a corporation with the tax efficiencies and operational flexibility of a partnership, governed by state laws and managed by members or appointed managers. A decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) operates through smart contracts on a blockchain, enabling automated decision-making and governance without centralized control, often lacking formal legal recognition depending on jurisdiction. Explore the evolving legal frameworks to understand how these distinct structures align with your business or investment goals.
Governance
A Limited Liability Company (LLC) features a traditional governance structure managed by appointed members or managers, offering clear legal frameworks and liability protections. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) operate through blockchain technology, enabling transparent, community-driven decision-making with smart contracts automating governance processes. Explore the detailed distinctions in governance between LLCs and DAOs to understand their strategic advantages.
Liability
Limited liability companies (LLCs) protect members by limiting personal liability for business debts and legal actions, ensuring only the company's assets are at risk. Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) provide limited personal liability owing to their blockchain-based structure, but regulatory uncertainty means members may face risks depending on jurisdiction. Explore the evolving legal landscapes and liability implications of LLCs and DAOs to understand which structure aligns with your business goals.
Source and External Links
Limited liability company - An LLC is a U.S.-specific business structure combining pass-through taxation of partnerships and limited liability of corporations, offering flexibility and protection to owners.
Limited Liability Company (LLC): What is it, Advantages ... - An LLC protects owners from personal liability for business debts, features flexible management, and benefits from pass-through taxation, making it popular for small businesses.
Limited liability company (LLC) | Internal Revenue Service - The IRS treats LLCs depending on member number and elections as corporations, partnerships, or disregarded entities, with ownership open to a variety of members including individuals and corporations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com