Entrepreneurship in the alternative protein sector is revolutionizing the food industry by developing innovative solutions such as cultured meats and fermented proteins, which offer sustainable and ethical alternatives to traditional animal products. Plant-based foods continue to gain market traction, driven by growing consumer demand for health-conscious and environmentally friendly options, creating vast opportunities for startups and investors. Explore how these dynamic trends are shaping the future of food innovation and investment.
Why it is important
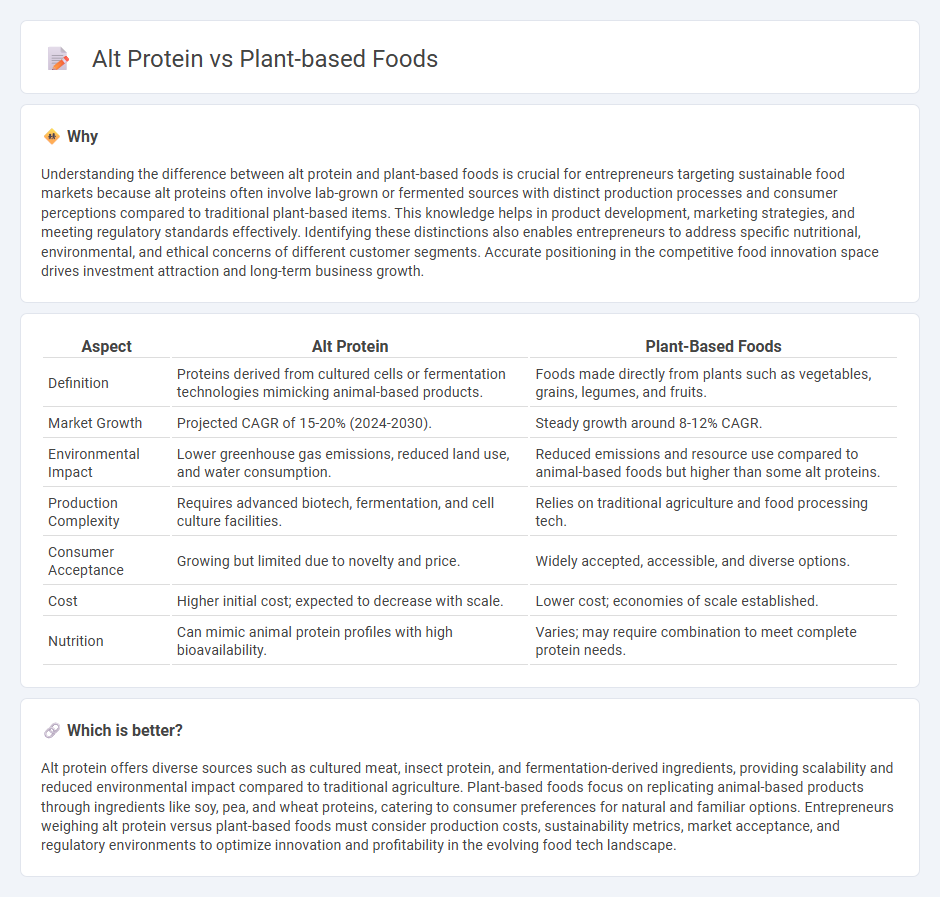
Understanding the difference between alt protein and plant-based foods is crucial for entrepreneurs targeting sustainable food markets because alt proteins often involve lab-grown or fermented sources with distinct production processes and consumer perceptions compared to traditional plant-based items. This knowledge helps in product development, marketing strategies, and meeting regulatory standards effectively. Identifying these distinctions also enables entrepreneurs to address specific nutritional, environmental, and ethical concerns of different customer segments. Accurate positioning in the competitive food innovation space drives investment attraction and long-term business growth.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Alt Protein | Plant-Based Foods |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Proteins derived from cultured cells or fermentation technologies mimicking animal-based products. | Foods made directly from plants such as vegetables, grains, legumes, and fruits. |
| Market Growth | Projected CAGR of 15-20% (2024-2030). | Steady growth around 8-12% CAGR. |
| Environmental Impact | Lower greenhouse gas emissions, reduced land use, and water consumption. | Reduced emissions and resource use compared to animal-based foods but higher than some alt proteins. |
| Production Complexity | Requires advanced biotech, fermentation, and cell culture facilities. | Relies on traditional agriculture and food processing tech. |
| Consumer Acceptance | Growing but limited due to novelty and price. | Widely accepted, accessible, and diverse options. |
| Cost | Higher initial cost; expected to decrease with scale. | Lower cost; economies of scale established. |
| Nutrition | Can mimic animal protein profiles with high bioavailability. | Varies; may require combination to meet complete protein needs. |
Which is better?
Alt protein offers diverse sources such as cultured meat, insect protein, and fermentation-derived ingredients, providing scalability and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional agriculture. Plant-based foods focus on replicating animal-based products through ingredients like soy, pea, and wheat proteins, catering to consumer preferences for natural and familiar options. Entrepreneurs weighing alt protein versus plant-based foods must consider production costs, sustainability metrics, market acceptance, and regulatory environments to optimize innovation and profitability in the evolving food tech landscape.
Connection
Alt protein and plant-based foods are interconnected through their shared goal of offering sustainable, ethical alternatives to traditional animal agriculture. These innovations leverage plant-derived ingredients and advanced food technologies to create products that mimic the taste, texture, and nutritional profile of animal-based foods. The growth of the plant-based sector significantly propels the alt protein market by driving consumer demand for environmentally friendly protein sources.
Key Terms
Sustainability
Plant-based foods contribute significantly to sustainability by reducing greenhouse gas emissions, conserving water, and lowering land use compared to traditional animal agriculture. Alternative proteins, including cultured meat and fermentation-based products, aim to enhance these benefits by offering scalable, resource-efficient options with reduced environmental footprints. Explore how innovations in alt protein technology can further drive sustainable food system transformation.
Consumer Acceptance
Consumer acceptance of plant-based foods hinges on factors like taste, texture, nutritional value, and environmental impact perception compared to traditional meat. Alternative proteins, including cultured meat and insect-based products, often face challenges related to unfamiliarity and skepticism despite their sustainability benefits. Explore how evolving consumer preferences are shaping the future of sustainable protein sources.
Innovation
Plant-based foods leverage natural ingredients like pea and soy proteins to mimic traditional animal products, driving innovation through taste and texture improvements. Alternative protein advancements incorporate novel sources such as cultured meat, mycoprotein, and insect-based proteins, emphasizing sustainability and scalability in food systems. Explore the latest breakthroughs in plant-based and alternative protein innovations to transform your dietary choices.
Source and External Links
How to Start a Plant-Based Diet | GoMacro - A whole-food, plant-based diet centers meals around vegetables, whole grains, fruits, legumes, nuts, and seeds, avoiding meat, fish, dairy, and highly processed foods, focusing on natural and minimally processed plant foods.
Plant-based Protein Infographic | American Heart Association - Plant-based protein sources include beans, legumes, nuts, seeds, tofu, tempeh, and whole grains, which are also rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
Plant-Based Diet: What It Is, Benefits, and Where To Start - ZOE - A plant-based diet prioritizes whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, and oils, with various types including vegan, vegetarian, pescatarian, flexitarian, and Mediterranean diets depending on the inclusion of animal products.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com