Print on demand allows entrepreneurs to create customized products with minimal upfront costs by producing items only after a sale is made, while licensing involves granting permission to use intellectual property in exchange for royalties, often requiring established brand value. Both strategies serve distinct business models: print on demand suits creators seeking direct control over design and inventory, whereas licensing benefits those aiming for passive income through brand extension. Explore further to understand which approach aligns best with your entrepreneurial goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Print on Demand and Licensing is crucial for entrepreneurs to optimize revenue streams and manage intellectual property effectively. Print on Demand allows entrepreneurs to produce and sell custom products without inventory risk, while Licensing grants permission to third parties to use intellectual property for royalties. Knowing these models helps entrepreneurs choose the right strategy for brand control, cost structure, and market reach. Accurate knowledge prevents legal issues and maximizes profitability in product-based businesses.
Comparison Table
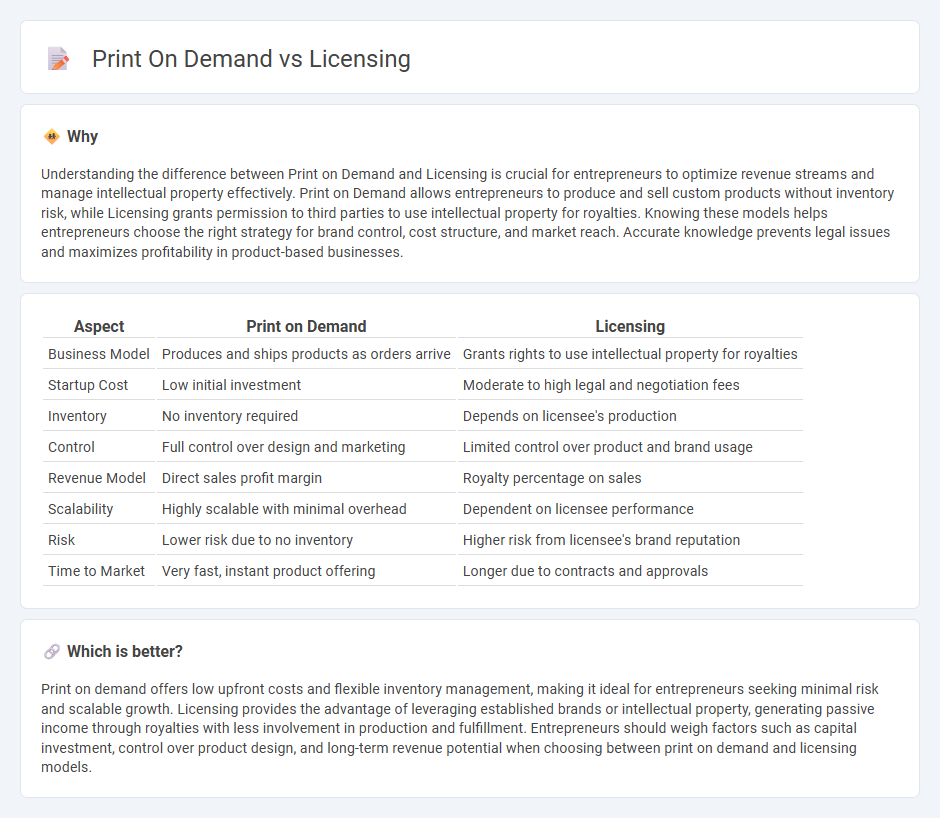
| Aspect | Print on Demand | Licensing |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model | Produces and ships products as orders arrive | Grants rights to use intellectual property for royalties |
| Startup Cost | Low initial investment | Moderate to high legal and negotiation fees |
| Inventory | No inventory required | Depends on licensee's production |
| Control | Full control over design and marketing | Limited control over product and brand usage |
| Revenue Model | Direct sales profit margin | Royalty percentage on sales |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with minimal overhead | Dependent on licensee performance |
| Risk | Lower risk due to no inventory | Higher risk from licensee's brand reputation |
| Time to Market | Very fast, instant product offering | Longer due to contracts and approvals |
Which is better?
Print on demand offers low upfront costs and flexible inventory management, making it ideal for entrepreneurs seeking minimal risk and scalable growth. Licensing provides the advantage of leveraging established brands or intellectual property, generating passive income through royalties with less involvement in production and fulfillment. Entrepreneurs should weigh factors such as capital investment, control over product design, and long-term revenue potential when choosing between print on demand and licensing models.
Connection
Print on demand empowers entrepreneurs to create customized products without inventory risks, while licensing allows them to legally use intellectual property to enhance product appeal. Combining print on demand with licensing agreements enables entrepreneurs to offer unique, brand-recognized merchandise quickly and cost-effectively. This integration boosts revenue opportunities by leveraging popular designs and reducing upfront costs in the entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Key Terms
Intellectual Property
Licensing allows creators to retain intellectual property rights while granting others permission to produce and sell their work, ensuring ongoing control and revenue streams. Print on demand offers a flexible distribution model but often involves agreements that may limit IP control and profit margins. Explore the benefits and limitations of each approach to safeguard your intellectual property effectively.
Royalty Fees
Licensing typically involves a fixed royalty fee based on a percentage of sales, providing consistent revenue for creators while allowing publishers to manage production and distribution costs. Print on demand eliminates upfront inventory expenses, with royalty fees often calculated per unit sold, resulting in variable but potentially lower earnings per item for artists. Explore detailed comparisons and maximize your profits by understanding the nuances of royalty fee structures in both licensing and print-on-demand models.
Inventory Management
Licensing minimizes inventory risks by allowing businesses to sell products without holding stock, as manufacturers handle production and distribution. Print on demand offers real-time inventory management, producing items only after an order is placed, which reduces storage costs and prevents overstock. Explore detailed comparisons to determine the best inventory strategy for your business model.
Source and External Links
What is Licensing - Licensing is an agreement where a licensee leases rights to a legally protected piece of intellectual property from a licensor, widely used as a marketing and brand extension tool across various industries like entertainment, sports, fashion, and corporate branding.
Licensing - FCC - The FCC manages and licenses the electromagnetic spectrum for commercial and non-commercial users, requiring registration through their COmmission REgistration System (CORES) to uniquely identify entities for transactions with the FCC.
Licensing Overview - U.S. Copyright Office - The Licensing Section manages compulsory and statutory licenses under copyright law, requiring electronic filing for cable and satellite accounts and payments through Pay.gov for royalty and fee transactions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com