Alt protein and cellular agriculture represent groundbreaking innovations in sustainable food production, leveraging biotechnology to create meat alternatives without traditional livestock farming. These methods significantly reduce environmental impact, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and address ethical concerns over animal welfare. Explore the potential of these technologies to revolutionize the future of food and entrepreneurial opportunities in this emerging sector.
Why it is important
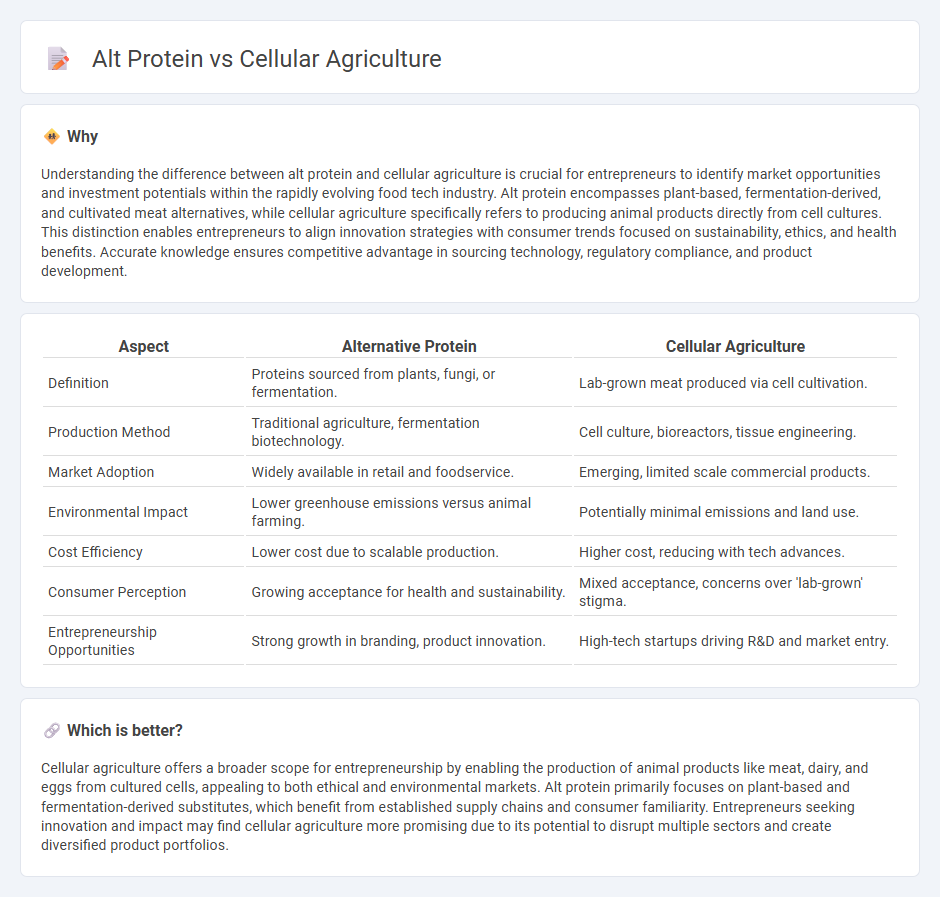
Understanding the difference between alt protein and cellular agriculture is crucial for entrepreneurs to identify market opportunities and investment potentials within the rapidly evolving food tech industry. Alt protein encompasses plant-based, fermentation-derived, and cultivated meat alternatives, while cellular agriculture specifically refers to producing animal products directly from cell cultures. This distinction enables entrepreneurs to align innovation strategies with consumer trends focused on sustainability, ethics, and health benefits. Accurate knowledge ensures competitive advantage in sourcing technology, regulatory compliance, and product development.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Alternative Protein | Cellular Agriculture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Proteins sourced from plants, fungi, or fermentation. | Lab-grown meat produced via cell cultivation. |
| Production Method | Traditional agriculture, fermentation biotechnology. | Cell culture, bioreactors, tissue engineering. |
| Market Adoption | Widely available in retail and foodservice. | Emerging, limited scale commercial products. |
| Environmental Impact | Lower greenhouse emissions versus animal farming. | Potentially minimal emissions and land use. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower cost due to scalable production. | Higher cost, reducing with tech advances. |
| Consumer Perception | Growing acceptance for health and sustainability. | Mixed acceptance, concerns over 'lab-grown' stigma. |
| Entrepreneurship Opportunities | Strong growth in branding, product innovation. | High-tech startups driving R&D and market entry. |
Which is better?
Cellular agriculture offers a broader scope for entrepreneurship by enabling the production of animal products like meat, dairy, and eggs from cultured cells, appealing to both ethical and environmental markets. Alt protein primarily focuses on plant-based and fermentation-derived substitutes, which benefit from established supply chains and consumer familiarity. Entrepreneurs seeking innovation and impact may find cellular agriculture more promising due to its potential to disrupt multiple sectors and create diversified product portfolios.
Connection
Alt protein and cellular agriculture are revolutionizing entrepreneurship by creating sustainable alternatives to traditional animal-based products. Cellular agriculture uses biotechnology to cultivate meat, dairy, and eggs from animal cells without raising livestock, reducing environmental impact and ethical concerns. Entrepreneurs leverage advancements in cellular agriculture to develop innovative alt protein products that meet growing consumer demand for eco-friendly, cruelty-free food options.
Key Terms
**Cultured Meat**
Cultured meat, a flagship product of cellular agriculture, is produced by cultivating animal cells in controlled environments, offering a sustainable alternative to conventional meat production with reduced environmental impact and ethical concerns. Unlike other alternative proteins derived from plant or microbial sources, cultured meat replicates real animal tissue, ensuring similar taste, texture, and nutritional profiles. Explore the latest advancements and market trends in cultured meat to understand its potential and challenges in transforming the future of food.
**Plant-Based Protein**
Plant-based protein, a core segment of alternative proteins, is derived primarily from legumes, grains, and seeds, offering sustainable nutrition with a lower environmental footprint than traditional animal agriculture. Cellular agriculture focuses on culturing animal cells for protein production, whereas plant-based protein relies on natural plant extraction and processing technologies. Discover more about how plant-based protein innovations are transforming global food systems and meeting consumer demand for sustainable alternatives.
**Scaling Technology**
Scaling technology in cellular agriculture involves optimizing bioreactors and cell culture conditions to produce large volumes of cultivated meat with consistent quality and safety, addressing challenges in cost reduction and production speed. Alternative protein scaling emphasizes fermentation and plant-based extraction processes that can be rapidly expanded using existing infrastructure, promoting sustainability and mass market accessibility. Explore the latest advancements in scaling technologies to understand the future potential of cellular agriculture and alternative proteins.
Source and External Links
What is Cellular Agriculture? - New Harvest - Cellular agriculture is the production of agricultural products from cell cultures rather than traditional agriculture, using biotechnologies to produce foods like meat, milk, and eggs without raising animals.
Cellular agriculture - Wikipedia - Cellular agriculture uses biotech, tissue engineering, and synthetic biology to create agricultural products from cell cultures, focusing mainly on cultured meat and other animal product alternatives to reduce environmental impact.
Cellular agriculture - Canada.ca - Cellular agriculture is an emerging food production technology using cell culture methods to produce animal-derived foods like meat and milk, also including precision fermentation and novel proteins made from both animal and non-animal cells.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com