Alternative protein sources are rapidly transforming the food industry by offering sustainable and ethical options compared to conventional dairy products, which rely heavily on animal farming with significant environmental impacts. Innovations in plant-based and cultured dairy alternatives cater to growing consumer demand for healthier, more eco-friendly nutrition. Explore how entrepreneurship drives breakthroughs in alt protein to reshape the future of food.
Why it is important
Entrepreneurs in the food industry must understand the difference between alternative protein and conventional dairy to innovate effectively and meet evolving consumer demands. Alternative proteins offer sustainability advantages, reduced environmental impact, and cater to health-conscious markets compared to traditional dairy products. Knowing these distinctions helps in product development, marketing strategies, and regulatory compliance. This knowledge is essential for positioning a startup competitively in the growing plant-based and cultured food sectors.
Comparison Table
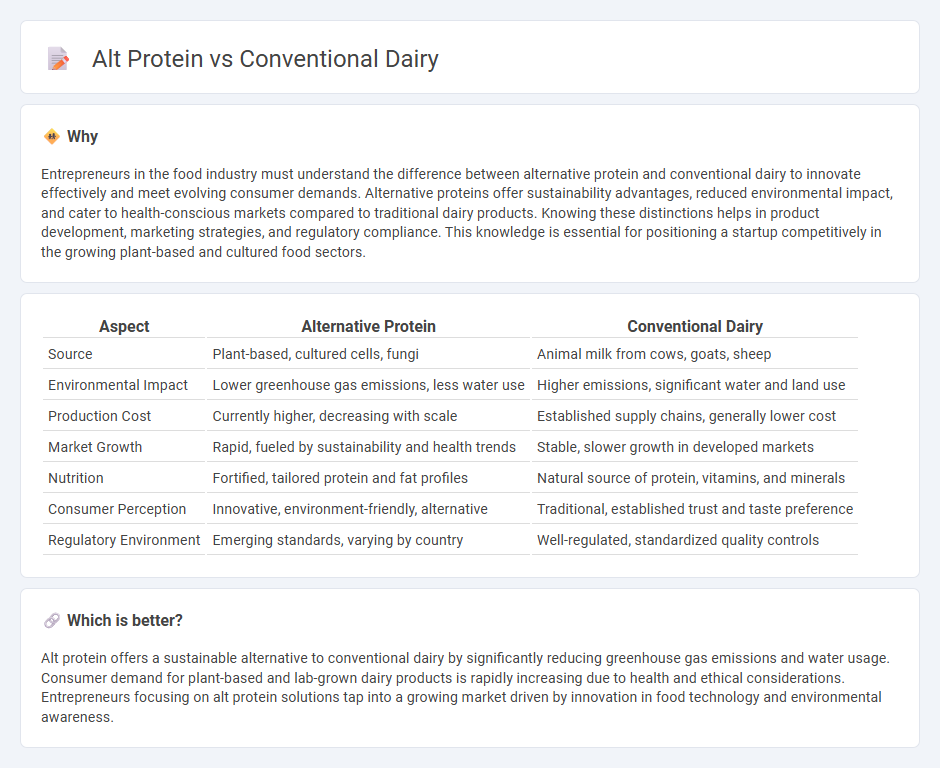
| Aspect | Alternative Protein | Conventional Dairy |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Plant-based, cultured cells, fungi | Animal milk from cows, goats, sheep |
| Environmental Impact | Lower greenhouse gas emissions, less water use | Higher emissions, significant water and land use |
| Production Cost | Currently higher, decreasing with scale | Established supply chains, generally lower cost |
| Market Growth | Rapid, fueled by sustainability and health trends | Stable, slower growth in developed markets |
| Nutrition | Fortified, tailored protein and fat profiles | Natural source of protein, vitamins, and minerals |
| Consumer Perception | Innovative, environment-friendly, alternative | Traditional, established trust and taste preference |
| Regulatory Environment | Emerging standards, varying by country | Well-regulated, standardized quality controls |
Which is better?
Alt protein offers a sustainable alternative to conventional dairy by significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions and water usage. Consumer demand for plant-based and lab-grown dairy products is rapidly increasing due to health and ethical considerations. Entrepreneurs focusing on alt protein solutions tap into a growing market driven by innovation in food technology and environmental awareness.
Connection
Alt protein startups are transforming the traditional dairy industry by developing plant-based and lab-grown alternatives that mimic the taste and nutrition of conventional dairy. This innovation addresses environmental concerns, reduces reliance on animal agriculture, and meets growing consumer demand for sustainable food sources. Investment in alt protein ventures accelerates the shift, creating collaborative opportunities between entrepreneurs and established dairy companies.
Key Terms
Value Proposition
Conventional dairy offers established nutritional benefits, affordability, and widespread availability, while alternative proteins provide sustainability advantages, lower environmental impact, and cater to lactose intolerance and vegan preferences. The value proposition of alt proteins emphasizes reduced carbon footprint, ethical production, and innovation in taste and texture that appeal to health-conscious consumers. Explore further to understand how each option drives market growth and consumer choice.
Supply Chain
Conventional dairy supply chains rely heavily on extensive livestock farming, which demands significant land, water, and feed resources, contributing to higher greenhouse gas emissions and vulnerability to disease outbreaks. Alternative protein supply chains, such as plant-based and cultured dairy, streamline production by reducing dependency on animal agriculture and enabling more localized, scalable distribution models with lower environmental impact. Explore how these supply chains transform sustainability and resilience in the food industry.
Market Differentiation
Conventional dairy maintains dominance through established distribution channels and consumer trust, emphasizing product variety and price competitiveness. Alternative proteins leverage innovation with plant-based, cultured, and fermentation-derived options, targeting sustainability and ethical concerns to attract health-conscious and environmentally aware consumers. Explore detailed market trends and growth projections to understand the evolving landscape of dairy and alternative protein sectors.
Source and External Links
Organic Vs Conventional Dairy: What Is the Difference? - BlueCart - Conventional dairy typically comes from large farms using synthetic growth hormones, GMOs, antibiotics, and pesticides, resulting in higher milk yield but shorter cow lifespans, unlike organic dairy which follows stricter USDA organic guidelines without these inputs.
COMPARING CONVENTIONAL AND ORGANIC DAIRY - The primary difference lies in farming practices; both conventional and organic milk have the same essential nutrients and quality standards, but conventional farms use pesticides and conventional feeds while organic farms follow USDA organic farming regulations.
Differences Between Organic and Conventional Dairy Farming - Conventional dairy farming focuses on maximizing supply through synthetic fertilizers, compact housing, antibiotic use, and artificial growth hormones (allowed in some countries), while organic farms emphasize animal welfare and natural feeds without synthetic hormone use.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com