Solopreneurship involves individuals independently managing all aspects of their business, leveraging personal skills and resources to maintain full control and decision-making authority. In contrast, joint ventures unite two or more parties to share expertise, resources, risks, and profits in a temporary or project-specific partnership. Explore the key differences, advantages, and challenges to determine the best entrepreneurial approach for your goals.
Why it is important
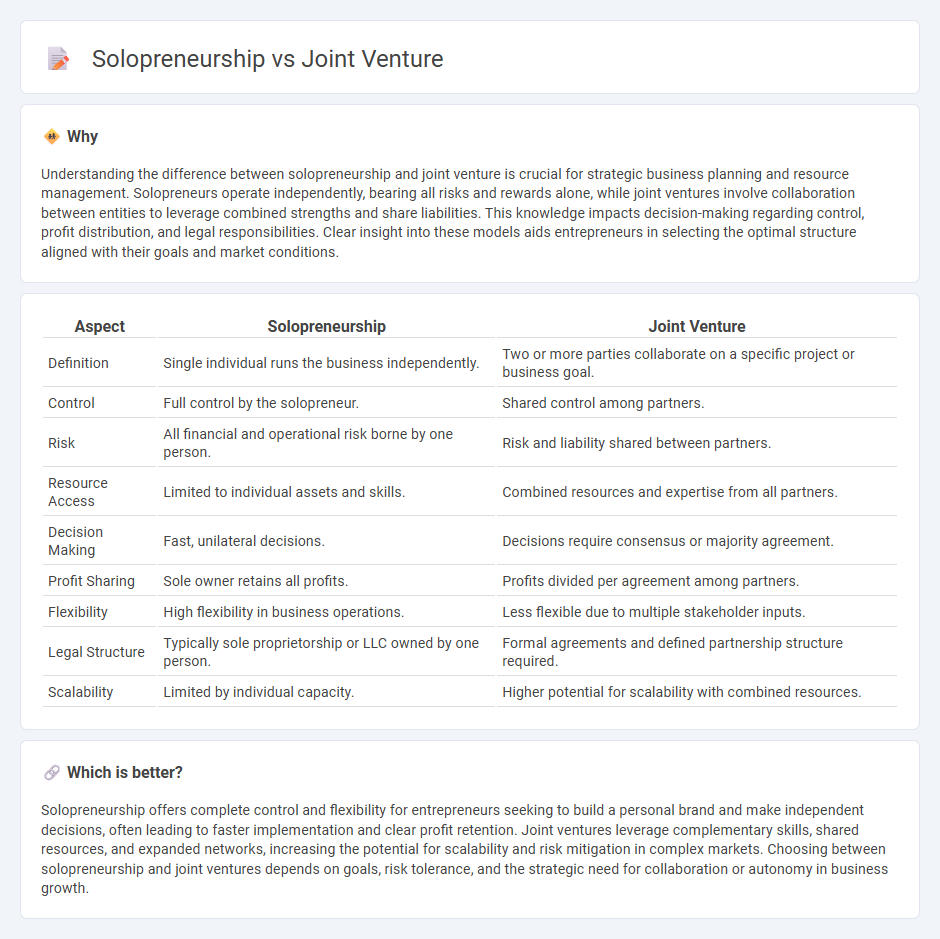
Understanding the difference between solopreneurship and joint venture is crucial for strategic business planning and resource management. Solopreneurs operate independently, bearing all risks and rewards alone, while joint ventures involve collaboration between entities to leverage combined strengths and share liabilities. This knowledge impacts decision-making regarding control, profit distribution, and legal responsibilities. Clear insight into these models aids entrepreneurs in selecting the optimal structure aligned with their goals and market conditions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Solopreneurship | Joint Venture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Single individual runs the business independently. | Two or more parties collaborate on a specific project or business goal. |
| Control | Full control by the solopreneur. | Shared control among partners. |
| Risk | All financial and operational risk borne by one person. | Risk and liability shared between partners. |
| Resource Access | Limited to individual assets and skills. | Combined resources and expertise from all partners. |
| Decision Making | Fast, unilateral decisions. | Decisions require consensus or majority agreement. |
| Profit Sharing | Sole owner retains all profits. | Profits divided per agreement among partners. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in business operations. | Less flexible due to multiple stakeholder inputs. |
| Legal Structure | Typically sole proprietorship or LLC owned by one person. | Formal agreements and defined partnership structure required. |
| Scalability | Limited by individual capacity. | Higher potential for scalability with combined resources. |
Which is better?
Solopreneurship offers complete control and flexibility for entrepreneurs seeking to build a personal brand and make independent decisions, often leading to faster implementation and clear profit retention. Joint ventures leverage complementary skills, shared resources, and expanded networks, increasing the potential for scalability and risk mitigation in complex markets. Choosing between solopreneurship and joint ventures depends on goals, risk tolerance, and the strategic need for collaboration or autonomy in business growth.
Connection
Solopreneurship and joint ventures intersect as solopreneurs often seek joint ventures to leverage complementary skills, resources, and market access. Collaborating through joint ventures enables solopreneurs to scale operations, share risks, and enhance innovation without relinquishing complete control. This strategic alliance fosters growth by combining individual entrepreneurship with collective strengths in the competitive business landscape.
Key Terms
Partnership
Joint ventures leverage the combined resources, expertise, and networks of multiple partners to achieve shared business goals and mitigate risks. In contrast, solopreneurship entails solo decision-making, full ownership, and direct control but bears the burden of all responsibilities and challenges. Explore the distinct advantages and strategic considerations of each model to determine the best fit for your entrepreneurial journey.
Autonomy
Joint ventures often dilute individual autonomy as decision-making is shared among partners, while solopreneurship provides complete control over business operations and strategic direction. Autonomy in solopreneurship enables faster pivoting and personalized brand development, crucial for dynamic market adaptation. Explore more on how these structures impact entrepreneurial freedom and growth potential.
Shared Resources
Joint ventures enable entrepreneurs to pool financial, technical, and human resources, maximizing operational efficiency and reducing individual risk. Solopreneurs rely entirely on their personal assets and skills, which may limit scalability but allow full control and flexibility. Explore how shared resources in partnerships can accelerate growth and mitigate challenges by learning more about joint ventures.
Source and External Links
Joint venture - A joint venture is a business entity created by two or more parties with shared ownership, returns, risks, and governance, often established to access new markets, share risks, or combine capabilities for specific projects or business purposes.
Joint Venture (JV) - Top 10 Advantages - A joint venture is a commercial enterprise where two or more organizations combine resources under a contractual agreement to grow faster, share costs and expertise, and access new markets strategically.
joint venture | Wex | US Law | LII / Legal Information Institute - A joint venture is a collaboration of two or more parties pooling capital, skills, and control to develop a single enterprise or project for profit, sharing associated risks, and often used to enter foreign markets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com