Exit planning and IPO strategy are critical components of entrepreneurship focused on maximizing business value and ensuring smooth ownership transition. Exit planning involves preparing a company for sale, succession, or merger to optimize financial returns and align with long-term personal and business goals. Explore more about how strategic exit planning and IPO choices can shape entrepreneurial success.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between exit planning and IPO strategy is crucial for entrepreneurs to align their business goals with the right financial and operational approach. Exit planning focuses on preparing a business for sale or transfer to maximize value and ensure continuity. IPO strategy involves structuring the company to meet regulatory requirements and attract investors during a public offering. Proper differentiation enhances decision-making, optimizes financial outcomes, and supports sustainable business growth.
Comparison Table
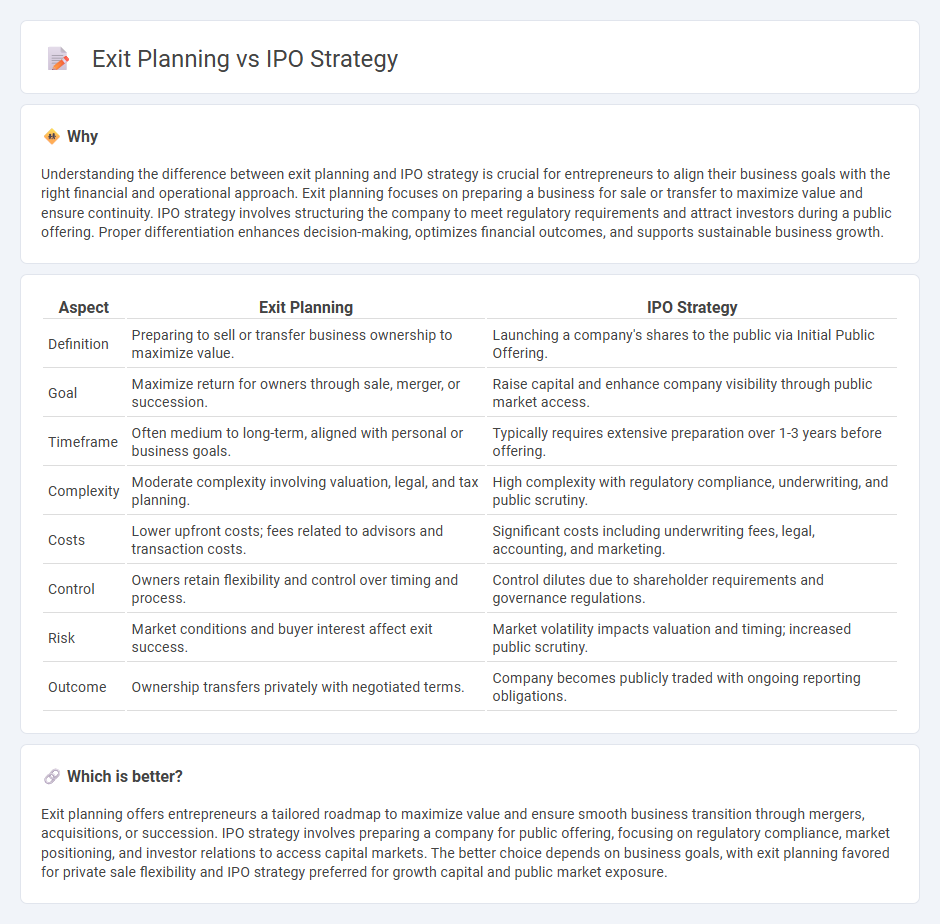
| Aspect | Exit Planning | IPO Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Preparing to sell or transfer business ownership to maximize value. | Launching a company's shares to the public via Initial Public Offering. |
| Goal | Maximize return for owners through sale, merger, or succession. | Raise capital and enhance company visibility through public market access. |
| Timeframe | Often medium to long-term, aligned with personal or business goals. | Typically requires extensive preparation over 1-3 years before offering. |
| Complexity | Moderate complexity involving valuation, legal, and tax planning. | High complexity with regulatory compliance, underwriting, and public scrutiny. |
| Costs | Lower upfront costs; fees related to advisors and transaction costs. | Significant costs including underwriting fees, legal, accounting, and marketing. |
| Control | Owners retain flexibility and control over timing and process. | Control dilutes due to shareholder requirements and governance regulations. |
| Risk | Market conditions and buyer interest affect exit success. | Market volatility impacts valuation and timing; increased public scrutiny. |
| Outcome | Ownership transfers privately with negotiated terms. | Company becomes publicly traded with ongoing reporting obligations. |
Which is better?
Exit planning offers entrepreneurs a tailored roadmap to maximize value and ensure smooth business transition through mergers, acquisitions, or succession. IPO strategy involves preparing a company for public offering, focusing on regulatory compliance, market positioning, and investor relations to access capital markets. The better choice depends on business goals, with exit planning favored for private sale flexibility and IPO strategy preferred for growth capital and public market exposure.
Connection
Exit planning and IPO strategy are interconnected as both focus on maximizing shareholder value and ensuring a smooth transition of ownership. Effective exit planning involves preparing the company for an IPO by improving financial performance, governance, and market positioning to attract investors. A well-executed IPO strategy serves as a planned exit route, providing liquidity to founders and early investors while fueling future growth.
Key Terms
Public Offering
An IPO strategy emphasizes preparing a company for a successful public offering by meeting regulatory requirements, optimizing financial performance, and enhancing market visibility to attract investors. Exit planning involves a broader approach focused on maximizing shareholder value through various options, including IPOs, mergers, or acquisitions. Explore further to understand how a tailored IPO strategy can be pivotal for a successful public market debut.
Valuation
An IPO strategy centers on maximizing company valuation through market readiness, investor confidence, and regulatory compliance to achieve the highest public offering price. Exit planning prioritizes strategic timing, liquidity optimization, and succession considerations to ensure shareholders realize maximum value upon sale or transfer. Explore comprehensive approaches to enhance valuation in both IPO strategy and exit planning.
Acquisition
IPO strategy targets raising capital and enhancing public market visibility through offering shares, while exit planning via acquisition centers on transferring business ownership to a buyer for liquidity and strategic alignment. Acquisition-focused exit planning emphasizes valuation optimization, due diligence, and integration readiness to maximize transaction success and shareholder returns. Explore comprehensive strategies to tailor your business exit for maximum financial and operational impact.
Source and External Links
Guide to going public - An effective IPO strategy includes early preparation, a multitrack approach, a compelling equity story, fair pricing, right timing, and readiness to meet capital market requirements and investor expectations.
IPO Strategy & Process Consulting | BCG - The IPO process typically involves three phases: conceptualize, prepare, and execute, focusing on assessing the rationale for an IPO, financial and reporting readiness, corporate governance changes, investor targeting, and equity story development.
Taking your company public? Let's get started on your IPO strategy - Successful IPOs rely on addressing IPO readiness gaps such as financial reporting, internal controls, and governance, assigning a project manager, and implementing a clear, structured plan to avoid delays and maintain investor trust.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com