No code startups leverage software platforms that require minimal coding, enabling rapid development and iteration with lower initial capital and technical barriers compared to hardware startups, which involve complex product design, manufacturing, and supply chain management. Hardware startups demand substantial upfront investment, longer development cycles, and intricate logistics, making scalability more challenging. Explore further to understand the distinct strategies and risk profiles of no code versus hardware startups.
Why it is important
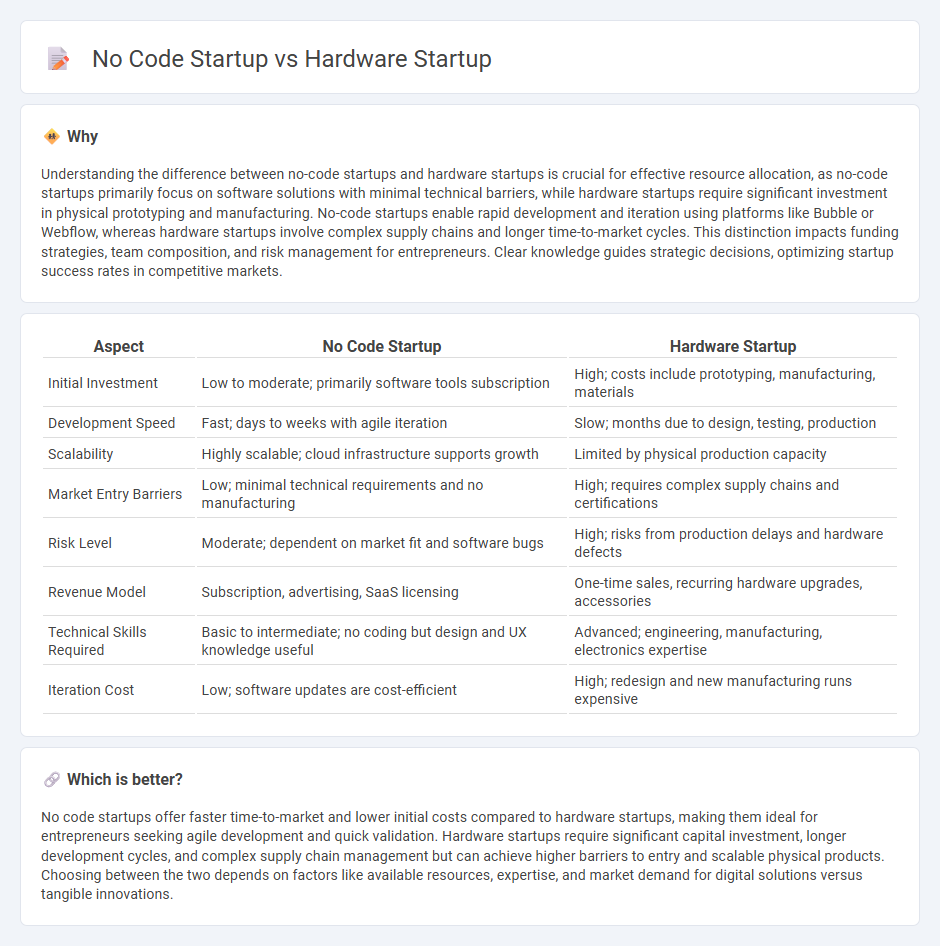
Understanding the difference between no-code startups and hardware startups is crucial for effective resource allocation, as no-code startups primarily focus on software solutions with minimal technical barriers, while hardware startups require significant investment in physical prototyping and manufacturing. No-code startups enable rapid development and iteration using platforms like Bubble or Webflow, whereas hardware startups involve complex supply chains and longer time-to-market cycles. This distinction impacts funding strategies, team composition, and risk management for entrepreneurs. Clear knowledge guides strategic decisions, optimizing startup success rates in competitive markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | No Code Startup | Hardware Startup |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Low to moderate; primarily software tools subscription | High; costs include prototyping, manufacturing, materials |
| Development Speed | Fast; days to weeks with agile iteration | Slow; months due to design, testing, production |
| Scalability | Highly scalable; cloud infrastructure supports growth | Limited by physical production capacity |
| Market Entry Barriers | Low; minimal technical requirements and no manufacturing | High; requires complex supply chains and certifications |
| Risk Level | Moderate; dependent on market fit and software bugs | High; risks from production delays and hardware defects |
| Revenue Model | Subscription, advertising, SaaS licensing | One-time sales, recurring hardware upgrades, accessories |
| Technical Skills Required | Basic to intermediate; no coding but design and UX knowledge useful | Advanced; engineering, manufacturing, electronics expertise |
| Iteration Cost | Low; software updates are cost-efficient | High; redesign and new manufacturing runs expensive |
Which is better?
No code startups offer faster time-to-market and lower initial costs compared to hardware startups, making them ideal for entrepreneurs seeking agile development and quick validation. Hardware startups require significant capital investment, longer development cycles, and complex supply chain management but can achieve higher barriers to entry and scalable physical products. Choosing between the two depends on factors like available resources, expertise, and market demand for digital solutions versus tangible innovations.
Connection
No code startups and hardware startups intersect through rapid prototyping and development, enabling entrepreneurs to accelerate product iteration without extensive coding or manufacturing delays. No code platforms streamline software creation for hardware interfaces, IoT devices, and embedded systems, lowering barriers for hardware startups to launch innovative solutions. This synergy enhances market entry speed and reduces initial capital requirements, fostering agile entrepreneurship across both domains.
Key Terms
Prototyping
Hardware startups require extensive prototyping to test physical components, materials, and assembly processes, involving iterative design, 3D printing, and circuit testing to ensure product feasibility. No-code startups accelerate prototyping through drag-and-drop platforms that enable quick development of user interfaces and workflows without traditional coding, significantly reducing time-to-market. Explore the distinct prototyping approaches to choose the best fit for your startup's innovation journey.
Scalability
Hardware startups face challenges in scalability due to physical production constraints, higher capital expenditure, and longer development cycles compared to no-code startups. No-code startups benefit from rapid deployment, minimal upfront investment, and easier iterations, enabling faster scaling and market adaptation. Explore the scalability advantages and limitations of both models to determine the best approach for your business growth.
Capital requirements
Hardware startups demand substantial capital for prototyping, manufacturing, inventory, and supply chain management, often requiring millions in upfront investment. No-code startups have significantly lower capital requirements, leveraging accessible platforms to build software solutions with minimal initial funding and operational costs. Explore the financial aspects further to determine the best fit for your startup ambitions.
Source and External Links
An Investor's Guide to Hardware Startups - Hardware startups differ significantly from software startups, requiring longer development cycles, more expensive resources, and mature engineering practices due to their complexity and the need to build low-level systems and custom infrastructure.
Hardware Startup Founders' First Steps - Onshape - Successful hardware startups must carefully navigate funding, intellectual property protection, and team building, with critical early steps often overlooked by founders eager to rush to market.
18 Top Hardware Startups in San Francisco To Know - Hardware startups in San Francisco are innovating across sectors such as smart security, WiFi, and neurotechnology, aiming to simplify and enhance everyday life through cutting-edge physical products.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com