Indie hacking involves building and launching independent startups, where entrepreneurs maintain full creative control and ownership, focusing on innovation and rapid iteration. Intrapreneurship empowers employees within established companies to develop new products or services, leveraging organizational resources while navigating corporate structures. Explore the core differences and benefits of indie hacking versus intrapreneurship to determine the best path for your entrepreneurial journey.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between indie hacking and intrapreneurship is crucial for entrepreneurs to align their goals, resources, and risk tolerance effectively. Indie hacking involves independently creating and growing a startup with personal ownership and autonomy, while intrapreneurship focuses on innovating within an existing company's structure. Knowing these distinctions helps in choosing the right environment for innovation, accessing appropriate funding, and fostering the intended impact on the market. Clear differentiation ensures entrepreneurs leverage suitable strategies and mindsets for success in either self-driven ventures or corporate initiatives.
Comparison Table
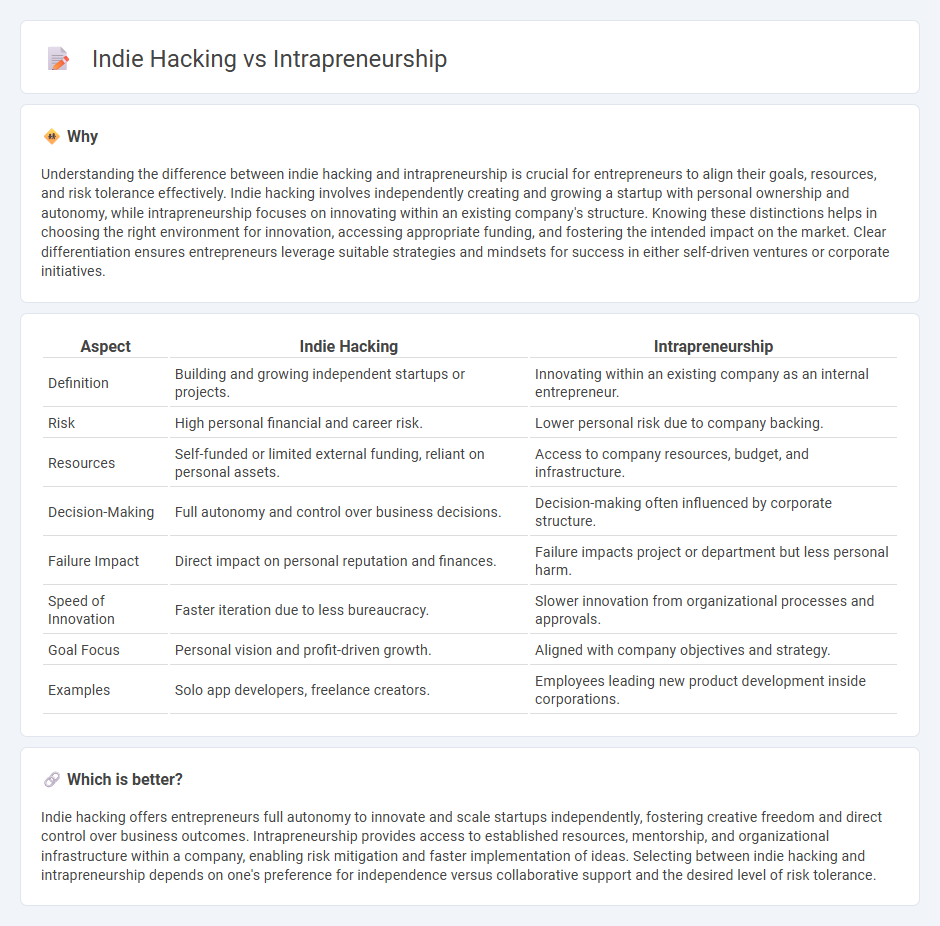
| Aspect | Indie Hacking | Intrapreneurship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Building and growing independent startups or projects. | Innovating within an existing company as an internal entrepreneur. |
| Risk | High personal financial and career risk. | Lower personal risk due to company backing. |
| Resources | Self-funded or limited external funding, reliant on personal assets. | Access to company resources, budget, and infrastructure. |
| Decision-Making | Full autonomy and control over business decisions. | Decision-making often influenced by corporate structure. |
| Failure Impact | Direct impact on personal reputation and finances. | Failure impacts project or department but less personal harm. |
| Speed of Innovation | Faster iteration due to less bureaucracy. | Slower innovation from organizational processes and approvals. |
| Goal Focus | Personal vision and profit-driven growth. | Aligned with company objectives and strategy. |
| Examples | Solo app developers, freelance creators. | Employees leading new product development inside corporations. |
Which is better?
Indie hacking offers entrepreneurs full autonomy to innovate and scale startups independently, fostering creative freedom and direct control over business outcomes. Intrapreneurship provides access to established resources, mentorship, and organizational infrastructure within a company, enabling risk mitigation and faster implementation of ideas. Selecting between indie hacking and intrapreneurship depends on one's preference for independence versus collaborative support and the desired level of risk tolerance.
Connection
Indie hacking and intrapreneurship both emphasize innovation and autonomy within business contexts, where indie hackers create independent startups and intrapreneurs drive entrepreneurial initiatives inside established companies. Both approaches rely on rapid experimentation, resourcefulness, and a strong focus on solving customer problems to generate value and foster growth. The shared mindset of ownership and proactive problem-solving connects indie hacking's self-driven ventures with intrapreneurship's corporate innovation efforts.
Key Terms
Corporate Innovation
Intrapreneurship drives corporate innovation by empowering employees to develop new ideas and solutions within established organizations, leveraging internal resources and market insights for growth. Indie hacking centers on individual entrepreneurs building startups independently, often prioritizing fast iteration and personal autonomy over large-scale corporate infrastructure. Explore how these approaches shape innovation strategies and business success.
Autonomy
Intrapreneurship offers autonomy within the structure and resources of established organizations, allowing individuals to innovate while leveraging company support and reducing financial risk. Indie hacking emphasizes complete independence, with entrepreneurs building and scaling ventures solo, often facing higher uncertainty but enjoying full creative and operational control. Explore how these contrasting approaches shape autonomy and entrepreneurial outcomes in dynamic business environments.
Resource Ownership
Intrapreneurship involves working within an established organization where resources such as funding, technology, and networks are provided by the company, allowing employees to innovate while leveraging existing assets. Indie hacking emphasizes individual or small-team ownership of all resources, including capital, tools, and marketing channels, fostering complete control and responsibility over product development and business growth. Explore these distinct approaches to resource ownership to determine which model aligns with your entrepreneurial goals.
Source and External Links
What is intrapreneurship, and how can you cultivate it at your company? - Intrapreneurship refers to employees within established companies who drive innovation and improvement by applying entrepreneurial skills internally without bearing the financial risks of entrepreneurship, thereby advancing the organization's growth and adaptability.
Intrapreneurship - Wikipedia - Intrapreneurship is the act of behaving like an entrepreneur while working inside a large organization, involving innovation, creativity, and risk-taking to transform ideas into profitable ventures, supported by corporate resources.
Why focus on Intrapreneurship? - Marymount University - Intrapreneurship enables individuals within organizations to find overlooked opportunities and use entrepreneurial behavior to create positive changes, fostering adaptability and innovation critical for success in today's economy.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com