Solopreneurs independently manage business operations, leveraging a diverse tech stack tailored for flexibility, automation, and growth, including tools like CRM software, project management apps, and digital marketing platforms. Intrapreneurs operate within established companies, focusing on innovation and driving change by utilizing internal resources and collaboration tools to enhance productivity and foster corporate entrepreneurship. Explore how these distinct approaches shape success in modern business environments.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between a solopreneur stack and an intrapreneur is crucial for effectively allocating resources and strategies tailored to individual business ownership versus corporate innovation roles. Solopreneurs prioritize flexible, all-in-one tools that support independent project management, marketing, and sales, while intrapreneurs leverage organizational resources to drive innovation within larger companies. Recognizing these distinctions optimizes productivity and aligns business approaches with specific entrepreneurial contexts. This knowledge ultimately enhances decision-making and the potential for success in either solo ventures or corporate entrepreneurial initiatives.
Comparison Table
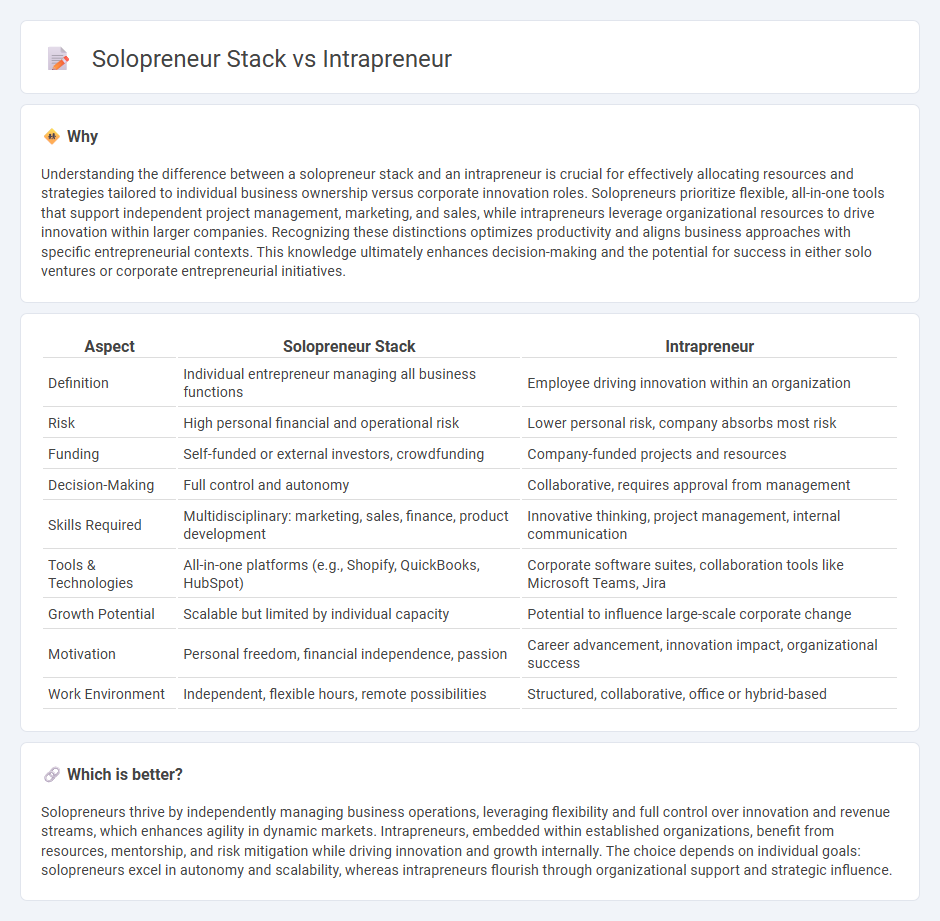
| Aspect | Solopreneur Stack | Intrapreneur |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual entrepreneur managing all business functions | Employee driving innovation within an organization |
| Risk | High personal financial and operational risk | Lower personal risk, company absorbs most risk |
| Funding | Self-funded or external investors, crowdfunding | Company-funded projects and resources |
| Decision-Making | Full control and autonomy | Collaborative, requires approval from management |
| Skills Required | Multidisciplinary: marketing, sales, finance, product development | Innovative thinking, project management, internal communication |
| Tools & Technologies | All-in-one platforms (e.g., Shopify, QuickBooks, HubSpot) | Corporate software suites, collaboration tools like Microsoft Teams, Jira |
| Growth Potential | Scalable but limited by individual capacity | Potential to influence large-scale corporate change |
| Motivation | Personal freedom, financial independence, passion | Career advancement, innovation impact, organizational success |
| Work Environment | Independent, flexible hours, remote possibilities | Structured, collaborative, office or hybrid-based |
Which is better?
Solopreneurs thrive by independently managing business operations, leveraging flexibility and full control over innovation and revenue streams, which enhances agility in dynamic markets. Intrapreneurs, embedded within established organizations, benefit from resources, mentorship, and risk mitigation while driving innovation and growth internally. The choice depends on individual goals: solopreneurs excel in autonomy and scalability, whereas intrapreneurs flourish through organizational support and strategic influence.
Connection
Solopreneurs and intrapreneurs share a foundational drive for innovation and business growth but operate in different contexts--solopreneurs independently managing their ventures while intrapreneurs innovate within existing organizations. Both leverage entrepreneurial skills such as risk-taking, creativity, and strategic problem-solving to create value and drive progress. Understanding their connection highlights how intrapreneurship fosters innovation within corporate structures, complementing the agility and autonomy characteristic of solopreneurship.
Key Terms
Autonomy
Intrapreneurs drive innovation within established companies, leveraging organizational resources while maintaining a degree of autonomy to implement new ideas. Solopreneurs operate independently, owning every aspect of their business and exercising full control over decisions, risks, and rewards. Explore the key differences in autonomy and operational scope to determine which entrepreneurial path aligns with your goals.
Resource Access
Intrapreneurs leverage corporate resources such as funding, technology, and mentorship, enabling them to innovate within established organizations. Solopreneurs rely primarily on personal capital, agile decision-making, and external networks to build and scale their ventures independently. Discover key strategies to maximize resource access in both intrapreneurial and solopreneurial environments.
Risk Bearing
Intrapreneurs operate within established organizations, leveraging company resources while facing limited personal financial risk, as their innovation efforts are backed by the firm's capital and infrastructure. Solopreneurs independently bear full financial risk, investing their own resources and managing all aspects of the business, which increases potential rewards but also heightens vulnerability. Explore more about the risk dynamics and decision-making differences between intrapreneurs and solopreneurs.
Source and External Links
What Is an Intrapreneur? (With Definition, Duties and Skills) - An intrapreneur is an employee within an organization who takes initiative to innovate by developing new products, methods, or processes and leads their implementation to drive business success.
Intrapreneurship - Intrapreneurship is the act of behaving like an entrepreneur inside a large company, taking responsibility to turn ideas into profitable innovations with risk-taking and creativity supported by corporate resources.
Intrapreneur, entrepreneur or extrapreneur, or all three? ... - Intrapreneurs apply entrepreneurial skills within an existing organization to innovate and create value by leveraging company assets and taking calculated risks to boost growth and competitiveness.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com