Solopreneurs are independent business owners who manage all aspects of their enterprise, driving innovation and decision-making solo. Intrapreneurs operate within established organizations, leveraging company resources to develop new products or services while mitigating risks. Explore the unique advantages and challenges of both roles to determine which entrepreneurial path suits you best.
Why it is important
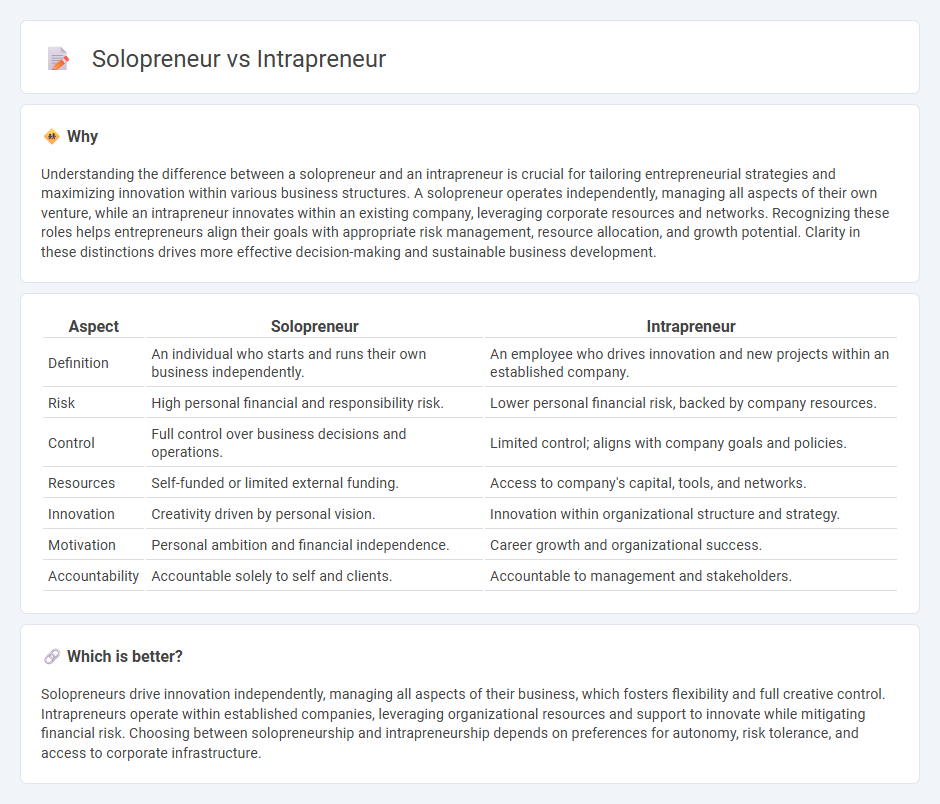
Understanding the difference between a solopreneur and an intrapreneur is crucial for tailoring entrepreneurial strategies and maximizing innovation within various business structures. A solopreneur operates independently, managing all aspects of their own venture, while an intrapreneur innovates within an existing company, leveraging corporate resources and networks. Recognizing these roles helps entrepreneurs align their goals with appropriate risk management, resource allocation, and growth potential. Clarity in these distinctions drives more effective decision-making and sustainable business development.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Solopreneur | Intrapreneur |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An individual who starts and runs their own business independently. | An employee who drives innovation and new projects within an established company. |
| Risk | High personal financial and responsibility risk. | Lower personal financial risk, backed by company resources. |
| Control | Full control over business decisions and operations. | Limited control; aligns with company goals and policies. |
| Resources | Self-funded or limited external funding. | Access to company's capital, tools, and networks. |
| Innovation | Creativity driven by personal vision. | Innovation within organizational structure and strategy. |
| Motivation | Personal ambition and financial independence. | Career growth and organizational success. |
| Accountability | Accountable solely to self and clients. | Accountable to management and stakeholders. |
Which is better?
Solopreneurs drive innovation independently, managing all aspects of their business, which fosters flexibility and full creative control. Intrapreneurs operate within established companies, leveraging organizational resources and support to innovate while mitigating financial risk. Choosing between solopreneurship and intrapreneurship depends on preferences for autonomy, risk tolerance, and access to corporate infrastructure.
Connection
Solopreneurs and intrapreneurs both drive innovation and business growth through entrepreneurial thinking, yet solopreneurs operate independently while intrapreneurs innovate within established organizations. Each applies risk-taking, creativity, and resourcefulness to identify opportunities and solve problems, contributing to competitive advantage. Understanding their roles highlights how entrepreneurial skills can enhance both solo ventures and corporate development.
Key Terms
Innovation
Intrapreneurs drive innovation within established organizations by leveraging company resources to develop new products or processes while mitigating risk. Solopreneurs innovate independently, creating unique offerings through personal creativity and direct market engagement, often shouldering all operational responsibilities alone. Explore the distinct innovation pathways of intrapreneurs and solopreneurs to understand how each fosters growth and value creation.
Autonomy
Intrapreneurs operate within established organizations, leveraging company resources while navigating internal structures to innovate and drive projects autonomously. Solopreneurs maintain full independence, owning every aspect of their business decisions, risks, and rewards without external oversight. Explore deeper insights into how autonomy shapes strategies and outcomes for intrapreneurs and solopreneurs.
Organizational Resources
Intrapreneurs leverage organizational resources such as dedicated teams, company infrastructure, and financial backing to innovate within an established business. Solopreneurs rely primarily on their individual skills, personal capital, and external networks to launch and grow their ventures independently. Explore how these approaches impact scalability and resource management to determine the best fit for your entrepreneurial goals.
Source and External Links
What Is an Intrapreneur? (With Definition, Duties and Skills) - Indeed - An intrapreneur is an employee within a company responsible for developing innovative business ideas or products to help the organization reach its goals, acting like an internal entrepreneur with company resources at their disposal.
Intrapreneurship - Wikipedia - Intrapreneurship is the practice of entrepreneurial behavior within a large organization, where intrapreneurs take responsibility to innovate and bring new ideas to profitable fruition with support and resources from their company.
7 Types of Intrapreneurship You Should Know About in 2025 - rready - Successful intrapreneurs are confident, proactive employees who identify opportunities for improvement, lead innovation initiatives, and are empowered to challenge existing processes within their organizations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com