Marketplace flipping involves buying undervalued products or assets and reselling them at a higher price for profit, leveraging market inefficiencies and demand trends. Dropshipping operates by selling products directly from suppliers to customers without maintaining inventory, reducing upfront costs and simplifying logistics. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which model aligns best with your entrepreneurial goals.
Why it is important
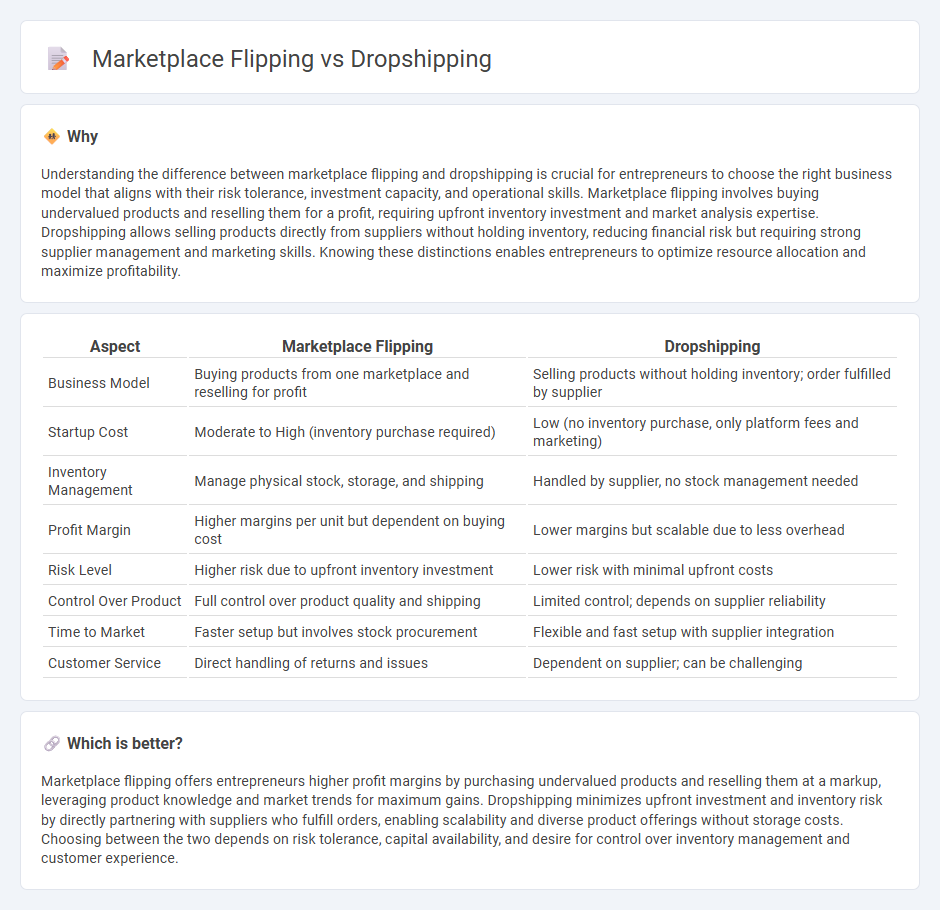
Understanding the difference between marketplace flipping and dropshipping is crucial for entrepreneurs to choose the right business model that aligns with their risk tolerance, investment capacity, and operational skills. Marketplace flipping involves buying undervalued products and reselling them for a profit, requiring upfront inventory investment and market analysis expertise. Dropshipping allows selling products directly from suppliers without holding inventory, reducing financial risk but requiring strong supplier management and marketing skills. Knowing these distinctions enables entrepreneurs to optimize resource allocation and maximize profitability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Marketplace Flipping | Dropshipping |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model | Buying products from one marketplace and reselling for profit | Selling products without holding inventory; order fulfilled by supplier |
| Startup Cost | Moderate to High (inventory purchase required) | Low (no inventory purchase, only platform fees and marketing) |
| Inventory Management | Manage physical stock, storage, and shipping | Handled by supplier, no stock management needed |
| Profit Margin | Higher margins per unit but dependent on buying cost | Lower margins but scalable due to less overhead |
| Risk Level | Higher risk due to upfront inventory investment | Lower risk with minimal upfront costs |
| Control Over Product | Full control over product quality and shipping | Limited control; depends on supplier reliability |
| Time to Market | Faster setup but involves stock procurement | Flexible and fast setup with supplier integration |
| Customer Service | Direct handling of returns and issues | Dependent on supplier; can be challenging |
Which is better?
Marketplace flipping offers entrepreneurs higher profit margins by purchasing undervalued products and reselling them at a markup, leveraging product knowledge and market trends for maximum gains. Dropshipping minimizes upfront investment and inventory risk by directly partnering with suppliers who fulfill orders, enabling scalability and diverse product offerings without storage costs. Choosing between the two depends on risk tolerance, capital availability, and desire for control over inventory management and customer experience.
Connection
Marketplace flipping and dropshipping are connected through their reliance on leveraging online platforms to sell products without maintaining inventory. Both strategies focus on sourcing discounted or wholesale items to resell at a profit, with dropshipping emphasizing direct shipment from suppliers to customers, while flipping involves purchasing items and reselling them on marketplaces like eBay or Amazon. These models minimize upfront investment and inventory risk, appealing to entrepreneurs seeking scalable e-commerce opportunities.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Dropshipping eliminates the need for inventory management by directly shipping products from suppliers to customers, reducing overhead and storage costs. Marketplace flipping requires maintaining inventory, managing stock levels, and handling shipping logistics to ensure timely order fulfillment. Explore more about which model aligns best with your operational capabilities and business goals.
Profit Margins
Dropshipping typically offers lower profit margins, averaging between 10% to 30%, due to reliance on suppliers and higher competition. Marketplace flipping can yield higher profit margins, often ranging from 40% to 100%, by purchasing undervalued items and reselling them for a premium on platforms like eBay or Amazon. Explore detailed strategies to maximize profit margins in both dropshipping and marketplace flipping for your e-commerce ventures.
Platform Fees
Dropshipping platforms often charge monthly subscription fees and transaction fees ranging from 2% to 5%, impacting profit margins for sellers. Marketplace flipping involves selling on established sites like eBay or Amazon, where sellers face listing fees, final value fees, and payment processing charges that can total around 10% to 15% per sale. Explore detailed fee structures and strategies to maximize profits in both business models.
Source and External Links
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? (2025) - Shopify - Dropshipping is a business model where the seller partners with a supplier who stores, packages, and ships products directly to customers, allowing the seller to operate without owning inventory or managing shipping logistics.
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? - Wix.com - Dropshipping is a retail fulfillment method where the merchant sells products without stocking inventory, forwarding customer orders to suppliers who handle warehousing and shipping.
Drop shipping - Wikipedia - Drop shipping is a supply chain management method in which the retailer accepts customer orders but transfers the order details to suppliers who ship the products directly, minimizing overhead and inventory costs for the seller.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com