Entrepreneurship involves creating diverse revenue channels, with passive income streams generating earnings from investments or automated systems requiring minimal ongoing effort. Residual income, often linked to royalties, subscriptions, or recurring sales, provides continuous cash flow from previous work or investments. Explore further to understand how these income models can drive financial freedom in your entrepreneurial journey.
Why it is important
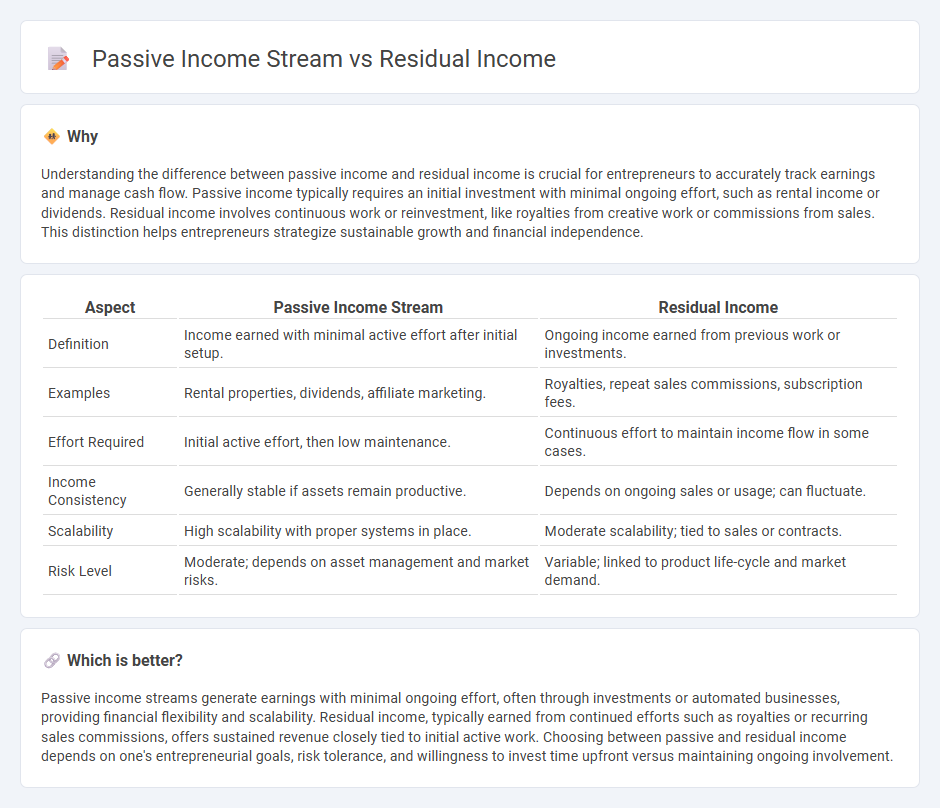
Understanding the difference between passive income and residual income is crucial for entrepreneurs to accurately track earnings and manage cash flow. Passive income typically requires an initial investment with minimal ongoing effort, such as rental income or dividends. Residual income involves continuous work or reinvestment, like royalties from creative work or commissions from sales. This distinction helps entrepreneurs strategize sustainable growth and financial independence.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Passive Income Stream | Residual Income |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Income earned with minimal active effort after initial setup. | Ongoing income earned from previous work or investments. |
| Examples | Rental properties, dividends, affiliate marketing. | Royalties, repeat sales commissions, subscription fees. |
| Effort Required | Initial active effort, then low maintenance. | Continuous effort to maintain income flow in some cases. |
| Income Consistency | Generally stable if assets remain productive. | Depends on ongoing sales or usage; can fluctuate. |
| Scalability | High scalability with proper systems in place. | Moderate scalability; tied to sales or contracts. |
| Risk Level | Moderate; depends on asset management and market risks. | Variable; linked to product life-cycle and market demand. |
Which is better?
Passive income streams generate earnings with minimal ongoing effort, often through investments or automated businesses, providing financial flexibility and scalability. Residual income, typically earned from continued efforts such as royalties or recurring sales commissions, offers sustained revenue closely tied to initial active work. Choosing between passive and residual income depends on one's entrepreneurial goals, risk tolerance, and willingness to invest time upfront versus maintaining ongoing involvement.
Connection
Passive income streams generate residual income by providing ongoing earnings from initial efforts, such as investments, royalties, or automated businesses. Residual income reflects the sustainability and profitability of these passive sources over time, measuring the true financial benefit beyond active work. Successful entrepreneurs leverage passive income streams to build scalable, long-term wealth without continuous direct involvement.
Key Terms
Active Involvement
Residual income requires ongoing active involvement to maintain revenue streams, often through continued sales, services, or content creation, whereas passive income streams generate earnings with minimal day-to-day effort once established, such as rental income or dividends. Understanding the difference helps in choosing the right strategy based on available time and desired financial independence. Explore more to determine which income type aligns best with your financial goals.
Recurring Revenue
Residual income and passive income streams both generate recurring revenue, but residual income typically comes from ongoing earnings after active work, such as royalties or commissions, while passive income often involves investments or automated businesses requiring minimal involvement. Recurring revenue from residual income provides a steady cash flow tied to previous efforts, whereas passive income streams can be built with upfront investment to generate continuous returns like rental income or dividends. Explore in-depth strategies to maximize recurring revenue through residual and passive income models.
Scalability
Residual income represents earnings generated from prior efforts, often capped by time or resource constraints, while passive income streams, particularly scalable ones like digital products or online courses, enable exponential growth with minimal ongoing input. Scalability is a key differentiator, as passive income models can leverage technology and automation to increase revenue without proportional increases in effort. Explore detailed strategies to scale passive income effectively and maximize financial freedom.
Source and External Links
Residual Income (RI) | Formula + Calculator - Residual income is the excess net operating income earned beyond the required rate of return on a company's operating assets, used as a financial metric to evaluate project feasibility and performance by subtracting the targeted return from actual operating income.
Residual Income: What it is and How to Generate it - Residual income is income that continues after work is done, such as royalties or income from investments, and it is calculated as net operating income minus the product of minimum required return and operating cost, representing earnings above the minimum expected return.
What Is Residual Income? Definition and Types - Residual income refers to the money left over after all expenses are paid, helping both individuals and businesses evaluate profitability and financial performance, calculated by subtracting the product of equity and cost of equity from net income.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com