Entrepreneurship in alternative proteins focuses on developing sustainable, plant-based or cultured meat solutions to meet rising global food demand while reducing environmental impact. Food waste valorization startups transform organic waste into valuable products like biofuels, fertilizers, and animal feed, addressing both sustainability and resource efficiency challenges. Explore innovative entrepreneurial approaches reshaping the future of food systems.
Why it is important
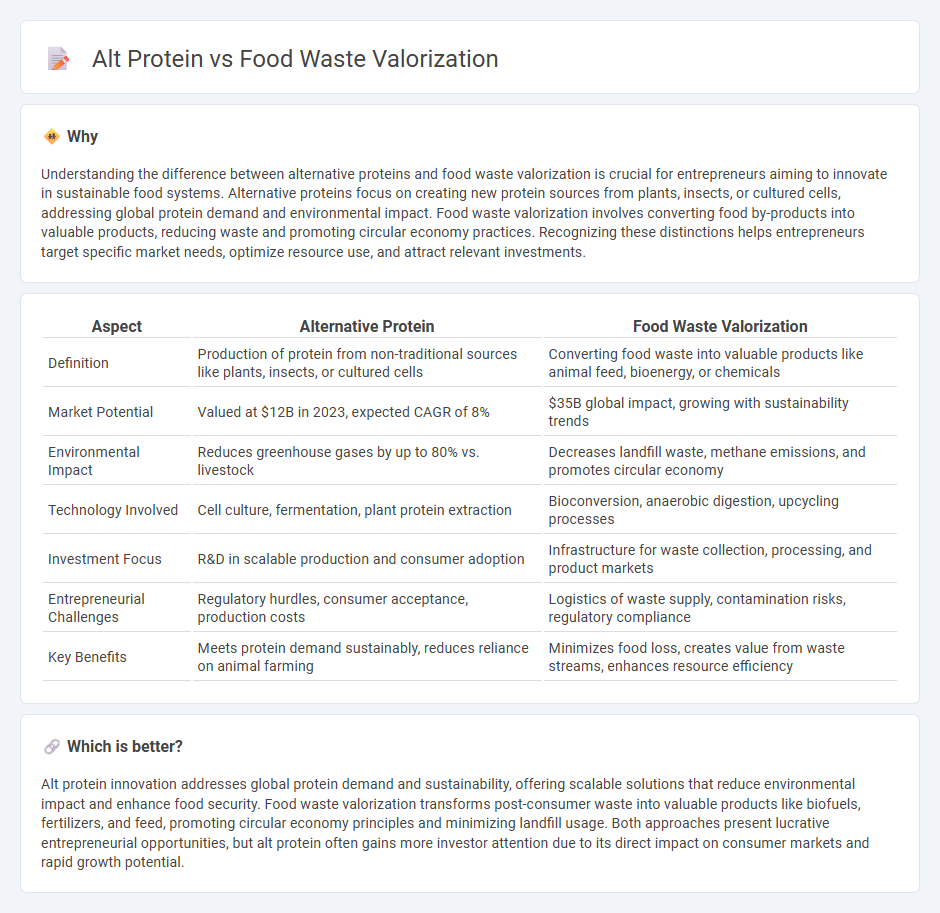
Understanding the difference between alternative proteins and food waste valorization is crucial for entrepreneurs aiming to innovate in sustainable food systems. Alternative proteins focus on creating new protein sources from plants, insects, or cultured cells, addressing global protein demand and environmental impact. Food waste valorization involves converting food by-products into valuable products, reducing waste and promoting circular economy practices. Recognizing these distinctions helps entrepreneurs target specific market needs, optimize resource use, and attract relevant investments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Alternative Protein | Food Waste Valorization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Production of protein from non-traditional sources like plants, insects, or cultured cells | Converting food waste into valuable products like animal feed, bioenergy, or chemicals |
| Market Potential | Valued at $12B in 2023, expected CAGR of 8% | $35B global impact, growing with sustainability trends |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces greenhouse gases by up to 80% vs. livestock | Decreases landfill waste, methane emissions, and promotes circular economy |
| Technology Involved | Cell culture, fermentation, plant protein extraction | Bioconversion, anaerobic digestion, upcycling processes |
| Investment Focus | R&D in scalable production and consumer adoption | Infrastructure for waste collection, processing, and product markets |
| Entrepreneurial Challenges | Regulatory hurdles, consumer acceptance, production costs | Logistics of waste supply, contamination risks, regulatory compliance |
| Key Benefits | Meets protein demand sustainably, reduces reliance on animal farming | Minimizes food loss, creates value from waste streams, enhances resource efficiency |
Which is better?
Alt protein innovation addresses global protein demand and sustainability, offering scalable solutions that reduce environmental impact and enhance food security. Food waste valorization transforms post-consumer waste into valuable products like biofuels, fertilizers, and feed, promoting circular economy principles and minimizing landfill usage. Both approaches present lucrative entrepreneurial opportunities, but alt protein often gains more investor attention due to its direct impact on consumer markets and rapid growth potential.
Connection
Alt protein production leverages food waste valorization by converting organic byproducts into sustainable protein sources, reducing environmental impact and resource consumption. Utilizing food waste streams as feedstock for fermentation or insect farming enhances circular economy practices and lowers greenhouse gas emissions in the food industry. This interconnected approach drives innovation in entrepreneurship focused on sustainable food systems and resource efficiency.
Key Terms
Food Waste Valorization:
Food waste valorization transforms organic waste into valuable products like biofuels, animal feed, and fertilizers, enhancing sustainability and reducing landfill burden. Technologies such as anaerobic digestion and black soldier fly larvae conversion optimize resource recovery and environmental impact. Explore innovative methods and market trends driving the future of food waste valorization.
Upcycling
Food waste valorization transforms discarded organic materials into valuable products, reducing landfill impact and promoting sustainability. Upcycling food waste into alternative proteins offers a promising solution by converting byproducts like fruit pulp or grain husks into nutritious, high-quality protein sources. Discover how innovative upcycling technologies are reshaping the future of sustainable food production.
Circular Economy
Food waste valorization transforms organic waste into valuable resources such as biofuels, fertilizers, and animal feed, significantly reducing environmental impact through waste reduction and resource recovery. Alternative protein production, including insect-based, lab-grown, and plant-based proteins, supports the Circular Economy by utilizing less land, water, and energy while creating sustainable protein sources. Explore further to understand how these innovations drive eco-efficient food systems and resource circularity.
Source and External Links
A comprehensive review of food waste valorization for the sustainable management of global food waste - This review discusses advanced options and integrated biorefinery strategies for converting food waste into valuable products, emphasizing sustainable technologies for global waste-to-wealth conversion aligned with UN sustainable development goals.
A Review on the Challenges and Choices for Food Waste Valorization - This paper analyzes methods to valorize food waste, producing value-added products while addressing the environmental, economic, and social impacts in transitioning toward a circular economy.
A Review on the Challenges and Choices for Food Waste Valorization - It highlights the importance of transdisciplinary efforts and stakeholder collaboration to reduce food waste and improve the sustainability of valorization processes with a broader environmental and economic impact perspective.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com