Passive houses maximize energy efficiency through advanced insulation, airtight construction, and renewable energy systems, significantly reducing utility costs and environmental impact for entrepreneurs in sustainable building. Tiny houses emphasize minimalism and affordability, offering flexible, low-cost living or office solutions ideal for startup founders looking to optimize space and capital. Explore the benefits and challenges of passive houses versus tiny houses to determine the best approach for your entrepreneurial goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Passive Houses and Tiny Houses is crucial for entrepreneurs in sustainable real estate development, as Passive Houses focus on energy efficiency through advanced insulation and ventilation, while Tiny Houses prioritize minimal space and affordability. This knowledge enables targeted marketing strategies and investment decisions that align with consumer demand for eco-friendly living or compact lifestyle solutions. Entrepreneurs can optimize resource allocation by recognizing that Passive Houses often require higher upfront costs but yield long-term energy savings, whereas Tiny Houses appeal to niche markets seeking low-cost, mobile housing. Grasping these distinctions supports innovation in product offerings and enhances competitive advantage in the green housing industry.
Comparison Table
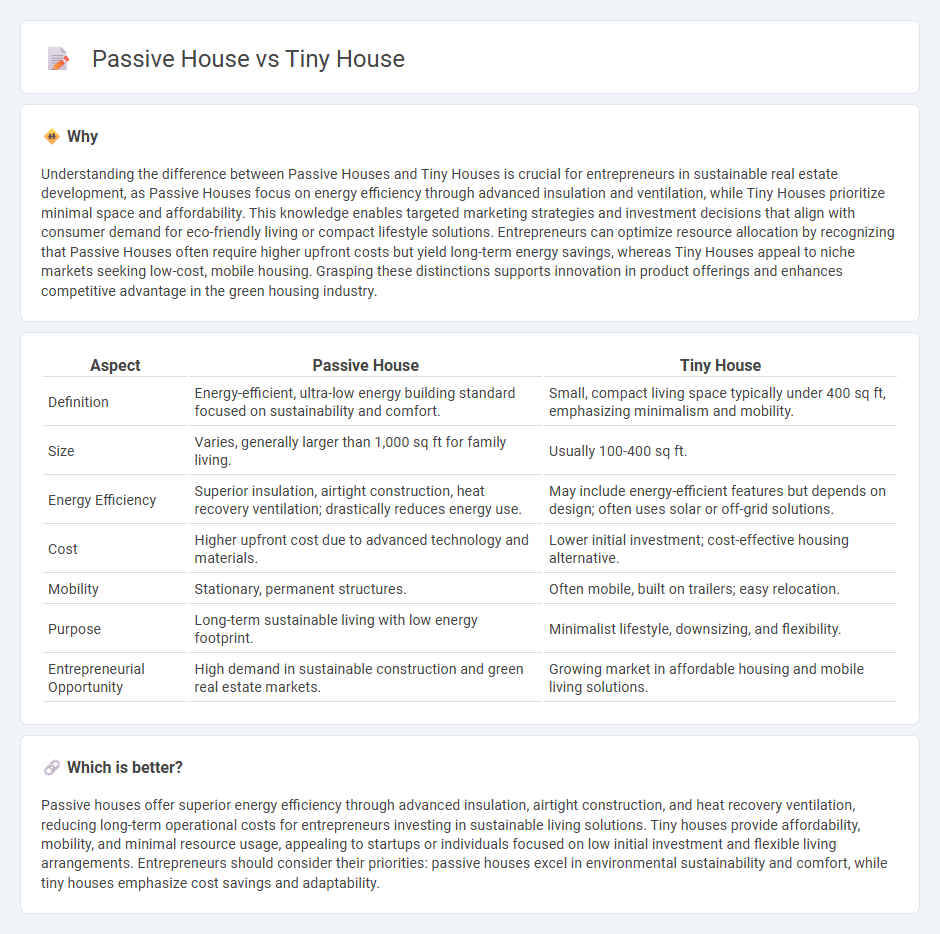
| Aspect | Passive House | Tiny House |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Energy-efficient, ultra-low energy building standard focused on sustainability and comfort. | Small, compact living space typically under 400 sq ft, emphasizing minimalism and mobility. |
| Size | Varies, generally larger than 1,000 sq ft for family living. | Usually 100-400 sq ft. |
| Energy Efficiency | Superior insulation, airtight construction, heat recovery ventilation; drastically reduces energy use. | May include energy-efficient features but depends on design; often uses solar or off-grid solutions. |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost due to advanced technology and materials. | Lower initial investment; cost-effective housing alternative. |
| Mobility | Stationary, permanent structures. | Often mobile, built on trailers; easy relocation. |
| Purpose | Long-term sustainable living with low energy footprint. | Minimalist lifestyle, downsizing, and flexibility. |
| Entrepreneurial Opportunity | High demand in sustainable construction and green real estate markets. | Growing market in affordable housing and mobile living solutions. |
Which is better?
Passive houses offer superior energy efficiency through advanced insulation, airtight construction, and heat recovery ventilation, reducing long-term operational costs for entrepreneurs investing in sustainable living solutions. Tiny houses provide affordability, mobility, and minimal resource usage, appealing to startups or individuals focused on low initial investment and flexible living arrangements. Entrepreneurs should consider their priorities: passive houses excel in environmental sustainability and comfort, while tiny houses emphasize cost savings and adaptability.
Connection
Entrepreneurship in the sustainable housing market leverages innovative designs like Passive House and Tiny House concepts to reduce energy consumption and minimize environmental impact. Both models emphasize efficient use of space and resources, appealing to eco-conscious consumers seeking affordable, low-maintenance living solutions. Entrepreneurs capitalize on growing demand for green building technologies by developing scalable, energy-efficient homes that promote sustainability and cost savings.
Key Terms
Cost-efficiency
Tiny houses typically offer lower initial construction costs due to their smaller size and simpler design, averaging between $30,000 and $60,000. Passive houses require a higher upfront investment, often ranging from $150 to $300 per square foot, but deliver significant long-term savings through reduced energy consumption and minimal operational costs. Explore more about balancing upfront expenses and lifetime value to determine the most cost-efficient option for your sustainable living goals.
Sustainability
Tiny houses minimize environmental impact through reduced materials and energy consumption, promoting sustainable living by maximizing space efficiency. Passive houses enhance sustainability with superior insulation, airtight construction, and energy-efficient systems that drastically lower heating and cooling demands. Explore the distinct benefits of these housing options to determine which best supports your green living goals.
Market differentiation
Tiny houses cater to minimalist lifestyles with compact spaces under 400 square feet, emphasizing affordability and mobility, while passive houses prioritize energy efficiency and sustainability through rigorous insulation and airtight construction, often in larger, permanent structures. The tiny house market targets urban dwellers and eco-conscious minimalists seeking low-cost, flexible living solutions, contrasted with passive houses appealing to homeowners investing in long-term energy savings and environmental impact reduction. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which housing model fits your lifestyle and sustainability goals best.
Source and External Links
Tiny-house movement - Wikipedia - The tiny-house movement is an architectural and social trend promoting smaller and simplified living spaces, typically under 400 to 600 square feet, offering lower-cost and eco-friendly housing alternatives, with variation in styles including mobile, fixed, treehouse, or floating homes, but facing challenges like legal zoning and storage limitations.
Modern-Minimalist Two-Trailer Tiny Home | A Genius DIY ... - YouTube - A detailed tour of a thoughtfully designed modern tiny home with efficient storage, social space integration, and elegant design details, showcasing the craftsmanship involved in creating a functional tiny house for long-term living.
No Loft - A Tiny House Designed for Long Term Living - YouTube - A review of a beautifully designed tiny home emphasizing comfortable living, ample built-in storage, natural ventilation, and indoor-outdoor connection, challenging common misconceptions that tiny homes cannot be comfortable for extended stays.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com