Marketplace flipping involves buying undervalued goods or businesses and reselling them at a profit, leveraging market demand and pricing inefficiencies. Digital products focus on creating and selling intangible assets like eBooks, software, or online courses, offering scalability and low overhead costs. Explore the advantages and challenges of both strategies to determine the best fit for your entrepreneurial goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between marketplace flipping and digital products is crucial for entrepreneurs to tailor their business strategies effectively and allocate resources efficiently. Marketplace flipping involves buying and reselling physical items for profit, demanding expertise in inventory management and market trends. Digital products focus on creating intangible goods like e-books, software, or courses, requiring skills in content creation and digital marketing. Clarity on these models enables entrepreneurs to optimize profit margins and scale sustainably in competitive environments.
Comparison Table
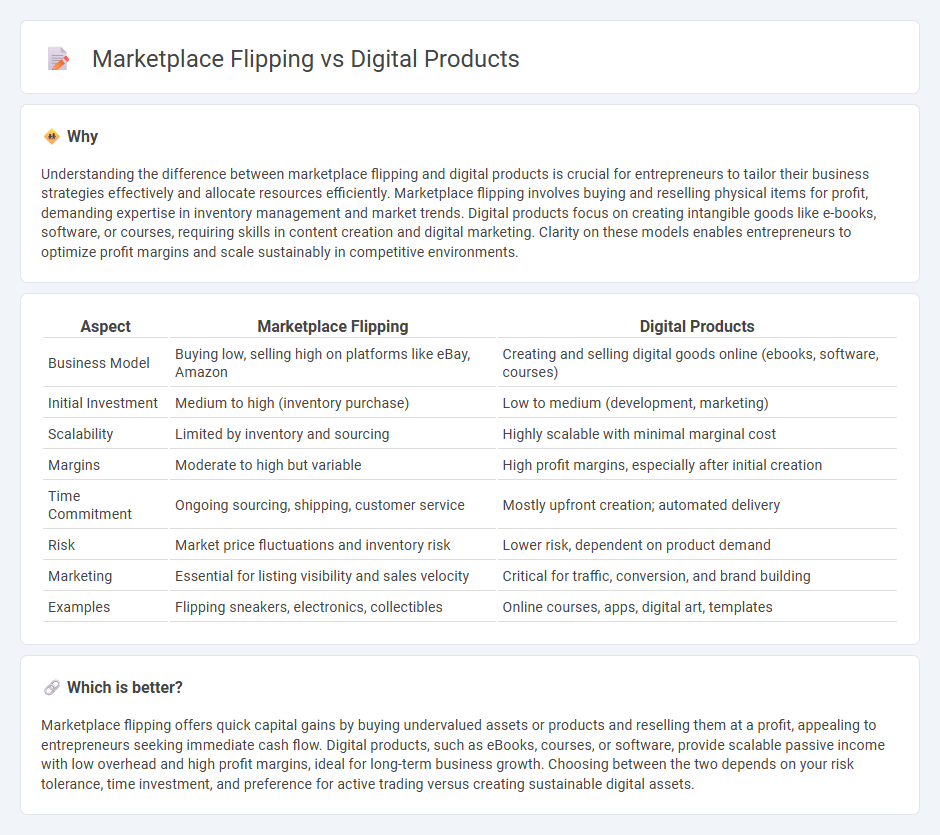
| Aspect | Marketplace Flipping | Digital Products |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model | Buying low, selling high on platforms like eBay, Amazon | Creating and selling digital goods online (ebooks, software, courses) |
| Initial Investment | Medium to high (inventory purchase) | Low to medium (development, marketing) |
| Scalability | Limited by inventory and sourcing | Highly scalable with minimal marginal cost |
| Margins | Moderate to high but variable | High profit margins, especially after initial creation |
| Time Commitment | Ongoing sourcing, shipping, customer service | Mostly upfront creation; automated delivery |
| Risk | Market price fluctuations and inventory risk | Lower risk, dependent on product demand |
| Marketing | Essential for listing visibility and sales velocity | Critical for traffic, conversion, and brand building |
| Examples | Flipping sneakers, electronics, collectibles | Online courses, apps, digital art, templates |
Which is better?
Marketplace flipping offers quick capital gains by buying undervalued assets or products and reselling them at a profit, appealing to entrepreneurs seeking immediate cash flow. Digital products, such as eBooks, courses, or software, provide scalable passive income with low overhead and high profit margins, ideal for long-term business growth. Choosing between the two depends on your risk tolerance, time investment, and preference for active trading versus creating sustainable digital assets.
Connection
Marketplace flipping and digital products are interconnected through the buying, improving, and reselling of digital assets such as websites, software, or online courses for profit. Entrepreneurs leverage market demand and digital product scalability to maximize returns while minimizing physical inventory costs. This synergy accelerates income streams by combining digital product flexibility with marketplace flipping strategies.
Key Terms
Scalability
Digital products offer unparalleled scalability due to low marginal costs and the ability to reach a global audience instantly, unlike marketplace flipping which requires constant inventory management and manual transactions. Marketplace flipping depends heavily on sourcing products and market demand fluctuations, limiting growth potential as volume increases. Explore how each model impacts long-term scalability and business growth opportunities.
Inventory management
Inventory management in digital products centers on unlimited stock and instant delivery, eliminating traditional warehousing challenges. Marketplace flipping requires careful tracking of physical items, storage capacity, and shipping logistics to maintain profitability. Explore effective inventory strategies tailored for both digital goods and marketplace flipping to optimize operations.
Platform fees
Platform fees for digital products typically range between 3% and 15%, depending on the marketplace, whereas flipping physical goods on marketplaces like eBay or Amazon often incurs fees closer to 10%-20%, including listing, final value, and payment processing fees. Digital products benefit from lower transaction costs and no shipping expenses, enhancing profit margins compared to physical goods that require inventory management and logistics. Explore detailed fee structures and strategies to maximize profits on each platform.
Source and External Links
What is a Digital Product? - Productfolio - A digital product is an intangible good or service based on digital technology, including software, digital content, online platforms, SaaS, and digital services, that exist and operate in a digital environment without physical form.
Digital goods - Wikipedia - Digital goods are intangible digital form products such as e-books, downloadable music, software, digital subscriptions, online courses, templates, and virtual goods used in online games and communities.
What Are Digital Products? Sell These 11 Products Online (2025) - Shopify - Digital products include printable items, digital templates, software, ebooks, online courses, NFTs, and digital art, which can be easily created, distributed online, and sold repeatedly without physical inventory.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com