Thrift flipping involves purchasing second-hand items to refurbish and resell for profit, capitalizing on sustainable consumer trends and lower initial investment costs. Digital product creation focuses on designing and selling intangible goods like e-books, courses, or software, leveraging scalability and global market reach. Explore the advantages and strategies of each entrepreneurial path to determine which best fits your business goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between thrift flipping and digital product creation is crucial for entrepreneurs to select the most scalable and sustainable business model. Thrift flipping involves reselling physical second-hand items, which requires inventory management and has limited profit margins, whereas digital product creation focuses on developing intangible assets like e-books, courses, or software that can be sold repeatedly with minimal overhead. Mastering these distinctions enables entrepreneurs to optimize resource allocation and align strategies with market demand. This knowledge directly impacts growth potential and long-term financial success in the competitive entrepreneurship landscape.
Comparison Table
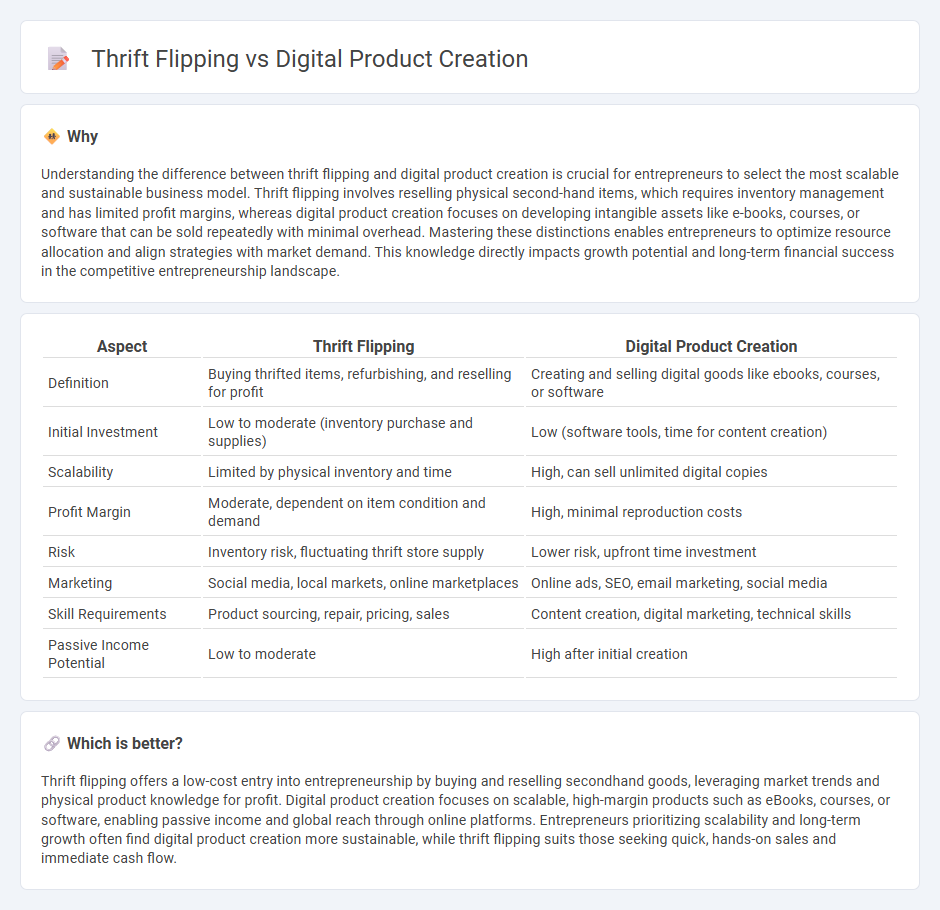
| Aspect | Thrift Flipping | Digital Product Creation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying thrifted items, refurbishing, and reselling for profit | Creating and selling digital goods like ebooks, courses, or software |
| Initial Investment | Low to moderate (inventory purchase and supplies) | Low (software tools, time for content creation) |
| Scalability | Limited by physical inventory and time | High, can sell unlimited digital copies |
| Profit Margin | Moderate, dependent on item condition and demand | High, minimal reproduction costs |
| Risk | Inventory risk, fluctuating thrift store supply | Lower risk, upfront time investment |
| Marketing | Social media, local markets, online marketplaces | Online ads, SEO, email marketing, social media |
| Skill Requirements | Product sourcing, repair, pricing, sales | Content creation, digital marketing, technical skills |
| Passive Income Potential | Low to moderate | High after initial creation |
Which is better?
Thrift flipping offers a low-cost entry into entrepreneurship by buying and reselling secondhand goods, leveraging market trends and physical product knowledge for profit. Digital product creation focuses on scalable, high-margin products such as eBooks, courses, or software, enabling passive income and global reach through online platforms. Entrepreneurs prioritizing scalability and long-term growth often find digital product creation more sustainable, while thrift flipping suits those seeking quick, hands-on sales and immediate cash flow.
Connection
Thrift flipping and digital product creation both harness creativity and resourcefulness to generate income streams with minimal initial investment. Thrift flipping transforms undervalued physical items into profitable assets, while digital product creation leverages intellectual property to scale revenue without inventory constraints. Together, they exemplify entrepreneurial strategies that maximize return on investment through innovative value addition.
Key Terms
Digital product creation:
Digital product creation involves developing intangible assets such as eBooks, software, online courses, and digital art, enabling scalability and passive income generation without inventory management. This model leverages technology and platforms like Shopify, Udemy, or Amazon Kindle to reach a global audience efficiently. Explore detailed strategies and tools to maximize your digital product success.
Scalability
Digital product creation offers unparalleled scalability by enabling creators to distribute unlimited copies globally without additional inventory costs. Thrift flipping relies on sourcing limited physical items, constraining potential growth and requiring continuous effort to maintain inventory. Explore the advantages of scalable digital products versus the hands-on nature of thrift flipping to determine the best path for expanding your business.
Intellectual property
Digital product creation involves developing original content such as eBooks, software, or online courses, where intellectual property rights ensure protection and monetization of unique ideas. Thrift flipping relies on purchasing second-hand items, refurbishing them, and reselling them, often raising concerns about trademark and design infringement in relation to brand logos or patented designs. Explore the nuances of intellectual property in these ventures to safeguard your business and leverage creative assets effectively.
Source and External Links
How to Create Digital Products | Thinkific - This guide outlines 6 key steps to creating digital products: finding a unique idea, researching market trends, identifying your target audience, planning, creating, and launching your product, emphasizing leveraging your skills and passions to monetize your expertise.
What Are Digital Products? Sell These 11 Products Online (2025) - Shopify explains digital products as goods existing in digital format like ebooks, courses, music, templates, and software, and offers advice on brainstorming ideas by connecting products to skills, customer needs, and community engagement.
How to create and sell your first digital product in 7 days - YouTube - A step-by-step, proven seven-day strategy to create and successfully sell a digital product from scratch, including downloadable planning tools to ensure no critical steps are missed.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com