Tiny acquisitions offer entrepreneurs rapid market entry and immediate cash flow by purchasing existing small businesses, reducing startup risks and operational uncertainties. Bootstrapping emphasizes organic growth using personal savings and reinvested profits, fostering financial discipline and control without external funding constraints. Explore these strategies to determine which path best suits your entrepreneurial goals and resources.
Why it is important
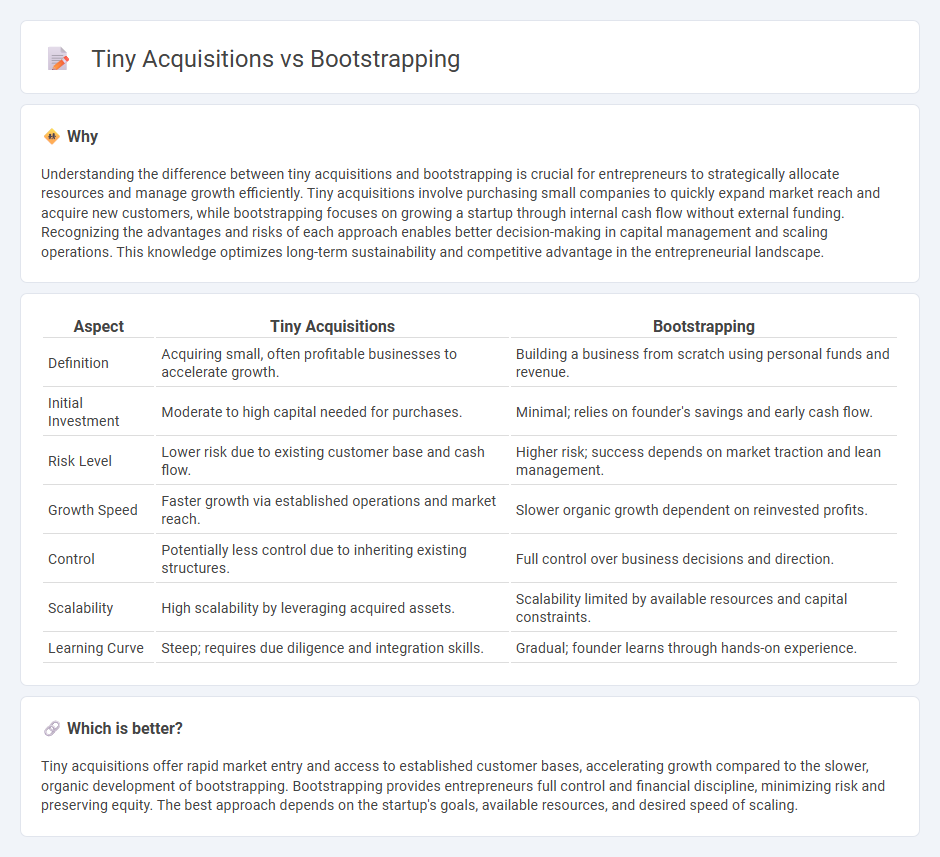
Understanding the difference between tiny acquisitions and bootstrapping is crucial for entrepreneurs to strategically allocate resources and manage growth efficiently. Tiny acquisitions involve purchasing small companies to quickly expand market reach and acquire new customers, while bootstrapping focuses on growing a startup through internal cash flow without external funding. Recognizing the advantages and risks of each approach enables better decision-making in capital management and scaling operations. This knowledge optimizes long-term sustainability and competitive advantage in the entrepreneurial landscape.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Tiny Acquisitions | Bootstrapping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Acquiring small, often profitable businesses to accelerate growth. | Building a business from scratch using personal funds and revenue. |
| Initial Investment | Moderate to high capital needed for purchases. | Minimal; relies on founder's savings and early cash flow. |
| Risk Level | Lower risk due to existing customer base and cash flow. | Higher risk; success depends on market traction and lean management. |
| Growth Speed | Faster growth via established operations and market reach. | Slower organic growth dependent on reinvested profits. |
| Control | Potentially less control due to inheriting existing structures. | Full control over business decisions and direction. |
| Scalability | High scalability by leveraging acquired assets. | Scalability limited by available resources and capital constraints. |
| Learning Curve | Steep; requires due diligence and integration skills. | Gradual; founder learns through hands-on experience. |
Which is better?
Tiny acquisitions offer rapid market entry and access to established customer bases, accelerating growth compared to the slower, organic development of bootstrapping. Bootstrapping provides entrepreneurs full control and financial discipline, minimizing risk and preserving equity. The best approach depends on the startup's goals, available resources, and desired speed of scaling.
Connection
Tiny acquisitions provide entrepreneurs with strategic opportunities to rapidly expand capabilities, access niche markets, or acquire technology without relying heavily on external funding. Bootstrapping complements this approach by emphasizing resourcefulness and reinvestment of early revenues to fund these small-scale acquisitions, thereby minimizing dilution and maintaining control. Together, they form a powerful synergy that accelerates growth while preserving financial independence in early-stage ventures.
Key Terms
Self-funding
Bootstrapping involves self-funding a startup using personal savings or revenue generated from the business, emphasizing financial independence and control without external investors. Tiny acquisitions refer to strategically purchasing small companies or assets with limited capital, enabling growth through targeted investments while maintaining operational autonomy. Explore the benefits and challenges of self-funding strategies to optimize your entrepreneurial journey.
Equity ownership
Bootstrapping maintains full equity ownership by using personal savings and reinvested profits to grow the business without external investors. Tiny acquisitions often involve exchanging equity stakes to gain control over smaller companies, which can dilute ownership but accelerate growth through strategic integration. Discover how each approach impacts equity structure and long-term control.
Growth strategy
Bootstrapping involves growing a business using personal savings and revenue, emphasizing organic growth and operational efficiency without external funding, which ensures control and sustainability. Tiny acquisitions focus on strategic growth by purchasing small, often complementary businesses to rapidly increase market share and capabilities with minimal risk. Explore the advantages of each growth strategy to determine the best fit for your business goals.
Source and External Links
Bootstrapping - Overview, Stages, and Advantages - Bootstrapping is the process of building a business from scratch without attracting investment or with minimal external capital, often relying on personal funds, credit cards, and limited financing sources through stages like initial savings, client revenue, and credit expansion.
Bootstrapping - Wikipedia - In business, bootstrapping refers to starting a company using personal savings or funds from friends and family, later funding growth through customer revenue and possibly loans or venture capital for expansion.
Bootstrapping (statistics) - Wikipedia - Bootstrapping in statistics is a resampling technique used to estimate the distribution, bias, variance, and confidence intervals of an estimator by repeatedly sampling with replacement from the observed data.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com