Secondment involves temporarily transferring an employee to a different role or organization to develop skills and expand professional networks, often enhancing career growth and organizational collaboration. Remote working allows employees to perform their job duties from outside the traditional office environment, utilizing digital tools to maintain productivity and work-life balance. Explore the key differences and benefits of secondment versus remote working to determine the best employment strategy for your needs.
Why it is important
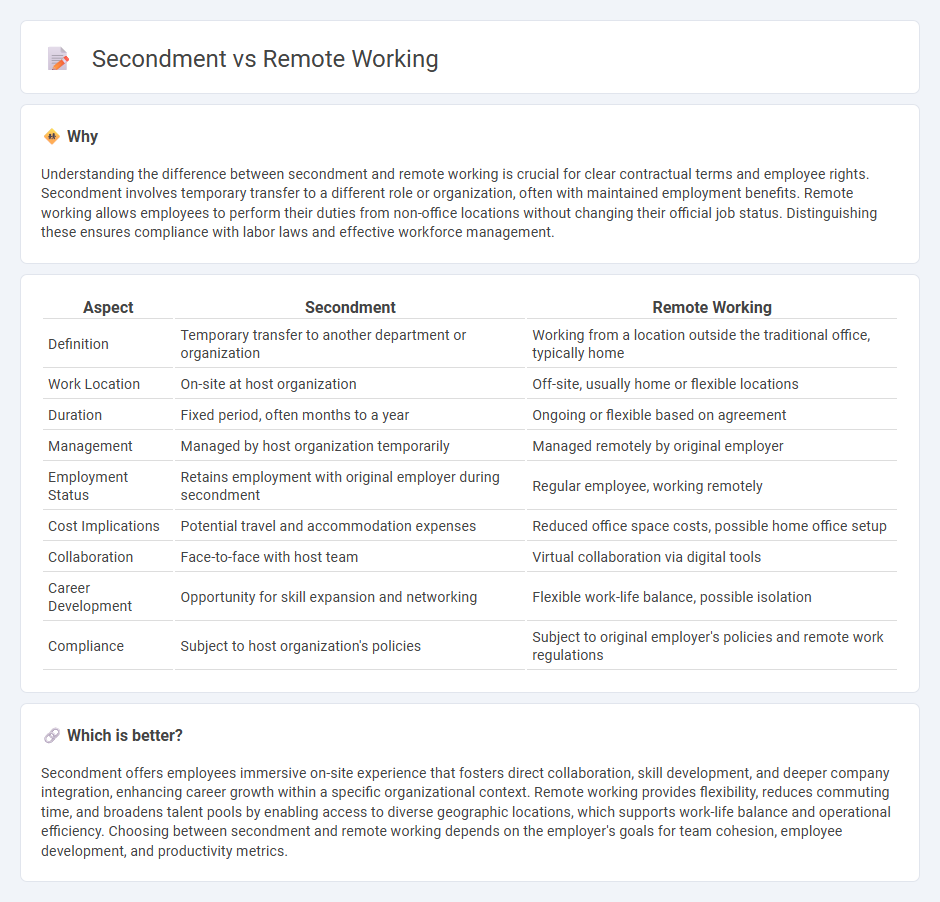
Understanding the difference between secondment and remote working is crucial for clear contractual terms and employee rights. Secondment involves temporary transfer to a different role or organization, often with maintained employment benefits. Remote working allows employees to perform their duties from non-office locations without changing their official job status. Distinguishing these ensures compliance with labor laws and effective workforce management.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Secondment | Remote Working |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temporary transfer to another department or organization | Working from a location outside the traditional office, typically home |
| Work Location | On-site at host organization | Off-site, usually home or flexible locations |
| Duration | Fixed period, often months to a year | Ongoing or flexible based on agreement |
| Management | Managed by host organization temporarily | Managed remotely by original employer |
| Employment Status | Retains employment with original employer during secondment | Regular employee, working remotely |
| Cost Implications | Potential travel and accommodation expenses | Reduced office space costs, possible home office setup |
| Collaboration | Face-to-face with host team | Virtual collaboration via digital tools |
| Career Development | Opportunity for skill expansion and networking | Flexible work-life balance, possible isolation |
| Compliance | Subject to host organization's policies | Subject to original employer's policies and remote work regulations |
Which is better?
Secondment offers employees immersive on-site experience that fosters direct collaboration, skill development, and deeper company integration, enhancing career growth within a specific organizational context. Remote working provides flexibility, reduces commuting time, and broadens talent pools by enabling access to diverse geographic locations, which supports work-life balance and operational efficiency. Choosing between secondment and remote working depends on the employer's goals for team cohesion, employee development, and productivity metrics.
Connection
Secondment and remote working both enhance workforce flexibility by enabling employees to contribute from different locations and time zones. Secondment often involves temporary relocation or assignment, which can be seamlessly managed through remote working technologies, reducing disruption and travel costs. Combining secondment with remote working strategies supports talent mobility, knowledge transfer, and organizational agility in today's dynamic employment landscape.
Key Terms
Work Location
Remote working allows employees to perform job duties from any location outside the traditional office, leveraging digital tools and cloud connectivity to maintain productivity. Secondment involves a temporary transfer to a different work site or company, enabling on-site experience and closer collaboration. Explore deeper insights into work location dynamics between remote working and secondment to optimize your workforce strategy.
Employment Contract
Employment contracts for remote working typically specify work hours, location flexibility, and data security measures to accommodate off-site productivity. In contrast, secondment agreements outline temporary employee relocation terms, including duration, reporting structure, and responsibilities under the host employer. Explore the nuances of these employment contracts to understand how they impact legal obligations and workforce management.
Supervision and Reporting
Remote working allows employees to maintain flexibility while supervisors oversee performance through digital communication tools like video calls, project management software, and regular reporting protocols. Secondment typically involves a temporary transfer to a different department or organization, where supervision is direct and reporting follows the host entity's standards. Explore deeper insights into managing supervision and reporting in both remote working and secondment scenarios.
Source and External Links
What Is Remote Work? Ultimate Guide - Remote work allows employees to work from any location outside their company's office, enabled by digital tools like Slack and Zoom, reshaping work-life balance and productivity norms.
Remote Work Requirements - Remote work participation requires reviewing policies, supervisor approval based on job suitability, completing training, and signing a remote work agreement, which is renewed annually.
20 Advantages of Remote Working for Employees and ... - Remote working boosts staff motivation, productivity, retention, and inclusivity, blending remote and office presence for flexible, effective work environments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com