Quiet quitting involves employees reducing effort and engagement without formally resigning, reflecting workplace dissatisfaction and burnout. Rage applying occurs when individuals aggressively seek new jobs following negative experiences or frustration with their current role. Explore deeper insights into these contrasting employment behaviors and their impact on organizational dynamics.
Why it is important
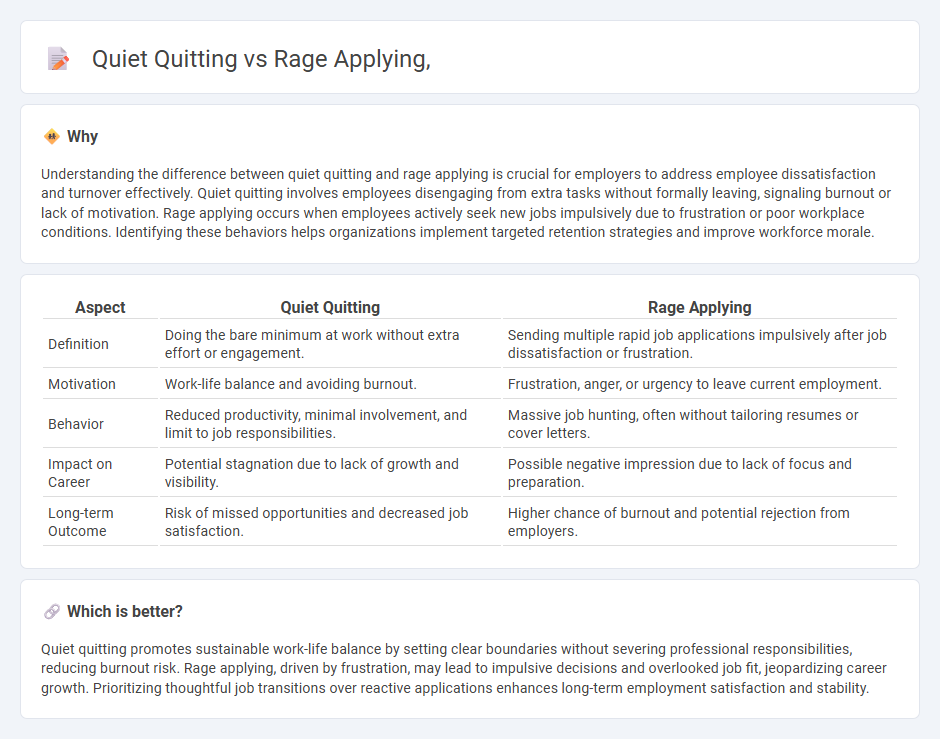
Understanding the difference between quiet quitting and rage applying is crucial for employers to address employee dissatisfaction and turnover effectively. Quiet quitting involves employees disengaging from extra tasks without formally leaving, signaling burnout or lack of motivation. Rage applying occurs when employees actively seek new jobs impulsively due to frustration or poor workplace conditions. Identifying these behaviors helps organizations implement targeted retention strategies and improve workforce morale.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quiet Quitting | Rage Applying |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Doing the bare minimum at work without extra effort or engagement. | Sending multiple rapid job applications impulsively after job dissatisfaction or frustration. |
| Motivation | Work-life balance and avoiding burnout. | Frustration, anger, or urgency to leave current employment. |
| Behavior | Reduced productivity, minimal involvement, and limit to job responsibilities. | Massive job hunting, often without tailoring resumes or cover letters. |
| Impact on Career | Potential stagnation due to lack of growth and visibility. | Possible negative impression due to lack of focus and preparation. |
| Long-term Outcome | Risk of missed opportunities and decreased job satisfaction. | Higher chance of burnout and potential rejection from employers. |
Which is better?
Quiet quitting promotes sustainable work-life balance by setting clear boundaries without severing professional responsibilities, reducing burnout risk. Rage applying, driven by frustration, may lead to impulsive decisions and overlooked job fit, jeopardizing career growth. Prioritizing thoughtful job transitions over reactive applications enhances long-term employment satisfaction and stability.
Connection
Quiet quitting and rage applying both reflect growing employee dissatisfaction in the modern workforce, often triggered by burnout and lack of recognition. Quiet quitting involves employees disengaging and doing the bare minimum to meet job requirements, while rage applying sees frustrated workers aggressively seeking new employment opportunities. These behaviors highlight a cycle where disengagement fuels urgent job hunting, signaling broader workplace morale and retention challenges.
Key Terms
Burnout
Rage applying involves aggressively seeking new jobs as a reaction to intense burnout, marked by frustration and urgency to escape a toxic work environment. Quiet quitting reflects a gradual disengagement, where employees limit their work effort to bare minimums, signaling chronic burnout and dissatisfaction. Explore the signs of burnout further to identify which behavior may be impacting your workplace dynamics.
Disengagement
Rage applying represents active disengagement where employees aggressively seek new opportunities due to dissatisfaction, contrasting with quiet quitting, which entails minimal effort while remaining in the role. Disengagement in rage applying signals high frustration and urgency, often leading to rapid turnover, whereas quiet quitting reflects passive withdrawal and emotional detachment without immediate departure. Explore the nuances of workplace disengagement to better understand and address these critical employee behaviors.
Job satisfaction
Rage applying reflects intense job dissatisfaction driving candidates to aggressively pursue new roles, while quiet quitting indicates employees remain physically present but disengaged due to unmet job expectations and low morale. Both phenomena highlight critical workplace issues such as burnout, lack of recognition, and poor work-life balance affecting overall job satisfaction. Explore the underlying causes and effective strategies to enhance employee engagement and retention.
Source and External Links
Rage applying - Wikipedia - Rage applying is the practice of applying to many jobs impulsively after frustration with one's current role, often triggered by being undervalued; it can be empowering but may lead to poor job fit long-term.
What is rage applying and how to deal with it? - aggity - Rage applying occurs when workers, driven by frustration or burnout, send numerous job applications indiscriminately, often without regard to qualifications, aiming to escape a dissatisfying work situation.
Stop and think before Rage Applying - Eptura - Rage applying is an impulsive reaction by employees fed up with their job situation, and experts recommend applying thoughtfully instead of broadly to avoid repeating similar issues in new roles.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com