No-collar work represents roles in emerging industries such as technology, creative arts, and digital services, often emphasizing innovation and flexibility over traditional labor. Blue-collar work typically involves manual labor in sectors like manufacturing, construction, and maintenance, where physical skills and hands-on tasks are primary. Explore the distinctions between these employment types to understand their impact on the modern workforce.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between no-collar work, which often involves technology and creative industries, and blue-collar work, typically associated with manual labor and skilled trades, is crucial for workforce planning and career development. Employers can optimize hiring strategies by recognizing the distinct skill sets and work environments associated with each category. This distinction influences training programs and educational focus tailored to market demands. Accurate knowledge of these differences helps workers navigate job opportunities aligned with their strengths and industry trends.
Comparison Table
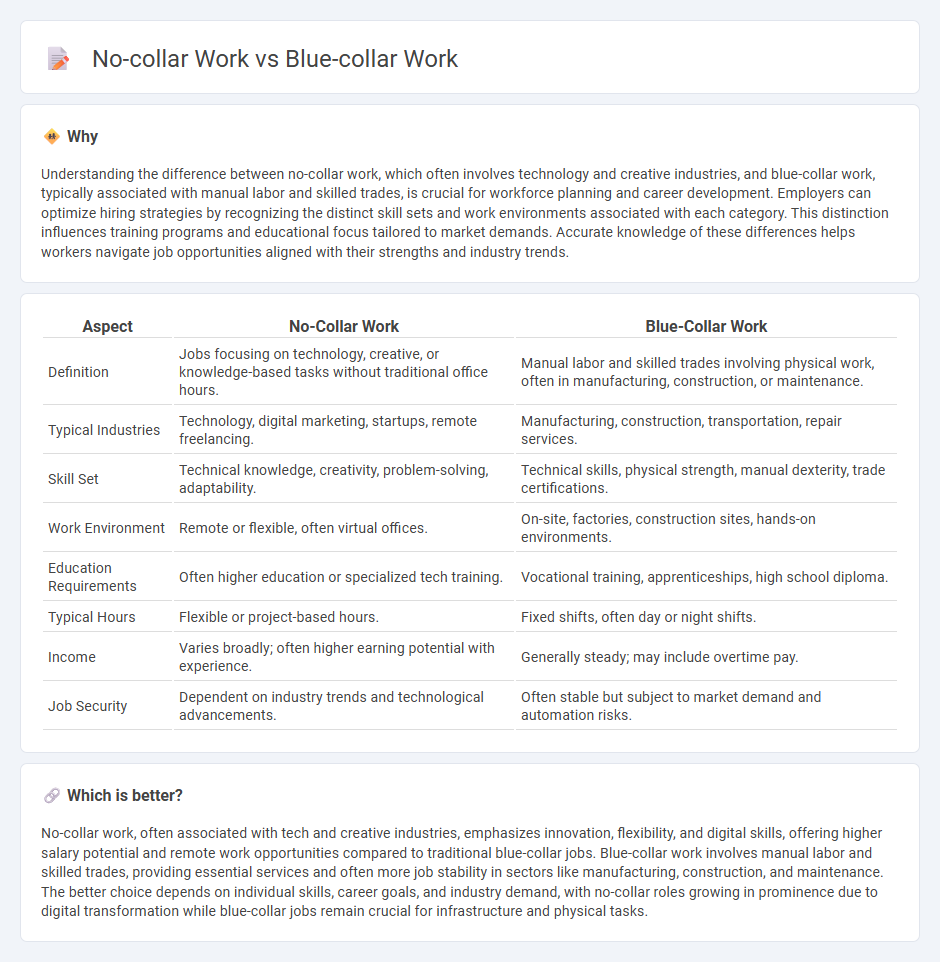
| Aspect | No-Collar Work | Blue-Collar Work |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Jobs focusing on technology, creative, or knowledge-based tasks without traditional office hours. | Manual labor and skilled trades involving physical work, often in manufacturing, construction, or maintenance. |
| Typical Industries | Technology, digital marketing, startups, remote freelancing. | Manufacturing, construction, transportation, repair services. |
| Skill Set | Technical knowledge, creativity, problem-solving, adaptability. | Technical skills, physical strength, manual dexterity, trade certifications. |
| Work Environment | Remote or flexible, often virtual offices. | On-site, factories, construction sites, hands-on environments. |
| Education Requirements | Often higher education or specialized tech training. | Vocational training, apprenticeships, high school diploma. |
| Typical Hours | Flexible or project-based hours. | Fixed shifts, often day or night shifts. |
| Income | Varies broadly; often higher earning potential with experience. | Generally steady; may include overtime pay. |
| Job Security | Dependent on industry trends and technological advancements. | Often stable but subject to market demand and automation risks. |
Which is better?
No-collar work, often associated with tech and creative industries, emphasizes innovation, flexibility, and digital skills, offering higher salary potential and remote work opportunities compared to traditional blue-collar jobs. Blue-collar work involves manual labor and skilled trades, providing essential services and often more job stability in sectors like manufacturing, construction, and maintenance. The better choice depends on individual skills, career goals, and industry demand, with no-collar roles growing in prominence due to digital transformation while blue-collar jobs remain crucial for infrastructure and physical tasks.
Connection
No-collar work, often characterized by creative, tech-driven roles, intersects with blue-collar work through the increasing integration of technology in traditionally manual industries. Automation, digital tools, and data analytics enhance productivity and safety in blue-collar sectors such as manufacturing, construction, and logistics. This convergence fosters collaboration between skilled laborers and tech professionals, driving innovation and efficiency in the modern workforce.
Key Terms
Manual Labor
Blue-collar work involves manual labor tasks such as construction, manufacturing, and maintenance, requiring physical skills and hands-on expertise. No-collar work typically refers to jobs in creative or tech-driven fields where manual labor is minimal or absent, emphasizing innovation and cognitive abilities. Explore the differences in job nature, skill sets, and career opportunities between these work types to better understand their economic impact.
Knowledge Work
Blue-collar work typically involves manual labor in industries like manufacturing and construction, whereas no-collar work emphasizes knowledge-based tasks centered on creativity, innovation, and problem-solving in fields such as technology and research. Knowledge work requires cognitive skills, critical thinking, and continuous learning, distinguishing it from traditional blue-collar roles that rely more on physical effort and routine processes. Explore the nuances and evolving dynamics between blue-collar and no-collar work to understand the future of labor markets and workforce development.
Automation
Blue-collar work traditionally involves manual labor in industries like manufacturing and construction, where automation increasingly replaces repetitive tasks, enhancing efficiency but reducing job availability. No-collar work, characterized by creative and knowledge-based roles often in tech and gig economies, benefits from automation through advanced AI tools that augment productivity and innovation. Explore the evolving impact of automation on these distinct workforce categories to understand future employment trends.
Source and External Links
Blue collar meaning: Job types, challenges, and workforce ... - Blue collar work involves manual labor usually requiring physical effort, found in industries such as construction and manufacturing, forming the backbone of operational excellence and organizational resilience through tasks that drive productivity, maintain quality, and enhance customer experience.
16 Examples of Blue Collar Jobs to Consider in 2025 | Huntr Blog - Blue collar jobs encompass roles like firefighters, elevator technicians, mechanics, and others that involve physical labor and specialized skills; they are critical for maintaining city infrastructure and safety, often providing competitive salaries without requiring formal higher education.
12 Examples of Blue-Collar Jobs (With Salaries) | Indeed.com - Blue-collar jobs typically involve skilled trades or physically demanding work in sectors like construction and manufacturing, generally not requiring a college degree but often requiring specialized expertise, distinguishing them from white-collar office-based roles.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com