Quiet quitting refers to employees reducing their effort and engagement without formally resigning, often leading to decreased productivity and morale. Quiet hiring involves companies filling skill gaps by reallocating current employees' responsibilities or hiring discreetly to avoid public scrutiny. Explore further to understand the impact of these trends on the modern workforce.
Why it is important
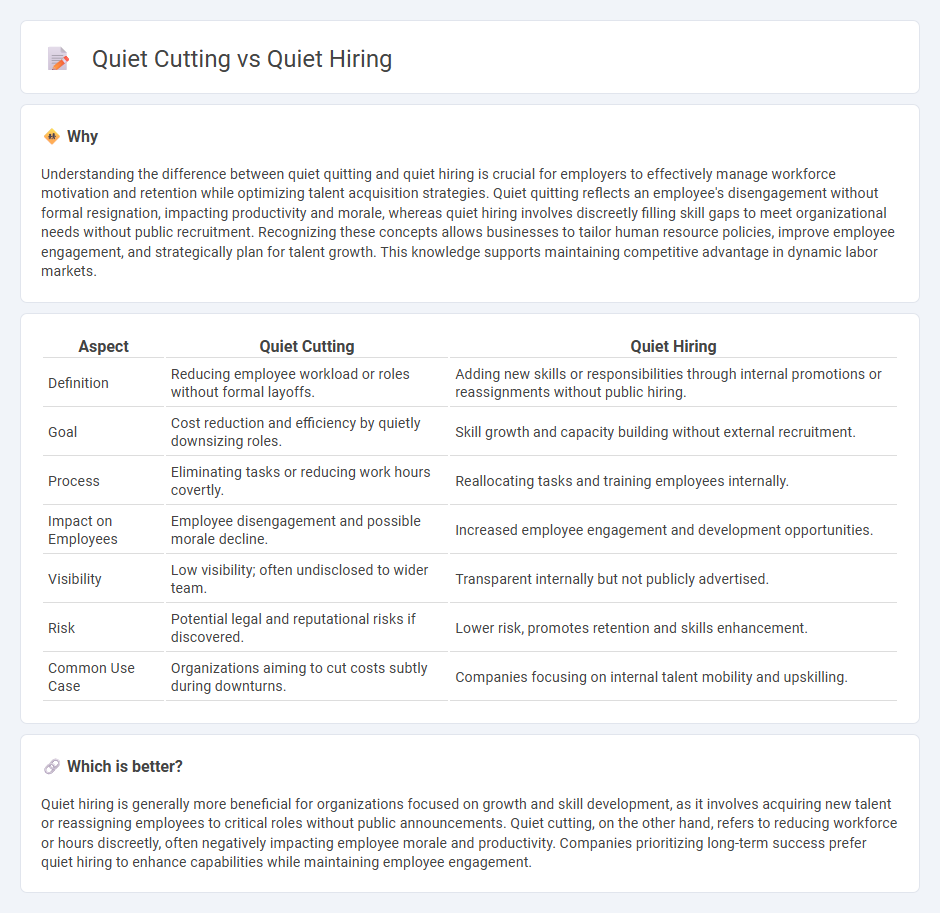
Understanding the difference between quiet quitting and quiet hiring is crucial for employers to effectively manage workforce motivation and retention while optimizing talent acquisition strategies. Quiet quitting reflects an employee's disengagement without formal resignation, impacting productivity and morale, whereas quiet hiring involves discreetly filling skill gaps to meet organizational needs without public recruitment. Recognizing these concepts allows businesses to tailor human resource policies, improve employee engagement, and strategically plan for talent growth. This knowledge supports maintaining competitive advantage in dynamic labor markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quiet Cutting | Quiet Hiring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reducing employee workload or roles without formal layoffs. | Adding new skills or responsibilities through internal promotions or reassignments without public hiring. |
| Goal | Cost reduction and efficiency by quietly downsizing roles. | Skill growth and capacity building without external recruitment. |
| Process | Eliminating tasks or reducing work hours covertly. | Reallocating tasks and training employees internally. |
| Impact on Employees | Employee disengagement and possible morale decline. | Increased employee engagement and development opportunities. |
| Visibility | Low visibility; often undisclosed to wider team. | Transparent internally but not publicly advertised. |
| Risk | Potential legal and reputational risks if discovered. | Lower risk, promotes retention and skills enhancement. |
| Common Use Case | Organizations aiming to cut costs subtly during downturns. | Companies focusing on internal talent mobility and upskilling. |
Which is better?
Quiet hiring is generally more beneficial for organizations focused on growth and skill development, as it involves acquiring new talent or reassigning employees to critical roles without public announcements. Quiet cutting, on the other hand, refers to reducing workforce or hours discreetly, often negatively impacting employee morale and productivity. Companies prioritizing long-term success prefer quiet hiring to enhance capabilities while maintaining employee engagement.
Connection
Quiet cutting and quiet hiring are interconnected strategies reshaping modern workforce management by subtly adjusting staffing levels without public announcements or formal layoffs. Quiet cutting reduces employee roles or hours discreetly, helping organizations manage costs, while quiet hiring fills critical skill gaps internally by reallocating existing talent or hiring new employees quietly. Both methods prioritize operational agility and confidentiality, enabling companies to adapt to market changes with minimal disruption and maintain competitive advantage.
Key Terms
Internal Mobility
Quiet hiring emphasizes internal mobility by reallocating existing employees to new roles that match emerging business needs without external recruitment. Quiet cutting involves reducing workforce size discreetly, often through attrition or reassigning roles internally to maintain productivity while minimizing layoffs. Explore the strategic benefits and challenges of these workforce management approaches to optimize talent utilization.
Workforce Optimization
Quiet hiring emphasizes strategic talent acquisition by redistributing existing roles and leveraging internal capabilities to enhance workforce efficiency without public announcements. Quiet cutting involves subtle workforce reductions through attrition, reassignments, or role eliminations aimed at cost savings while minimizing impact on morale and reputation. Explore deeper insights into how these approaches optimize organizational agility and talent management.
Talent Redeployment
Quiet hiring emphasizes internal talent redeployment to fill critical roles without external recruitment, optimizing workforce agility and cost-efficiency. In contrast, quiet cutting strategically reduces headcount by not refilling positions and reallocates responsibilities among existing employees to maintain productivity. Discover how organizations leverage these approaches to maximize talent utilization and drive business resilience.
Source and External Links
What Is Quiet Hiring and Should You Do It in 2025? - Folks RH - Quiet hiring is a discreet recruitment practice where companies do not publicly advertise jobs but approach candidates privately, often leading to internal promotions, new responsibilities for existing staff, or hiring temporary workers, commonly used in tech and startups to protect strategic plans.
Quiet Hiring in Times of Uncertainty: Opportunity or Red Flag? - The Muse - Quiet hiring occurs when employees are assigned more work or new duties without formal promotions or raises, meaning workers take on additional roles silently without clarity on compensation or permanency.
Is Quiet Hiring the Employer Response To Quiet Quitting? - Indeed - Quiet hiring involves companies relying on current employees or contract workers to cover roles beyond their original job scopes, aiming to maximize productivity without new hires, as exemplified by Google's approach combining internal feedback and selective external recruitment.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com