Algorithmic management leverages data-driven systems and artificial intelligence to monitor, evaluate, and optimize employee performance, enhancing efficiency and consistency in organizational workflows. Participatory management emphasizes employee involvement in decision-making processes, fostering collaboration, job satisfaction, and innovation by valuing worker insights and feedback. Explore how these contrasting approaches shape modern employment dynamics and workplace culture.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between algorithmic management, which relies on data-driven automation and AI to optimize workforce performance, and participatory management, which involves employee input and collaboration in decision-making, is crucial for effective workforce strategy. This knowledge enables organizations to balance efficiency and employee engagement, improving productivity and job satisfaction. Employing the appropriate management style can reduce turnover rates and enhance organizational adaptability in the evolving job market. Recognizing these differences helps leaders implement ethical and inclusive management practices that align with company values and goals.
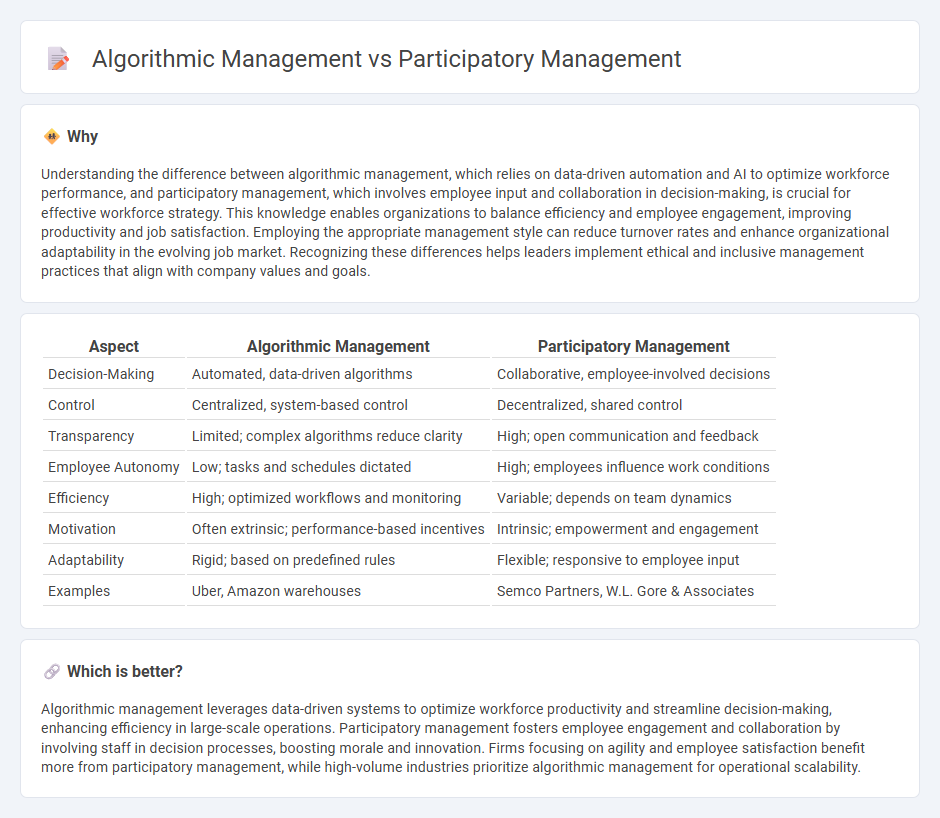
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Algorithmic Management | Participatory Management |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-Making | Automated, data-driven algorithms | Collaborative, employee-involved decisions |
| Control | Centralized, system-based control | Decentralized, shared control |
| Transparency | Limited; complex algorithms reduce clarity | High; open communication and feedback |
| Employee Autonomy | Low; tasks and schedules dictated | High; employees influence work conditions |
| Efficiency | High; optimized workflows and monitoring | Variable; depends on team dynamics |
| Motivation | Often extrinsic; performance-based incentives | Intrinsic; empowerment and engagement |
| Adaptability | Rigid; based on predefined rules | Flexible; responsive to employee input |
| Examples | Uber, Amazon warehouses | Semco Partners, W.L. Gore & Associates |
Which is better?
Algorithmic management leverages data-driven systems to optimize workforce productivity and streamline decision-making, enhancing efficiency in large-scale operations. Participatory management fosters employee engagement and collaboration by involving staff in decision processes, boosting morale and innovation. Firms focusing on agility and employee satisfaction benefit more from participatory management, while high-volume industries prioritize algorithmic management for operational scalability.
Connection
Algorithmic management utilizes data-driven algorithms to optimize workforce scheduling, performance tracking, and task allocation, enhancing operational efficiency in employment. Participatory management emphasizes employee involvement in decision-making processes, fostering collaboration and job satisfaction. Integrating algorithmic management with participatory management enables organizations to leverage technology while maintaining employee engagement, resulting in balanced productivity and worker empowerment.
Key Terms
Decision-making
Participatory management emphasizes collaborative decision-making by involving employees at various levels, fostering transparency, and enhancing commitment to outcomes. Algorithmic management leverages data-driven algorithms and artificial intelligence to automate decision processes, optimizing efficiency and minimizing human biases. Explore the distinct impacts of these approaches on organizational effectiveness and employee engagement.
Autonomy
Participatory management emphasizes employee autonomy by involving workers in decision-making processes, fostering a sense of ownership and intrinsic motivation. In contrast, algorithmic management relies on automated systems to monitor and control tasks, often reducing individual autonomy through data-driven directives. Explore how balancing these approaches impacts workforce empowerment and productivity.
Data-driven control
Participatory management emphasizes collaborative decision-making and employee involvement, fostering a culture of trust and innovation through transparent data sharing. In contrast, algorithmic management relies on automated data-driven control systems that monitor performance metrics, optimize workflows, and enforce compliance with minimal human intervention. Explore how integrating these approaches can balance human insight and data precision for enhanced organizational outcomes.
Source and External Links
Participative management: Definition and implementation - Participative management is a horizontal management style where all employees are actively involved in decision-making, based on principles like active participation, open communication, autonomy, collaboration, and collective decision-making.
Participatory management - Wikipedia - Participatory management empowers employees or group members to participate in organizational decision making, allowing them to voice opinions while leaders retain final authority, fostering industrial democracy and organizational learning.
Empowering Employees With Participatory Management - This management style emphasizes transparency, trust, delegation, ownership, decision-making by those with knowledge, and collaboration, enabling employees to actively shape company policies and decisions at appropriate levels.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com