Ghost jobs refer to employment listings that remain open despite being filled or created without the intention of hiring, distorting the job market and prolonging job searches. Dead-end jobs lack growth potential, offering limited advancement or skill development, which traps workers in stagnant roles without career progression. Explore how understanding ghost jobs versus dead-end jobs can improve your job hunt and career planning.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between ghost jobs and dead-end jobs is crucial for effective career planning and job market navigation. Ghost jobs refer to unadvertised or fake job listings that waste candidates' time, while dead-end jobs are positions with limited growth and advancement opportunities. Identifying ghost jobs helps job seekers avoid scams and focus efforts on legitimate openings, whereas recognizing dead-end jobs enables individuals to seek roles with better long-term career prospects. This knowledge improves job search efficiency and supports informed decisions towards sustainable employment.
Comparison Table
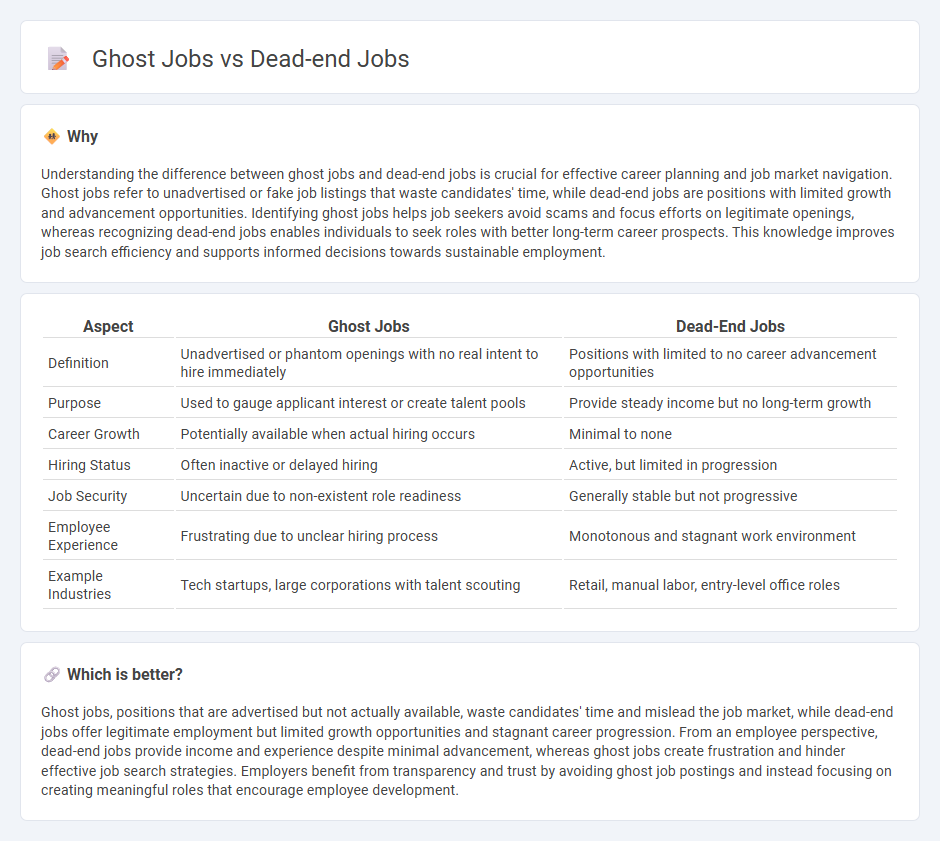
| Aspect | Ghost Jobs | Dead-End Jobs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unadvertised or phantom openings with no real intent to hire immediately | Positions with limited to no career advancement opportunities |
| Purpose | Used to gauge applicant interest or create talent pools | Provide steady income but no long-term growth |
| Career Growth | Potentially available when actual hiring occurs | Minimal to none |
| Hiring Status | Often inactive or delayed hiring | Active, but limited in progression |
| Job Security | Uncertain due to non-existent role readiness | Generally stable but not progressive |
| Employee Experience | Frustrating due to unclear hiring process | Monotonous and stagnant work environment |
| Example Industries | Tech startups, large corporations with talent scouting | Retail, manual labor, entry-level office roles |
Which is better?
Ghost jobs, positions that are advertised but not actually available, waste candidates' time and mislead the job market, while dead-end jobs offer legitimate employment but limited growth opportunities and stagnant career progression. From an employee perspective, dead-end jobs provide income and experience despite minimal advancement, whereas ghost jobs create frustration and hinder effective job search strategies. Employers benefit from transparency and trust by avoiding ghost job postings and instead focusing on creating meaningful roles that encourage employee development.
Connection
Ghost jobs, characterized by positions advertised but never intended to be filled, contribute to a misleading labor market that entices job seekers into pursuing dead-end jobs, which offer limited career growth and stagnant wages. Employers may use ghost jobs to gather resumes or fulfill compliance metrics, while dead-end jobs often trap workers in low-skill roles with minimal advancement opportunities. This connection undermines workforce development by inflating job availability figures while perpetuating employment situations that hinder long-term economic mobility.
Key Terms
Career Advancement
Dead-end jobs often lack growth opportunities, limiting employees' career advancement and skill development, leading to stagnation in professional progress. Ghost jobs are positions advertised to attract talent without actual vacancies, wasting candidate time and resources, which can mislead job seekers about available career prospects. Explore strategies to identify genuine career opportunities and avoid pitfalls associated with dead-end and ghost jobs.
Job Posting Authenticity
Dead-end jobs often lack clear advancement opportunities and skill development, leaving employees stuck in stagnant roles, whereas ghost jobs represent fraudulent or misleading job postings that never intend to hire. Job posting authenticity is critical for job seekers to avoid wasting time on non-existent roles and to find genuine career opportunities. Explore more insights on identifying authentic job listings to optimize your job search strategy.
Employee Morale
Dead-end jobs often lead to stagnant career growth, causing decreased employee morale due to lack of advancement opportunities and unchallenging work. Ghost jobs, positions listed by employers without genuine hiring intentions, frustrate job seekers and create mistrust in the labor market, ultimately impacting organizational reputation and internal morale. Explore effective strategies to boost employee morale and address the issues of dead-end and ghost jobs for a healthier workplace dynamic.
Source and External Links
15 Dead-end jobs to avoid - A dead-end job is one with little or no chance of promotion or career advancement, examples include retail cashier, social media expert, and computer programmer roles that face automation threats.
Dead-end job - Wikipedia - A dead-end job has minimal opportunity for career development, often characterized by no promotion, lack of challenging tasks, or risk of automation making the role obsolete.
15 Dead End Jobs To Avoid at All Costs - Common dead-end jobs include telemarketer, data entry clerk, bank teller, and retail cashier, all facing declining demand due to technological changes and automation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com