Labor hoarding involves retaining more employees than necessary during economic downturns to preserve workforce stability and institutional knowledge, while downsizing aggressively reduces staff to cut costs and improve short-term financial performance. Companies practicing labor hoarding often maintain higher morale and faster recovery post-recession, whereas downsizing may lead to skill loss and decreased productivity in the long term. Explore the strategic implications of labor hoarding versus downsizing to determine the best approach for sustainable employment management.
Why it is important
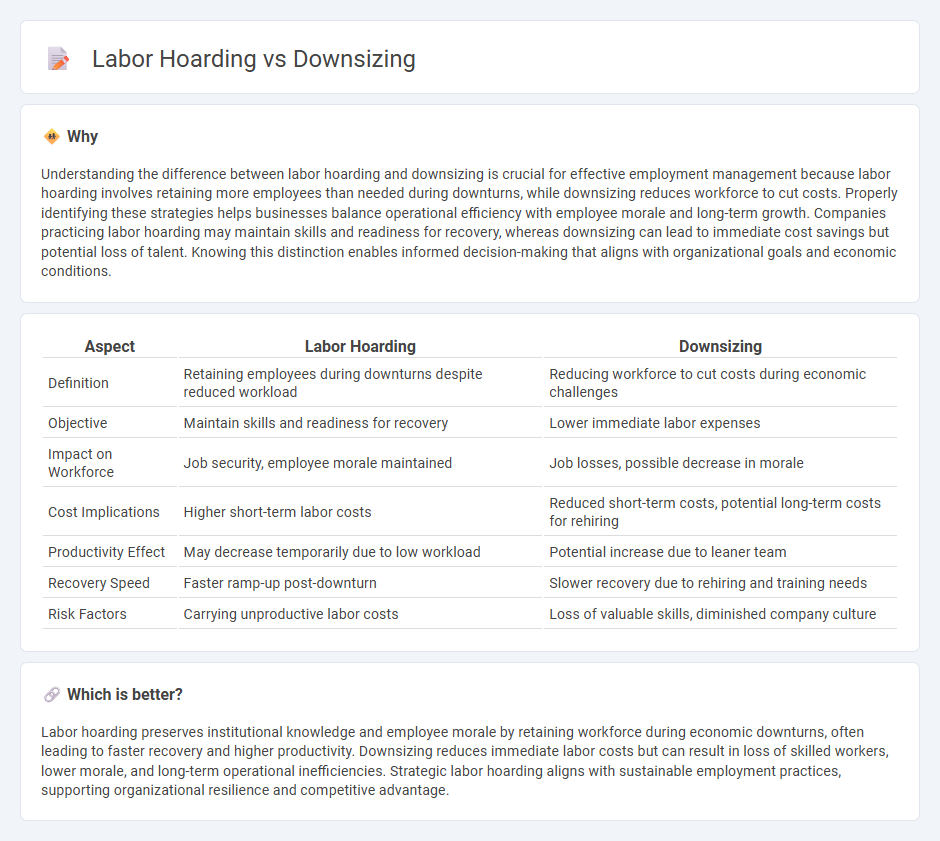
Understanding the difference between labor hoarding and downsizing is crucial for effective employment management because labor hoarding involves retaining more employees than needed during downturns, while downsizing reduces workforce to cut costs. Properly identifying these strategies helps businesses balance operational efficiency with employee morale and long-term growth. Companies practicing labor hoarding may maintain skills and readiness for recovery, whereas downsizing can lead to immediate cost savings but potential loss of talent. Knowing this distinction enables informed decision-making that aligns with organizational goals and economic conditions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Labor Hoarding | Downsizing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Retaining employees during downturns despite reduced workload | Reducing workforce to cut costs during economic challenges |
| Objective | Maintain skills and readiness for recovery | Lower immediate labor expenses |
| Impact on Workforce | Job security, employee morale maintained | Job losses, possible decrease in morale |
| Cost Implications | Higher short-term labor costs | Reduced short-term costs, potential long-term costs for rehiring |
| Productivity Effect | May decrease temporarily due to low workload | Potential increase due to leaner team |
| Recovery Speed | Faster ramp-up post-downturn | Slower recovery due to rehiring and training needs |
| Risk Factors | Carrying unproductive labor costs | Loss of valuable skills, diminished company culture |
Which is better?
Labor hoarding preserves institutional knowledge and employee morale by retaining workforce during economic downturns, often leading to faster recovery and higher productivity. Downsizing reduces immediate labor costs but can result in loss of skilled workers, lower morale, and long-term operational inefficiencies. Strategic labor hoarding aligns with sustainable employment practices, supporting organizational resilience and competitive advantage.
Connection
Labor hoarding occurs when companies retain more employees than needed during economic downturns to preserve institutional knowledge and avoid future rehiring costs. Downsizing involves reducing the workforce to cut costs, often leading to loss of skills and decreased employee morale. These strategies are interconnected as firms must balance short-term financial savings from downsizing against long-term productivity risks associated with labor hoarding.
Key Terms
Workforce Reduction
Workforce reduction strategies like downsizing aim to improve efficiency by cutting excess labor costs, whereas labor hoarding prioritizes retaining employees despite economic downturns to maintain organizational capabilities. Downsizing results in immediate cost savings but may lead to skill loss and morale decline, while labor hoarding preserves human capital at the risk of increased short-term expenses. Explore the economic impacts and strategic outcomes of these contrasting workforce management approaches to understand their business implications.
Retention Costs
Downsizing reduces labor costs by cutting workforce size, which may lower retention costs but can lead to loss of key talent and institutional knowledge. Labor hoarding maintains employment levels despite decreased demand, increasing retention costs but preserving human capital and organizational capability. Explore how balancing retention costs influences long-term business strategy between downsizing and labor hoarding.
Productivity
Downsizing reduces workforce size to cut costs, often aiming to improve short-term productivity by removing underperforming employees. Labor hoarding retains excess staff during downturns, preserving institutional knowledge and employee morale, but can temporarily lower productivity due to underutilization. Explore strategies balancing downsizing and labor hoarding to maximize long-term productivity outcomes.
Source and External Links
Downsizing 101: Your Guide to Moving to a Smaller Home - Downsizing here refers to moving to a smaller living space, often motivated by retirement, financial savings, or lifestyle changes, and involves budgeting and adjusting possessions to fit the smaller home.
Downsizing (film) - In this 2017 film, downsizing is a fictional medical procedure that shrinks people to about 5 inches tall to reduce consumption and live in small, upscale communities.
Downsizing (2017) - This social satire film by Alexander Payne explores a man who chooses to shrink himself for a better life, highlighting themes of consumerism and societal issues through the concept of downsizing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com