Algorithmic management leverages data-driven algorithms to monitor and optimize employee performance, enabling real-time decision-making without human bias. Supervisory management relies on human judgment and interpersonal skills to guide, motivate, and evaluate employees, emphasizing personalized leadership. Explore how these management approaches impact workplace efficiency and employee satisfaction.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between algorithmic management and supervisory management is crucial for optimizing workforce efficiency and ensuring fair employee treatment. Algorithmic management uses data-driven systems to assign tasks and evaluate performance, while supervisory management relies on human judgment and interpersonal skills. Awareness of these management styles helps employees adapt to workplace expectations and informs organizations on implementing balanced, transparent management practices. Recognizing the impact of algorithmic management on job security and autonomy is essential for navigating modern employment landscapes.
Comparison Table
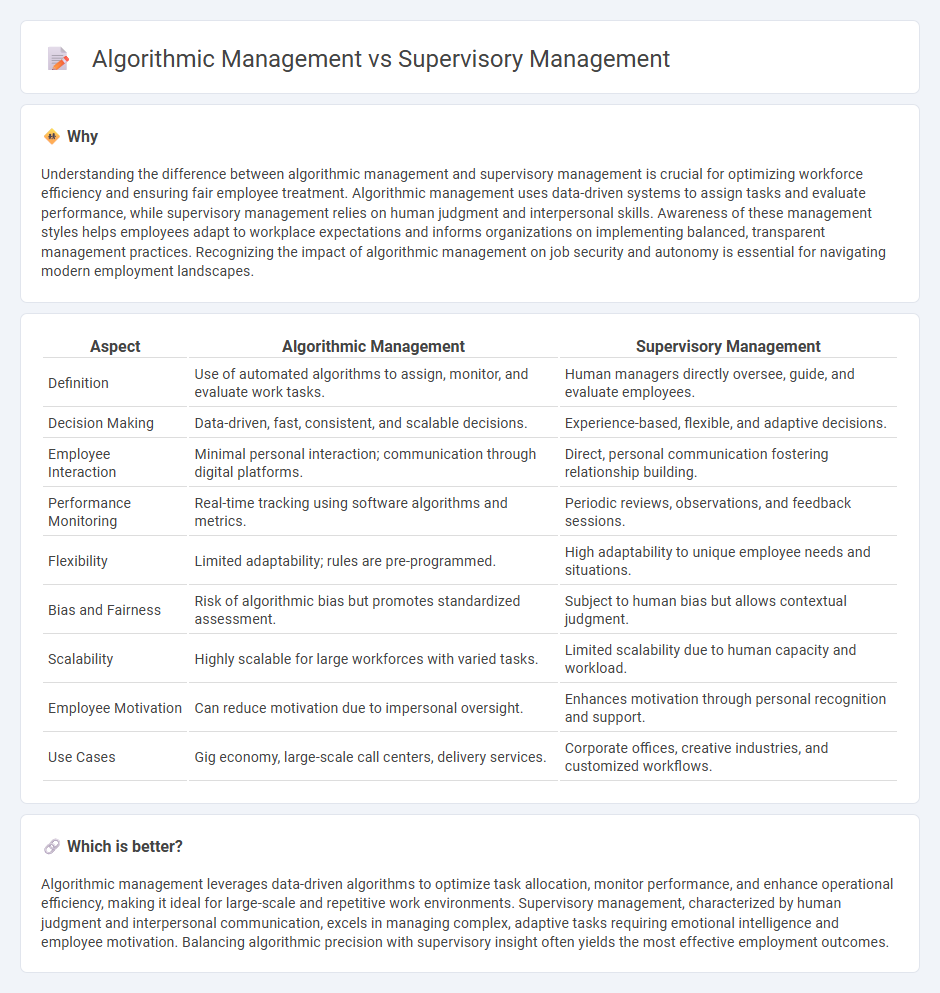
| Aspect | Algorithmic Management | Supervisory Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of automated algorithms to assign, monitor, and evaluate work tasks. | Human managers directly oversee, guide, and evaluate employees. |
| Decision Making | Data-driven, fast, consistent, and scalable decisions. | Experience-based, flexible, and adaptive decisions. |
| Employee Interaction | Minimal personal interaction; communication through digital platforms. | Direct, personal communication fostering relationship building. |
| Performance Monitoring | Real-time tracking using software algorithms and metrics. | Periodic reviews, observations, and feedback sessions. |
| Flexibility | Limited adaptability; rules are pre-programmed. | High adaptability to unique employee needs and situations. |
| Bias and Fairness | Risk of algorithmic bias but promotes standardized assessment. | Subject to human bias but allows contextual judgment. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable for large workforces with varied tasks. | Limited scalability due to human capacity and workload. |
| Employee Motivation | Can reduce motivation due to impersonal oversight. | Enhances motivation through personal recognition and support. |
| Use Cases | Gig economy, large-scale call centers, delivery services. | Corporate offices, creative industries, and customized workflows. |
Which is better?
Algorithmic management leverages data-driven algorithms to optimize task allocation, monitor performance, and enhance operational efficiency, making it ideal for large-scale and repetitive work environments. Supervisory management, characterized by human judgment and interpersonal communication, excels in managing complex, adaptive tasks requiring emotional intelligence and employee motivation. Balancing algorithmic precision with supervisory insight often yields the most effective employment outcomes.
Connection
Algorithmic management leverages data-driven algorithms to automate and optimize task assignments, performance tracking, and workflow coordination within employment settings. Supervisory management complements this by providing human judgment, feedback, and interpersonal support essential for addressing nuanced employee needs and fostering workplace motivation. The integration of algorithmic and supervisory management enhances operational efficiency while maintaining employee engagement and adaptability.
Key Terms
Decision-making Authority
Supervisory management relies on human decision-making authority to guide team performance through judgment, experience, and interpersonal skills, while algorithmic management employs data-driven algorithms to automate decisions based on real-time analytics and performance metrics. Human supervisors handle complex, ambiguous situations requiring emotional intelligence, whereas algorithmic systems excel in processing large datasets to optimize efficiency and consistency in task allocation. Explore further to understand how these contrasting decision-making approaches impact organizational productivity.
Human Judgment
Supervisory management emphasizes human judgment, relying on managers' experience, intuition, and interpersonal skills to guide decision-making and team coordination. In contrast, algorithmic management uses data-driven algorithms and automated processes to optimize task allocation and performance monitoring, reducing subjective biases. Explore how blending human insight with algorithmic precision can enhance organizational effectiveness.
Automated Oversight
Supervisory management relies on human judgment and experience to oversee employee performance and operational tasks, whereas algorithmic management uses automated systems and data analytics to monitor, evaluate, and guide work processes. Automated oversight in algorithmic management enables real-time decision-making, enhancing efficiency and consistency while reducing managerial bias. Explore how automated oversight transforms traditional supervisory roles and drives operational innovation.
Source and External Links
Supervisory Management: Definition, Skills and Steps | Indeed.com - Supervisory management involves overseeing teams and daily business operations by acting as the link between employees and executive management, requiring skills like problem-solving, mentoring, strategic planning, honesty, and analysis.
What Is Supervisory Management? - Courses For Success - Supervisory management is a mid-level management role that guides employee performance, manages operational targets, and fosters teamwork, aiming to balance demands from executives and employees while improving productivity and professional development.
Supervisory Management Skills - UpTrack Training - A supervisory management course covers critical areas such as communication, team leadership, performance management, time management, problem-solving, and conflict resolution to equip supervisors with essential skills for effective management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com