Ghost work involves performing digital tasks remotely and anonymously, often through online platforms, with flexible hours but limited job security. Part-time work offers scheduled, paid employment with defined responsibilities and consistent interaction with employers, providing more stability but fewer hours than full-time jobs. Explore the nuances between ghost work and part-time employment to understand their impact on the modern labor market.
Why it is important
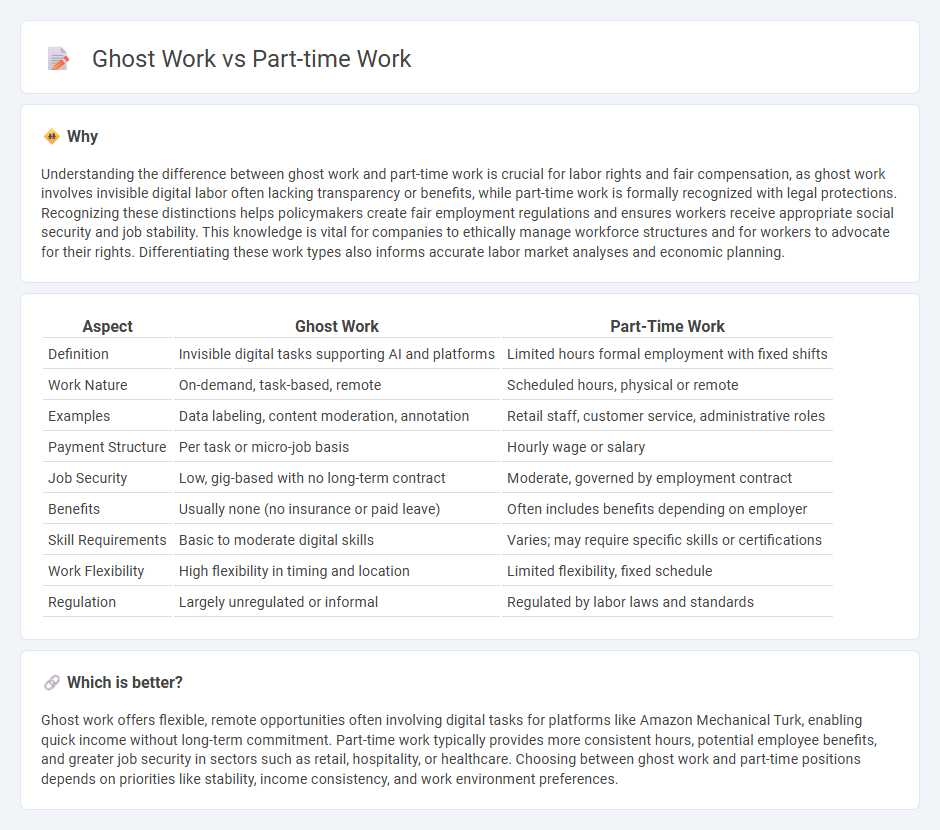
Understanding the difference between ghost work and part-time work is crucial for labor rights and fair compensation, as ghost work involves invisible digital labor often lacking transparency or benefits, while part-time work is formally recognized with legal protections. Recognizing these distinctions helps policymakers create fair employment regulations and ensures workers receive appropriate social security and job stability. This knowledge is vital for companies to ethically manage workforce structures and for workers to advocate for their rights. Differentiating these work types also informs accurate labor market analyses and economic planning.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Work | Part-Time Work |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Invisible digital tasks supporting AI and platforms | Limited hours formal employment with fixed shifts |
| Work Nature | On-demand, task-based, remote | Scheduled hours, physical or remote |
| Examples | Data labeling, content moderation, annotation | Retail staff, customer service, administrative roles |
| Payment Structure | Per task or micro-job basis | Hourly wage or salary |
| Job Security | Low, gig-based with no long-term contract | Moderate, governed by employment contract |
| Benefits | Usually none (no insurance or paid leave) | Often includes benefits depending on employer |
| Skill Requirements | Basic to moderate digital skills | Varies; may require specific skills or certifications |
| Work Flexibility | High flexibility in timing and location | Limited flexibility, fixed schedule |
| Regulation | Largely unregulated or informal | Regulated by labor laws and standards |
Which is better?
Ghost work offers flexible, remote opportunities often involving digital tasks for platforms like Amazon Mechanical Turk, enabling quick income without long-term commitment. Part-time work typically provides more consistent hours, potential employee benefits, and greater job security in sectors such as retail, hospitality, or healthcare. Choosing between ghost work and part-time positions depends on priorities like stability, income consistency, and work environment preferences.
Connection
Ghost work and part-time work intersect through the gig economy, where individuals perform tasks remotely or on flexible schedules without traditional employment benefits. Both forms of work rely on digital platforms that allocate microtasks, enabling workers to earn income while maintaining autonomy over their hours. This trend underscores challenges in labor rights and job security as the boundary between formal and informal employment becomes increasingly blurred.
Key Terms
Work hours
Part-time work typically involves scheduled hours ranging from 10 to 30 per week with transparent tasks and consistent employer interactions. Ghost work consists of on-demand, micro-tasks often completed remotely with irregular hours, lacking traditional employer oversight or benefits. Explore how work hours impact job stability and income in both models.
Job visibility
Part-time work offers clear job visibility with defined hours and responsibilities, allowing workers to build a recognizable employment history. Ghost work, often performed remotely and behind the scenes on digital platforms, lacks transparency, making it difficult for workers to showcase their contributions. Explore the nuances of job visibility in these work types to understand their impact on career development.
Employee status
Part-time workers typically have a clear employee status with defined rights, such as minimum wage, benefits, and legal protections under labor laws. Ghost workers, often engaged in platform-based or gig economy roles, usually lack formal employee classification, resulting in limited access to employment benefits and protections. Explore the nuances of employee status to understand how these distinctions impact worker rights and economic security.
Source and External Links
Part-time job - Wikipedia - A part-time job is defined as working fewer hours than full-time employment, typically under 30 hours per week, with various reasons for such work including less stressful schedules or reduced employer hours.
Part Time Jobs in Sumter, SC (NOW HIRING) - ZipRecruiter - Part-time jobs generally involve working 20 to 30 hours per week with shifts during business hours or nights/weekends and commonly lead to full-time roles, especially in retail, hospitality, and food service.
part time jobs in sumter, sc - Indeed - There are more than 1300 part-time job openings in Sumter, SC across a variety of industries including retail, food service, and healthcare, offering flexible schedules to fit diverse needs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com