Talent arbitrage leverages global wage disparities by sourcing skilled professionals from lower-cost regions, optimizing labor expenses without compromising quality. Outsourcing involves delegating business processes or tasks to external firms, often focusing on operational efficiency and access to specialized expertise. Explore the nuances between talent arbitrage and outsourcing to determine the best strategic fit for your organization.
Why it is important
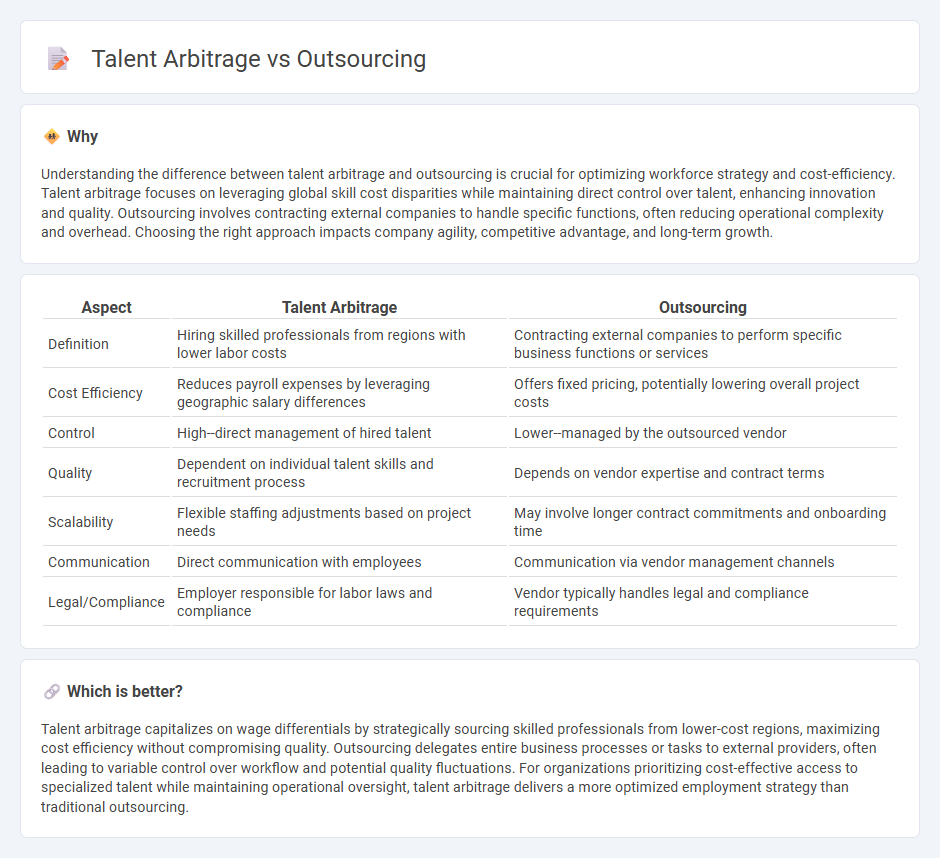
Understanding the difference between talent arbitrage and outsourcing is crucial for optimizing workforce strategy and cost-efficiency. Talent arbitrage focuses on leveraging global skill cost disparities while maintaining direct control over talent, enhancing innovation and quality. Outsourcing involves contracting external companies to handle specific functions, often reducing operational complexity and overhead. Choosing the right approach impacts company agility, competitive advantage, and long-term growth.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Talent Arbitrage | Outsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hiring skilled professionals from regions with lower labor costs | Contracting external companies to perform specific business functions or services |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces payroll expenses by leveraging geographic salary differences | Offers fixed pricing, potentially lowering overall project costs |
| Control | High--direct management of hired talent | Lower--managed by the outsourced vendor |
| Quality | Dependent on individual talent skills and recruitment process | Depends on vendor expertise and contract terms |
| Scalability | Flexible staffing adjustments based on project needs | May involve longer contract commitments and onboarding time |
| Communication | Direct communication with employees | Communication via vendor management channels |
| Legal/Compliance | Employer responsible for labor laws and compliance | Vendor typically handles legal and compliance requirements |
Which is better?
Talent arbitrage capitalizes on wage differentials by strategically sourcing skilled professionals from lower-cost regions, maximizing cost efficiency without compromising quality. Outsourcing delegates entire business processes or tasks to external providers, often leading to variable control over workflow and potential quality fluctuations. For organizations prioritizing cost-effective access to specialized talent while maintaining operational oversight, talent arbitrage delivers a more optimized employment strategy than traditional outsourcing.
Connection
Talent arbitrage and outsourcing are interconnected through the strategic relocation of skilled labor to regions with lower labor costs, enabling companies to optimize expenses while accessing specialized expertise. Outsourcing leverages this concept by contracting external firms or remote teams in cost-effective geographies, enhancing operational efficiency and scalability. This synergy drives competitive advantage by aligning global workforce distribution with market-driven cost-benefit analyses.
Key Terms
Cost Efficiency
Outsourcing leverages external resources to reduce operational expenses by accessing specialized skills at lower costs, while talent arbitrage capitalizes on wage differentials across regions to maximize cost efficiency in talent acquisition. Companies utilizing talent arbitrage can achieve significant savings by hiring skilled professionals from lower-cost labor markets without compromising quality. Explore detailed strategies and cost comparisons to optimize your business's financial performance.
Skill Availability
Outsourcing often emphasizes access to specialized skills unavailable internally, leveraging external vendors to fill gaps in expertise. Talent arbitrage capitalizes on cost differentials across regions by sourcing equally skilled professionals in lower-wage markets, prioritizing economic efficiency. Explore how skill availability impacts strategic decisions between outsourcing and talent arbitrage to optimize your workforce.
Geographic Flexibility
Outsourcing leverages external vendors to perform tasks, often prioritizing cost savings and specialized expertise regardless of location, while talent arbitrage specifically exploits geographic wage differences by hiring skilled professionals in lower-cost regions. Geographic flexibility in outsourcing allows companies to tap into diverse global markets for quality and scalability, whereas talent arbitrage focuses primarily on relocating or contracting talent to optimize wage expenses. Explore deeper insights on how geographic flexibility impacts your business strategy and operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
What Is Outsourcing? (Including Types and Advantages) - Outsourcing is the practice of hiring external companies or contractors to perform business functions, helping firms reduce costs and improve efficiency by leveraging skills they may lack internally.
What is Outsourcing and How Does it Work? - Outsourcing involves contracting a third-party provider to handle tasks or operations, either onsite or offsite, and is considered more about managing a partnership than just service contracts.
What is Outsourcing? Definition, Advantages, and Examples - Outsourcing enables businesses to focus on core activities while contracting specialized external providers for tasks like IT support and customer service, emphasizing cost savings and operational efficiency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com