Talent arbitrage leverages global wage differences to hire skilled professionals at lower costs, optimizing company expenses while accessing diverse expertise. Remote work enables employees to operate from any location, enhancing flexibility and tapping into a broader talent pool without geographical constraints. Explore how these employment strategies transform workforce management and business growth.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between talent arbitrage and remote work is crucial for optimizing global hiring strategies and cost management. Talent arbitrage focuses on leveraging wage differences across regions to reduce labor costs, while remote work emphasizes location-independent job execution for flexibility and access to a broader talent pool. Businesses that distinguish these concepts can better tailor compensation models and operational structures to maximize productivity and employee satisfaction. Recognizing this distinction enhances strategic workforce planning and competitive advantage in the global employment market.
Comparison Table
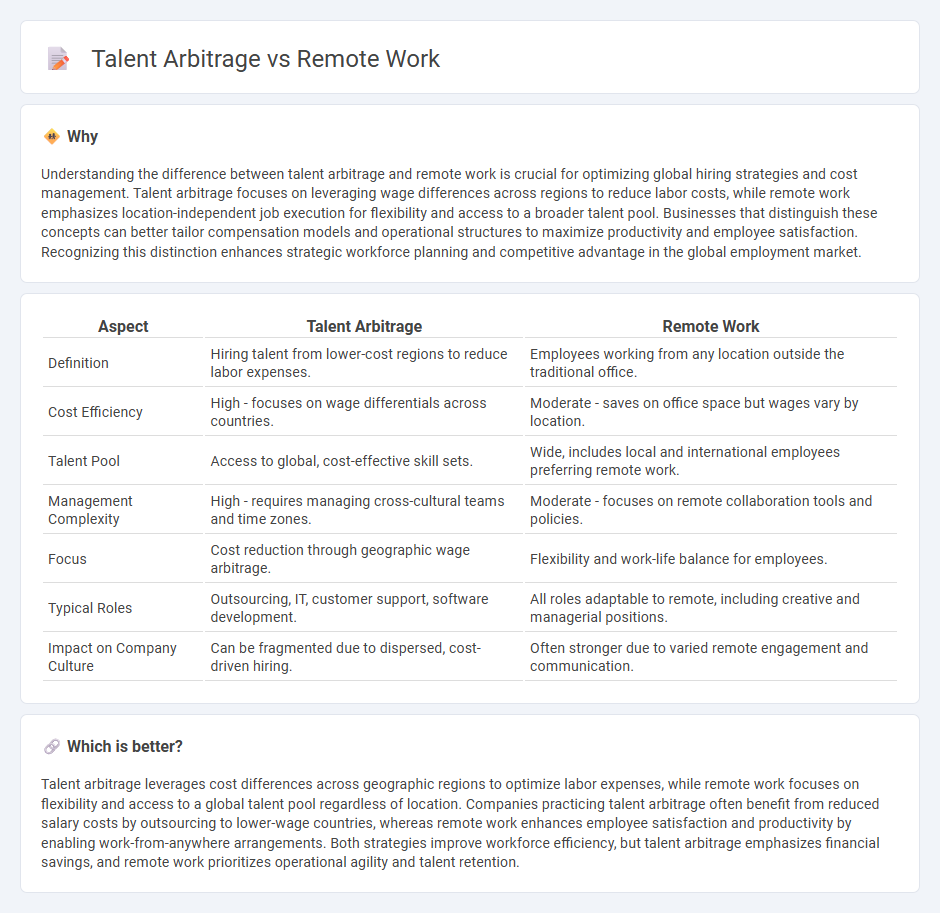
| Aspect | Talent Arbitrage | Remote Work |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hiring talent from lower-cost regions to reduce labor expenses. | Employees working from any location outside the traditional office. |
| Cost Efficiency | High - focuses on wage differentials across countries. | Moderate - saves on office space but wages vary by location. |
| Talent Pool | Access to global, cost-effective skill sets. | Wide, includes local and international employees preferring remote work. |
| Management Complexity | High - requires managing cross-cultural teams and time zones. | Moderate - focuses on remote collaboration tools and policies. |
| Focus | Cost reduction through geographic wage arbitrage. | Flexibility and work-life balance for employees. |
| Typical Roles | Outsourcing, IT, customer support, software development. | All roles adaptable to remote, including creative and managerial positions. |
| Impact on Company Culture | Can be fragmented due to dispersed, cost-driven hiring. | Often stronger due to varied remote engagement and communication. |
Which is better?
Talent arbitrage leverages cost differences across geographic regions to optimize labor expenses, while remote work focuses on flexibility and access to a global talent pool regardless of location. Companies practicing talent arbitrage often benefit from reduced salary costs by outsourcing to lower-wage countries, whereas remote work enhances employee satisfaction and productivity by enabling work-from-anywhere arrangements. Both strategies improve workforce efficiency, but talent arbitrage emphasizes financial savings, and remote work prioritizes operational agility and talent retention.
Connection
Talent arbitrage leverages salary differentials across global markets by enabling companies to hire skilled professionals from lower-cost regions. Remote work technology facilitates this by removing geographical barriers, allowing businesses to access diverse talent pools efficiently. This connection optimizes workforce costs while maintaining high productivity and expertise.
Key Terms
Geographic Flexibility
Geographic flexibility in remote work allows companies to tap into a global talent pool without relocation constraints, enhancing diversity and innovation within teams. Talent arbitrage leverages cost differentials by hiring skilled professionals in lower-cost regions, optimizing budgets while maintaining productivity. Explore how geographic flexibility can transform your hiring strategy and drive competitive advantage.
Cost Efficiency
Remote work significantly reduces overhead costs by eliminating the need for physical office space and related expenses, thereby enhancing cost efficiency for businesses. Talent arbitrage leverages regional salary disparities by outsourcing roles to lower-cost locations without compromising quality, further driving financial savings. Explore detailed strategies to optimize cost efficiency through remote work and talent arbitrage.
Labor Market Access
Remote work expands labor market access by enabling companies to recruit talent globally, breaking geographical barriers and increasing diversity. Talent arbitrage leverages wage differentials between regions, allowing businesses to optimize costs by hiring skilled professionals in lower-cost markets. Explore how integrating remote work and talent arbitrage strategies can maximize labor market efficiency and competitiveness.
Source and External Links
What Is Remote Work? Ultimate Guide - Remote work means employees perform their jobs from home or any location outside the traditional office, often enabled by digital collaboration tools like Slack and Zoom, making remote work common for digital nomads and reshaping workplace dynamics.
What is the definition of remote work? - Remote work is a flexible arrangement where employees have a written agreement to work at an alternative worksite, not expected to perform work regularly at the agency's physical site.
Working Nomads: Remote Jobs - This platform lists 100% fully remote jobs worldwide for digital nomads and remote workers across various employment types, enabling work from anywhere in the world.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com