Ghost work involves performing microtasks or short-term gigs often mediated by online platforms, creating a layer of invisible labor behind many digital services. Telecommuting, on the other hand, enables employees to work remotely, leveraging technology to maintain productivity outside traditional office environments. Explore the evolving dynamics of modern employment by delving deeper into the contrasts between ghost work and telecommuting.
Why it is important
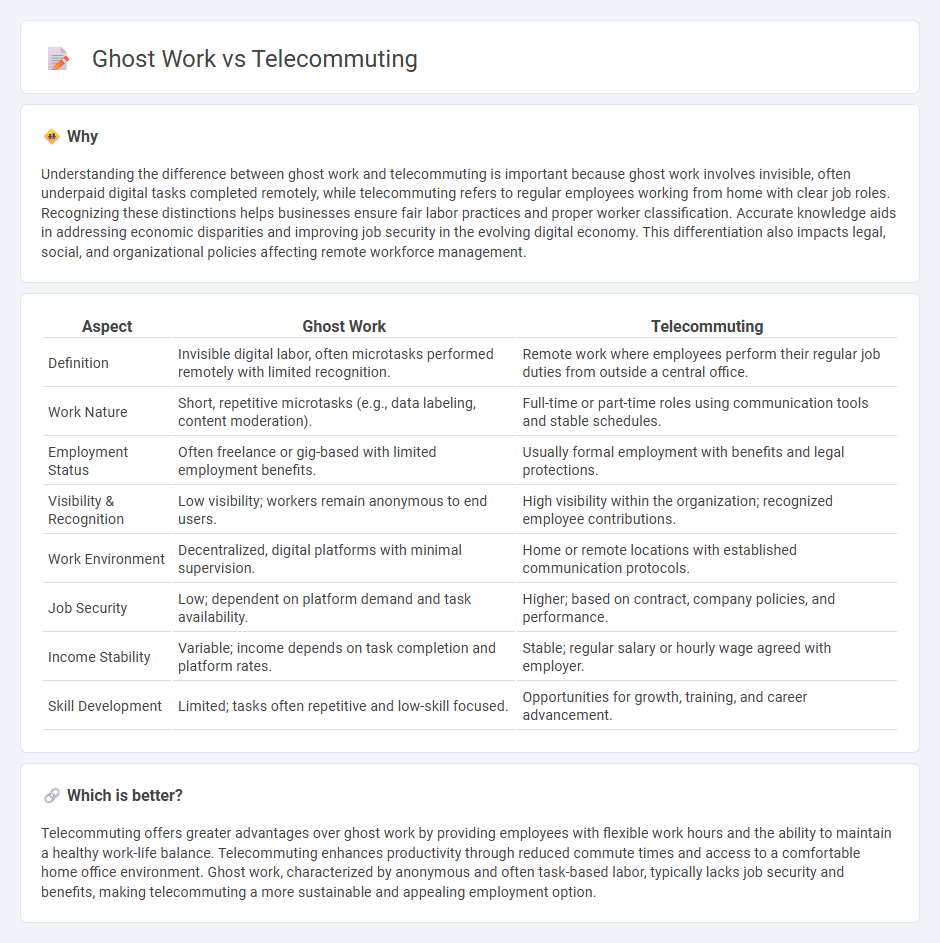
Understanding the difference between ghost work and telecommuting is important because ghost work involves invisible, often underpaid digital tasks completed remotely, while telecommuting refers to regular employees working from home with clear job roles. Recognizing these distinctions helps businesses ensure fair labor practices and proper worker classification. Accurate knowledge aids in addressing economic disparities and improving job security in the evolving digital economy. This differentiation also impacts legal, social, and organizational policies affecting remote workforce management.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Work | Telecommuting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Invisible digital labor, often microtasks performed remotely with limited recognition. | Remote work where employees perform their regular job duties from outside a central office. |
| Work Nature | Short, repetitive microtasks (e.g., data labeling, content moderation). | Full-time or part-time roles using communication tools and stable schedules. |
| Employment Status | Often freelance or gig-based with limited employment benefits. | Usually formal employment with benefits and legal protections. |
| Visibility & Recognition | Low visibility; workers remain anonymous to end users. | High visibility within the organization; recognized employee contributions. |
| Work Environment | Decentralized, digital platforms with minimal supervision. | Home or remote locations with established communication protocols. |
| Job Security | Low; dependent on platform demand and task availability. | Higher; based on contract, company policies, and performance. |
| Income Stability | Variable; income depends on task completion and platform rates. | Stable; regular salary or hourly wage agreed with employer. |
| Skill Development | Limited; tasks often repetitive and low-skill focused. | Opportunities for growth, training, and career advancement. |
Which is better?
Telecommuting offers greater advantages over ghost work by providing employees with flexible work hours and the ability to maintain a healthy work-life balance. Telecommuting enhances productivity through reduced commute times and access to a comfortable home office environment. Ghost work, characterized by anonymous and often task-based labor, typically lacks job security and benefits, making telecommuting a more sustainable and appealing employment option.
Connection
Ghost work and telecommuting intersect through the rise of remote, digital labor performed via online platforms, enabling workers to complete tasks invisibly from any location. This seamless integration of technology facilitates flexible employment models where ghost workers provide essential support services without direct visibility or traditional employer-employee relationships. The growth of telecommuting accelerates demand for ghost work by expanding access to distributed, on-demand gig economy jobs in sectors like content moderation, data tagging, and customer support.
Key Terms
Remote Work
Remote work encompasses both telecommuting and ghost work, where telecommuting refers to employees performing their regular job tasks from home or outside the traditional office environment. Ghost work involves digital platform workers who complete microtasks or gig assignments anonymously, often without direct interaction with employers or recognition. Explore more to understand the distinct dynamics and implications of these remote work models.
Gig Economy
Telecommuting involves remote work where employees perform tasks for a single employer, often leveraging digital technologies to maintain consistent communication and workflow. Ghost work, prevalent in the gig economy, consists of microtasks completed anonymously by gig workers through online platforms, typically lacking formal employment status or direct employer visibility. Explore the dynamics of telecommuting and ghost work to understand their impact on labor rights and economic opportunities in the gig economy.
Digital Labor
Digital labor encompasses telecommuting, where employees work remotely using digital tools, and ghost work, involving hidden human tasks supporting AI systems. Telecommuting offers autonomy and flexibility through virtual collaboration, while ghost work remains largely invisible, often performing microtasks critical to machine learning. Explore the evolving landscape of digital labor to understand the impact on workforce dynamics and technology integration.
Source and External Links
What Is Telecommuting in Today's Work Environment? - Telecommuting allows employees to use their own or company-provided devices and an internet connection to work remotely by connecting to their company's network, with the practice becoming widespread during and after the COVID-19 pandemic as a mainstream work method.
What is telecommuting? | Definition from TechTarget - Telecommuting refers to completing work assignments remotely using telecommunications tools, with arrangements varying between full-time, part-time, temporary, or freelance remote work.
What Is Telecommuting? Definition and Benefits - Telecommuting includes several work arrangements such as full-time remote work, part-time, hybrid, temporary, hoteling, and freelancing, enabling employees to perform job duties outside traditional workplaces with flexibility.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com