Ghost work involves remote tasks completed anonymously through digital platforms, often characterized by repetitive, low-wage assignments. On-demand work refers to flexible, task-based jobs facilitated by apps or websites, enabling workers to accept gigs as needed. Explore the nuances between ghost work and on-demand work to understand their impact on the modern labor market.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between ghost work and on-demand work is crucial for accurately assessing job security, worker rights, and compensation models in the evolving gig economy. Ghost work involves hidden digital labor often unrecognized by employers, while on-demand work typically features visible tasks assigned via platforms. Recognizing these distinctions helps policymakers design better labor regulations to protect vulnerable workers. Clear differentiation also enables workers to make informed career choices based on job stability and income predictability.
Comparison Table
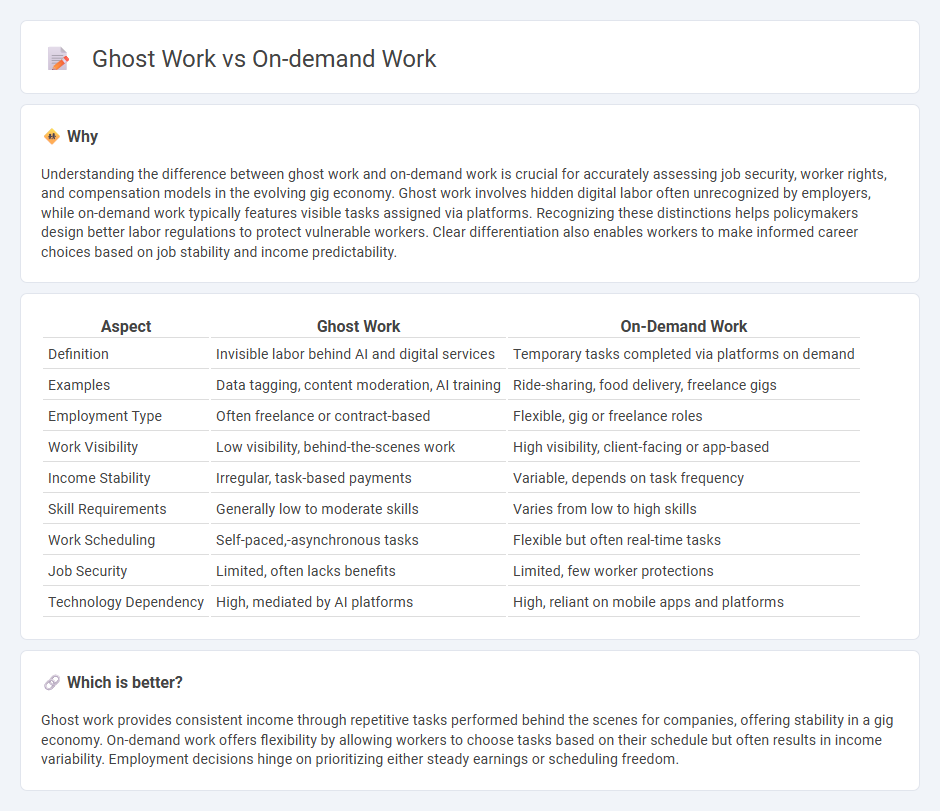
| Aspect | Ghost Work | On-Demand Work |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Invisible labor behind AI and digital services | Temporary tasks completed via platforms on demand |
| Examples | Data tagging, content moderation, AI training | Ride-sharing, food delivery, freelance gigs |
| Employment Type | Often freelance or contract-based | Flexible, gig or freelance roles |
| Work Visibility | Low visibility, behind-the-scenes work | High visibility, client-facing or app-based |
| Income Stability | Irregular, task-based payments | Variable, depends on task frequency |
| Skill Requirements | Generally low to moderate skills | Varies from low to high skills |
| Work Scheduling | Self-paced,-asynchronous tasks | Flexible but often real-time tasks |
| Job Security | Limited, often lacks benefits | Limited, few worker protections |
| Technology Dependency | High, mediated by AI platforms | High, reliant on mobile apps and platforms |
Which is better?
Ghost work provides consistent income through repetitive tasks performed behind the scenes for companies, offering stability in a gig economy. On-demand work offers flexibility by allowing workers to choose tasks based on their schedule but often results in income variability. Employment decisions hinge on prioritizing either steady earnings or scheduling freedom.
Connection
Ghost work and on-demand work both rely heavily on digital platforms that connect workers with short-term, task-based jobs, enabling flexible employment. These forms of work often involve microtasks or gig assignments performed remotely, emphasizing speed and scalability for companies seeking cost efficiency. The common reliance on algorithm-driven task allocation blurs the line between traditional employment and freelance labor, reshaping modern workforce dynamics.
Key Terms
Flexibility
On-demand work offers flexibility by allowing individuals to choose when and where they work, often through apps that match tasks with worker availability, creating a dynamic labor environment. Ghost work, characterized by hidden human contributions in digital systems, provides flexible opportunities but lacks visibility and recognition despite its critical role in AI training and content moderation. Explore further to understand how flexibility shapes the future of both on-demand and ghost work roles.
Gig Economy
On-demand work in the gig economy involves flexible, task-based jobs like ride-sharing or food delivery, where workers control their schedules and service selection. Ghost work refers to behind-the-scenes digital labor such as data labeling, content moderation, and AI training, often invisible but essential for technology platforms. Explore the evolving dynamics and challenges of gig economy labor models to understand their impact on employment trends and worker rights.
Task Invisibilization
On-demand work often highlights visible tasks completed by gig workers, while ghost work involves hidden labor crucial for AI and digital platform functionality, emphasizing task invisibilization. This invisibilization undermines recognition and fair compensation for ghost workers who perform essential data annotation, moderation, and algorithm training tasks. Explore deeper insights into task invisibilization and its implications for labor rights and platform accountability.
Source and External Links
What Is An On-Demand Worker, Benefits and Career in Future? - On-demand workers enjoy a flexible, zero-hours environment, choosing their own schedules without fixed contracts, which benefits both workers seeking work-life balance and employers looking to cut costs by avoiding benefits and fixed salaries.
Target Store On-Demand Team Members - Target's on-demand team members use an app to pick available shifts that fit their schedules, work up to 40 hours a week, and must work at least one shift every four weeks to remain active, with access to some company benefits.
Bacon Work On-Demand - The Bacon app connects users with local on-demand hourly jobs across various industries, allowing them to choose shifts, apply instantly, and get paid quickly, while building a work history within the platform.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com