Talent hoarding occurs when managers retain skilled employees within their own teams, limiting opportunities for broader organizational growth and innovation. Redeployment involves strategically reallocating talent across departments to maximize workforce efficiency and address evolving business needs. Discover how balancing talent hoarding and redeployment can drive sustainable success in your organization.
Why it is important
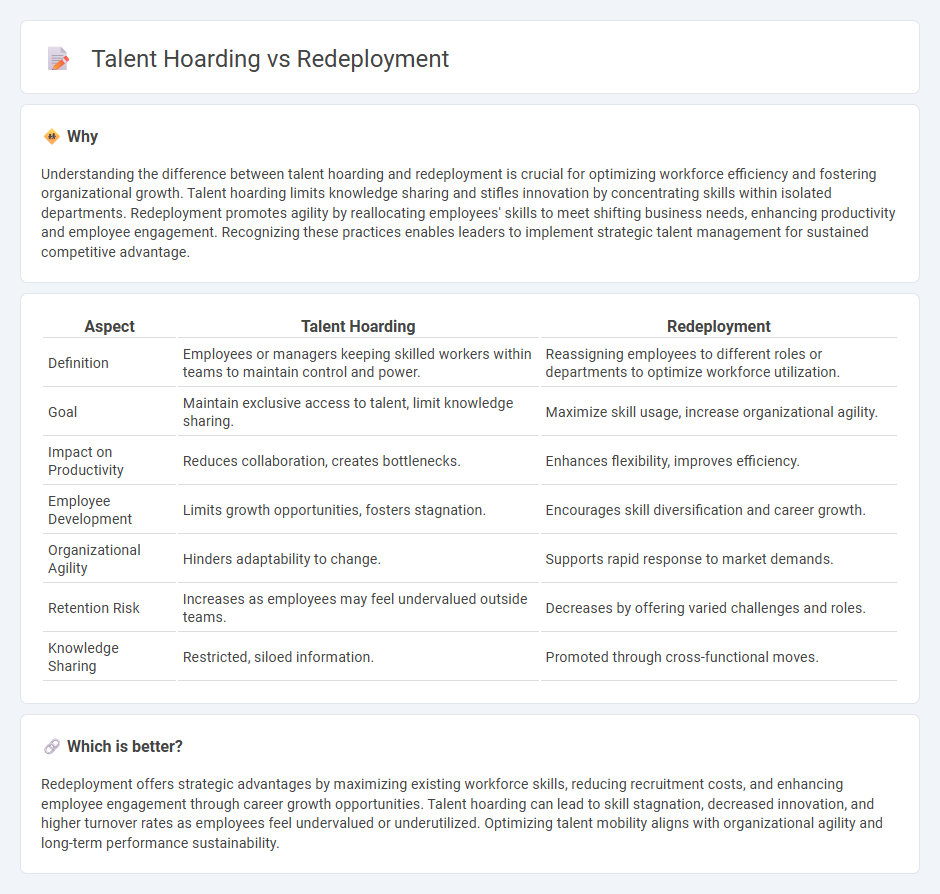
Understanding the difference between talent hoarding and redeployment is crucial for optimizing workforce efficiency and fostering organizational growth. Talent hoarding limits knowledge sharing and stifles innovation by concentrating skills within isolated departments. Redeployment promotes agility by reallocating employees' skills to meet shifting business needs, enhancing productivity and employee engagement. Recognizing these practices enables leaders to implement strategic talent management for sustained competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Talent Hoarding | Redeployment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employees or managers keeping skilled workers within teams to maintain control and power. | Reassigning employees to different roles or departments to optimize workforce utilization. |
| Goal | Maintain exclusive access to talent, limit knowledge sharing. | Maximize skill usage, increase organizational agility. |
| Impact on Productivity | Reduces collaboration, creates bottlenecks. | Enhances flexibility, improves efficiency. |
| Employee Development | Limits growth opportunities, fosters stagnation. | Encourages skill diversification and career growth. |
| Organizational Agility | Hinders adaptability to change. | Supports rapid response to market demands. |
| Retention Risk | Increases as employees may feel undervalued outside teams. | Decreases by offering varied challenges and roles. |
| Knowledge Sharing | Restricted, siloed information. | Promoted through cross-functional moves. |
Which is better?
Redeployment offers strategic advantages by maximizing existing workforce skills, reducing recruitment costs, and enhancing employee engagement through career growth opportunities. Talent hoarding can lead to skill stagnation, decreased innovation, and higher turnover rates as employees feel undervalued or underutilized. Optimizing talent mobility aligns with organizational agility and long-term performance sustainability.
Connection
Talent hoarding limits workforce flexibility by keeping skilled employees confined to specific roles, reducing opportunities for effective redeployment across departments. Redeployment leverages internal talent mobility to fill critical skill gaps and adapt to organizational changes, enhancing overall productivity. Organizations that balance talent hoarding with strategic redeployment improve employee engagement and optimize resource allocation.
Key Terms
Workforce Mobility
Workforce mobility enhances organizational agility by enabling redeployment of employees to critical roles based on evolving business needs, whereas talent hoarding restricts growth by retaining employees in familiar positions, limiting skill development and innovation. Redeployment fosters skills diversification and maximizes talent utilization, directly impacting productivity and employee engagement. Explore strategic workforce mobility solutions to unlock the full potential of your talent pool.
Skill Utilization
Redeployment maximizes skill utilization by strategically assigning employees to roles that align with their competencies, improving organizational agility and reducing the need for external hiring. Talent hoarding, conversely, restricts skill flow by keeping employees in roles that underutilize their abilities, leading to stagnation and decreased innovation. Explore effective practices to enhance skill utilization through redeployment and avoid talent hoarding pitfalls.
Internal Opportunity
Redeployment leverages existing employee skills to fill new roles, maximizing internal talent utilization and reducing hiring costs. Talent hoarding, on the other hand, limits workforce agility by retaining employees in current roles to avoid sharing expertise, hindering organizational growth. Explore strategies to enhance internal opportunities and foster a culture of effective redeployment.
Source and External Links
Redeployment: A Guide for HR Managers & Employers - Redeployment is when an employer moves an employee from one role to another, typically to avoid making staff redundant, involving a process of offering alternative employment and a trial period in the new position.
Talent redeployment: what it is and why do it - Talent redeployment strategically shifts employees from lower-priority roles to higher-priority ones within the organization, requiring a clear understanding of workforce skills and organizational needs to ensure effective internal mobility.
What Is Redeployment? - Redeployment refers to the internal movement of employees to fill vacancies, which can reduce recruitment costs, promote adaptability, and strengthen company culture by recognizing and utilizing existing talent.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com