Blue collar tech jobs focus on specialized technical skills, including equipment repair, installation, and maintenance in industries like manufacturing and utilities. The service industry emphasizes customer-facing roles such as hospitality, retail, and food service, requiring strong interpersonal skills and adaptability. Explore the unique opportunities and challenges within these sectors to understand their impact on the job market.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between blue collar tech and service industry employment is crucial for targeted career development and skill acquisition. Blue collar tech jobs typically require specialized technical skills and involve working with machinery or technology, leading to higher wage potential and job stability. Service industry roles focus on customer interaction and support tasks, often offering more entry-level opportunities but lower average earnings. Knowing these distinctions helps job seekers align their education and training with industry demands for better employment outcomes.
Comparison Table
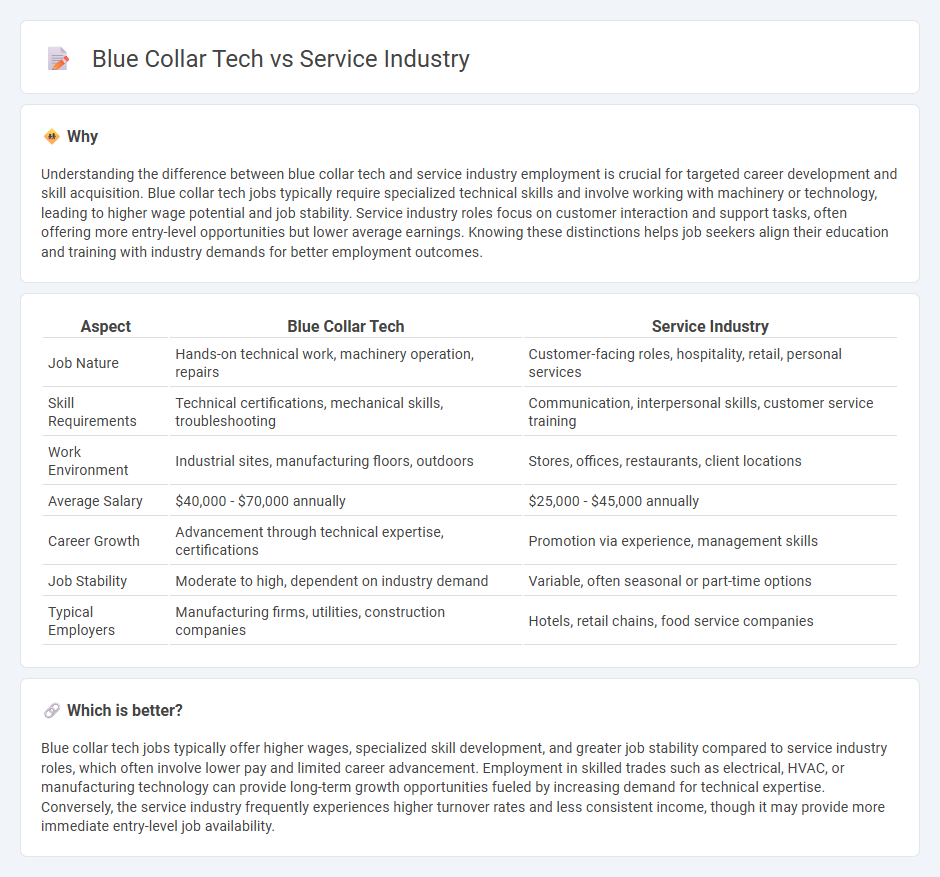
| Aspect | Blue Collar Tech | Service Industry |
|---|---|---|
| Job Nature | Hands-on technical work, machinery operation, repairs | Customer-facing roles, hospitality, retail, personal services |
| Skill Requirements | Technical certifications, mechanical skills, troubleshooting | Communication, interpersonal skills, customer service training |
| Work Environment | Industrial sites, manufacturing floors, outdoors | Stores, offices, restaurants, client locations |
| Average Salary | $40,000 - $70,000 annually | $25,000 - $45,000 annually |
| Career Growth | Advancement through technical expertise, certifications | Promotion via experience, management skills |
| Job Stability | Moderate to high, dependent on industry demand | Variable, often seasonal or part-time options |
| Typical Employers | Manufacturing firms, utilities, construction companies | Hotels, retail chains, food service companies |
Which is better?
Blue collar tech jobs typically offer higher wages, specialized skill development, and greater job stability compared to service industry roles, which often involve lower pay and limited career advancement. Employment in skilled trades such as electrical, HVAC, or manufacturing technology can provide long-term growth opportunities fueled by increasing demand for technical expertise. Conversely, the service industry frequently experiences higher turnover rates and less consistent income, though it may provide more immediate entry-level job availability.
Connection
Blue collar workers in the tech and service industries drive critical operational functions, such as equipment maintenance, network installation, and facility management, ensuring business continuity. Their roles directly support technical infrastructure and customer-facing services, bridging the gap between technology deployment and user experience. This integration enhances productivity and innovation across sectors reliant on hands-on expertise and technical skills.
Key Terms
Skills specialization
Service industry jobs emphasize interpersonal skills, customer service, and adaptability, while blue collar tech roles require specialized technical skills such as machinery operation, electronics repair, or IT maintenance. Skills specialization in blue collar tech often demands formal training or certification in fields like HVAC, electrical work, or network infrastructure. Explore detailed skill requirements and training pathways to better understand the distinctions.
Work environment
The service industry typically involves direct customer interaction in dynamic, fast-paced settings such as retail stores, restaurants, or hospitality venues, often requiring strong interpersonal skills and adaptability. Blue collar tech roles, such as electricians, HVAC technicians, or mechanics, focus on hands-on technical tasks, frequently performed in varied environments including construction sites, industrial facilities, or clients' homes, with emphasis on problem-solving and physical labor. Explore further to understand how these work environments shape career growth, skill requirements, and job satisfaction.
Customer interaction
Customer interaction in the service industry relies heavily on direct communication, empathy, and personalized experiences to foster client satisfaction and loyalty. Blue collar tech roles emphasize practical problem-solving skills and hands-on technical knowledge, often with limited direct customer engagement but crucial in service delivery and support. Explore how these distinct approaches shape career paths and customer relationships in each sector.
Source and External Links
Service industries - Wikipedia - Service industries provide intangible products or services not directly related to manufacturing, covering fields like healthcare, education, retail, transportation, and more, and make up around 70-80% of employment in modern economies.
Service Industry Definition, Types & List - Lesson - Study.com - The service industry includes consumer services (e.g., hairstyling), business services (e.g., machinery maintenance), and public services (e.g., law enforcement), all rendering intangible services to customers rather than manufacturing goods.
What Is a Service Industry? Plus 26 Examples | Indeed.com - A service industry encompasses any business providing a service rather than a physical product, spanning diverse sectors like communications, hospitality, banking, retail, and education crucial for the economy and daily life.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com