Reverse recruitment shifts the hiring paradigm by allowing candidates to showcase their skills and preferences, empowering employers to select from a pool of pre-qualified applicants. Mass hiring focuses on rapidly filling a large number of positions, often for roles with similar requirements, to meet immediate organizational demands efficiently. Explore the benefits and applications of both strategies to optimize your recruitment process.
Why it is important
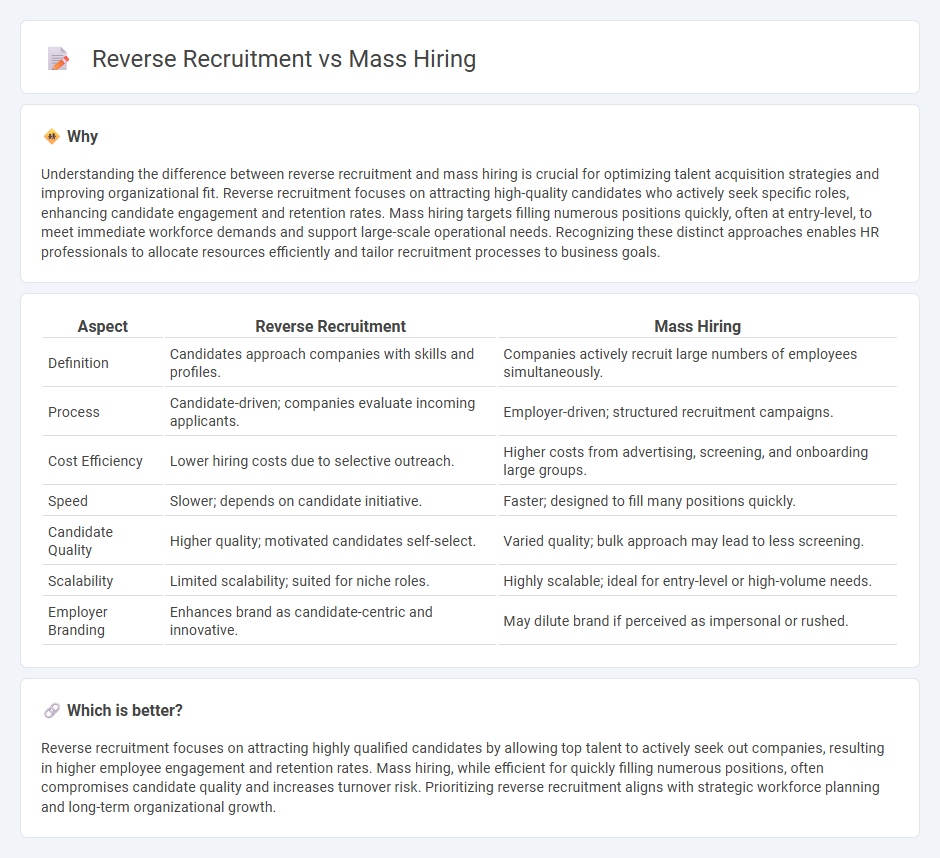
Understanding the difference between reverse recruitment and mass hiring is crucial for optimizing talent acquisition strategies and improving organizational fit. Reverse recruitment focuses on attracting high-quality candidates who actively seek specific roles, enhancing candidate engagement and retention rates. Mass hiring targets filling numerous positions quickly, often at entry-level, to meet immediate workforce demands and support large-scale operational needs. Recognizing these distinct approaches enables HR professionals to allocate resources efficiently and tailor recruitment processes to business goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Reverse Recruitment | Mass Hiring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Candidates approach companies with skills and profiles. | Companies actively recruit large numbers of employees simultaneously. |
| Process | Candidate-driven; companies evaluate incoming applicants. | Employer-driven; structured recruitment campaigns. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower hiring costs due to selective outreach. | Higher costs from advertising, screening, and onboarding large groups. |
| Speed | Slower; depends on candidate initiative. | Faster; designed to fill many positions quickly. |
| Candidate Quality | Higher quality; motivated candidates self-select. | Varied quality; bulk approach may lead to less screening. |
| Scalability | Limited scalability; suited for niche roles. | Highly scalable; ideal for entry-level or high-volume needs. |
| Employer Branding | Enhances brand as candidate-centric and innovative. | May dilute brand if perceived as impersonal or rushed. |
Which is better?
Reverse recruitment focuses on attracting highly qualified candidates by allowing top talent to actively seek out companies, resulting in higher employee engagement and retention rates. Mass hiring, while efficient for quickly filling numerous positions, often compromises candidate quality and increases turnover risk. Prioritizing reverse recruitment aligns with strategic workforce planning and long-term organizational growth.
Connection
Reverse recruitment and mass hiring are interconnected strategies that streamline talent acquisition by shifting the recruitment initiative to candidates and efficiently filling large volumes of positions. Reverse recruitment empowers job seekers to proactively present their skills, while mass hiring leverages this influx of qualified applicants to rapidly scale workforce needs. Together, these methods optimize hiring processes by accelerating candidate engagement and reducing time-to-fill metrics in high-demand industries.
Key Terms
Talent Pool
Mass hiring targets large candidate influx to quickly fill numerous roles, often emphasizing quantity over individual fit, while reverse recruitment concentrates on actively engaging a curated talent pool tailored to specific organizational needs. Talent pool management in reverse recruitment enhances long-term candidate relationship building, improving retention and quality of hire compared to traditional mass hiring strategies. Explore how optimizing talent pools through reverse recruitment can transform your hiring outcomes.
Candidate Sourcing
Mass hiring leverages broad candidate sourcing strategies, utilizing job boards, social media platforms, and recruitment agencies to quickly fill a large volume of positions. Reverse recruitment focuses on targeted candidate sourcing by engaging passive candidates through personalized outreach, employer branding, and talent pools tailored to niche skills. Explore the detailed benefits and methods of each approach to optimize your talent acquisition process.
Employer Branding
Mass hiring strategies often overlook personalized candidate experiences, potentially weakening employer branding by treating applicants as numbers rather than individuals. Reverse recruitment, where companies proactively engage top talent based on fit and culture alignment, strengthens employer branding through tailored communication and positive candidate impressions. Explore how integrating reverse recruitment can elevate your employer brand and attract high-quality candidates effectively.
Source and External Links
Mass Hiring - Mass hiring is the process of recruiting a large number of employees within a short time, often driven by business growth, seasonal demands, or new projects, requiring close coordination and planning to efficiently fill many positions at once.
How to Make Mass Hiring More Efficient - Mass hiring involves recruiting high volumes of employees quickly to meet surges in demand or expansion, and success depends on detailed planning before, during, and after the hiring phase.
Mass Hiring: What to Know Before You Start - Mass hiring is defined by the relative size and speed of hiring for a given company, requiring careful internal planning and collaboration to ensure candidate experience, onboarding, and retention during rapid workforce growth.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com