Ghost work refers to tasks completed by remote, anonymous freelancers often supporting AI systems, while temping involves short-term positions with predefined hours and duties within organizations. Both forms of employment offer flexible labor solutions but differ in structure, job security, and worker visibility. Explore the nuances of ghost work and temping to understand their impact on the modern labor market.
Why it is important
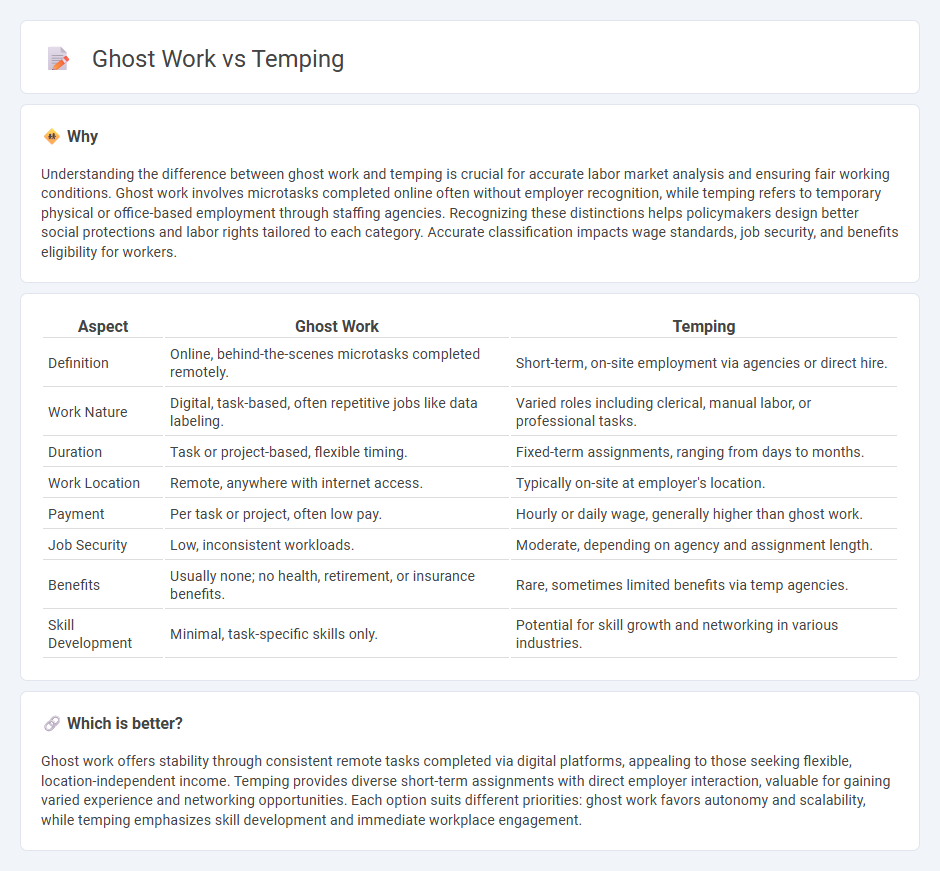
Understanding the difference between ghost work and temping is crucial for accurate labor market analysis and ensuring fair working conditions. Ghost work involves microtasks completed online often without employer recognition, while temping refers to temporary physical or office-based employment through staffing agencies. Recognizing these distinctions helps policymakers design better social protections and labor rights tailored to each category. Accurate classification impacts wage standards, job security, and benefits eligibility for workers.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Work | Temping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Online, behind-the-scenes microtasks completed remotely. | Short-term, on-site employment via agencies or direct hire. |
| Work Nature | Digital, task-based, often repetitive jobs like data labeling. | Varied roles including clerical, manual labor, or professional tasks. |
| Duration | Task or project-based, flexible timing. | Fixed-term assignments, ranging from days to months. |
| Work Location | Remote, anywhere with internet access. | Typically on-site at employer's location. |
| Payment | Per task or project, often low pay. | Hourly or daily wage, generally higher than ghost work. |
| Job Security | Low, inconsistent workloads. | Moderate, depending on agency and assignment length. |
| Benefits | Usually none; no health, retirement, or insurance benefits. | Rare, sometimes limited benefits via temp agencies. |
| Skill Development | Minimal, task-specific skills only. | Potential for skill growth and networking in various industries. |
Which is better?
Ghost work offers stability through consistent remote tasks completed via digital platforms, appealing to those seeking flexible, location-independent income. Temping provides diverse short-term assignments with direct employer interaction, valuable for gaining varied experience and networking opportunities. Each option suits different priorities: ghost work favors autonomy and scalability, while temping emphasizes skill development and immediate workplace engagement.
Connection
Ghost work and temping both involve flexible, often short-term employment arrangements that prioritize task-based jobs over traditional full-time roles. These types of work enable businesses to quickly scale their workforce with contingent labor, relying on digital platforms or agencies for rapid staffing solutions. The rise of the gig economy further blurs the lines between ghost work, such as microtasks performed online, and temping, which includes physical or office-based temporary positions.
Key Terms
Gig Economy
Temping in the gig economy involves short-term, flexible jobs where workers are officially employed for specific tasks or durations, often facilitated by agencies or platforms. Ghost work refers to behind-the-scenes digital labor, such as data labeling or content moderation, performed anonymously without formal employment status. Explore the dynamics and implications of temping and ghost work within the gig economy to understand their impact on labor rights and economic trends.
Contract Labor
Contract labor encompasses temping and ghost work, two distinct forms of contingent employment crucial to modern gig economies. Temping involves short-term assignments through staffing agencies, offering workers flexibility and businesses scalable workforce solutions, while ghost work consists of online microtasks often hidden from public view, requiring minimal commitment but substantial digital labor contribution. Explore the evolving landscape and implications of contract labor in the digital economy.
Digital Microtasks
Digital microtasks involve small, discrete jobs completed online, often through platforms that connect workers with temporary tasks. Temping generally refers to short-term employment assignments in various industries, while ghost work specifically denotes the unnoticed, often underpaid digital labor behind AI data labeling and content moderation. Explore the evolving landscape of digital microtasks and their impact on the future of work.
Source and External Links
What is Temping & How do Temp Agencies Work? | DEDICATED - Temping is short-term work through a recruitment agency where the candidate is on the agency's payroll and paid hourly, providing flexibility and covering roles like absence or leave with no long-term commitment required from either party.
Top Ten Reasons for Temping | Unitemps Career Advice - Temping can offer valuable career experience, paid work during study, and opportunities to convert temporary assignments into permanent roles.
TEMPING | definition in the Cambridge English Dictionary - Temping means being employed for a short period, usually to cover someone's absence or to manage extra work, often providing flexibility for the worker.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com