Labor hoarding involves retaining employees during economic downturns despite reduced demand, helping companies maintain skilled workforces and reduce rehiring costs. Furloughs, by contrast, temporarily suspend employee work without pay to cut immediate labor expenses while preserving job positions. Explore the strategic benefits and risks of labor hoarding versus furloughs to optimize workforce management.
Why it is important
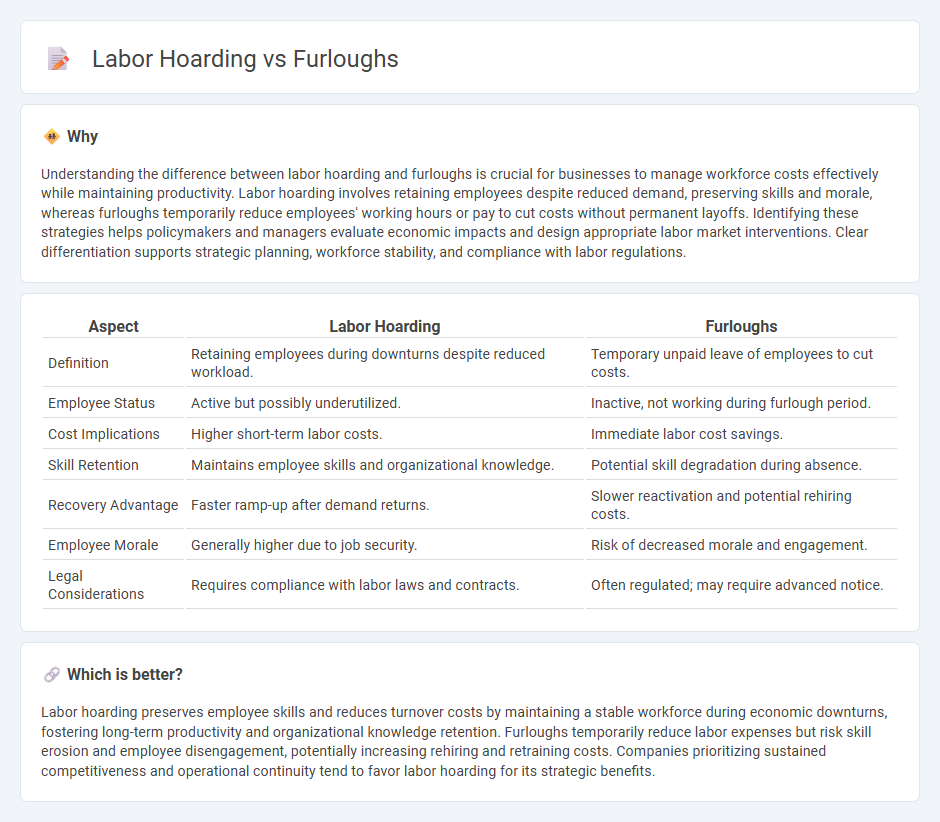
Understanding the difference between labor hoarding and furloughs is crucial for businesses to manage workforce costs effectively while maintaining productivity. Labor hoarding involves retaining employees despite reduced demand, preserving skills and morale, whereas furloughs temporarily reduce employees' working hours or pay to cut costs without permanent layoffs. Identifying these strategies helps policymakers and managers evaluate economic impacts and design appropriate labor market interventions. Clear differentiation supports strategic planning, workforce stability, and compliance with labor regulations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Labor Hoarding | Furloughs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Retaining employees during downturns despite reduced workload. | Temporary unpaid leave of employees to cut costs. |
| Employee Status | Active but possibly underutilized. | Inactive, not working during furlough period. |
| Cost Implications | Higher short-term labor costs. | Immediate labor cost savings. |
| Skill Retention | Maintains employee skills and organizational knowledge. | Potential skill degradation during absence. |
| Recovery Advantage | Faster ramp-up after demand returns. | Slower reactivation and potential rehiring costs. |
| Employee Morale | Generally higher due to job security. | Risk of decreased morale and engagement. |
| Legal Considerations | Requires compliance with labor laws and contracts. | Often regulated; may require advanced notice. |
Which is better?
Labor hoarding preserves employee skills and reduces turnover costs by maintaining a stable workforce during economic downturns, fostering long-term productivity and organizational knowledge retention. Furloughs temporarily reduce labor expenses but risk skill erosion and employee disengagement, potentially increasing rehiring and retraining costs. Companies prioritizing sustained competitiveness and operational continuity tend to favor labor hoarding for its strategic benefits.
Connection
Labor hoarding and furloughs are connected as strategic responses employers use to manage workforce fluctuations during economic downturns. Labor hoarding involves retaining more employees than immediately needed to avoid future hiring costs, while furloughs temporarily reduce employee hours without severing employment. Both practices aim to balance labor costs and workforce stability, enabling quicker recovery when demand improves.
Key Terms
Workforce Management
Furloughs and labor hoarding represent contrasting workforce management strategies during economic uncertainty, where furloughs involve temporary unpaid leave to reduce labor costs, while labor hoarding retains employees despite reduced demand to preserve skills and morale. Organizations employing furloughs can achieve immediate cost savings but risk losing valuable talent and affecting employee engagement. Explore detailed analyses and case studies on effective workforce management strategies to optimize labor costs and maintain operational resilience.
Cost Reduction
Furloughs reduce labor costs by temporarily laying off employees without pay, providing immediate financial relief but risking workforce morale and productivity. Labor hoarding maintains employee retention by preserving jobs and wages during downturns, potentially increasing short-term costs but supporting long-term organizational knowledge and efficiency. Explore detailed strategies on cost reduction through furloughs and labor hoarding to enhance workforce management.
Talent Retention
Furloughs temporarily reduce workforce costs by placing employees on unpaid leave while retaining their employment status, minimizing immediate layoffs but risking disengagement. Labor hoarding involves maintaining a larger-than-necessary workforce during downturns to preserve organizational knowledge, skills, and morale, which supports long-term talent retention and smoother recovery. Explore strategies to balance operational efficiency and employee retention in fluctuating economic conditions for sustaining business resilience.
Source and External Links
Furlough vs Laid Off: What is the Difference? - ADP - A furlough is a temporary unpaid leave of absence or reduction in hours due to lack of work or budget cuts, after which employees typically resume their normal schedule; furloughs can apply differently to salaried (exempt) and hourly (non-exempt) employees.
Furloughs vs. Layoffs: What Are the Practical and Legal Differences? - Furloughs temporarily reduce or eliminate employee hours without terminating employment, allowing businesses to retain employees and resume work later, with strict rules requiring furloughed salaried employees not to work during furlough periods.
Furlough - Wikipedia - Furloughs are temporary cessations of paid employment often used to address budget shortfalls or special needs, famously implemented during the 2013 U.S. federal government budget sequestration and shutdowns to reduce federal spending without permanent layoffs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com