Secondment involves temporarily transferring an employee to another role or organization to gain specialized skills and experience while maintaining their original employment status. Internships are typically short-term, structured programs designed for students or recent graduates to acquire practical work experience in a specific field. Explore further to understand the key differences and benefits of secondments and internships in career development.
Why it is important
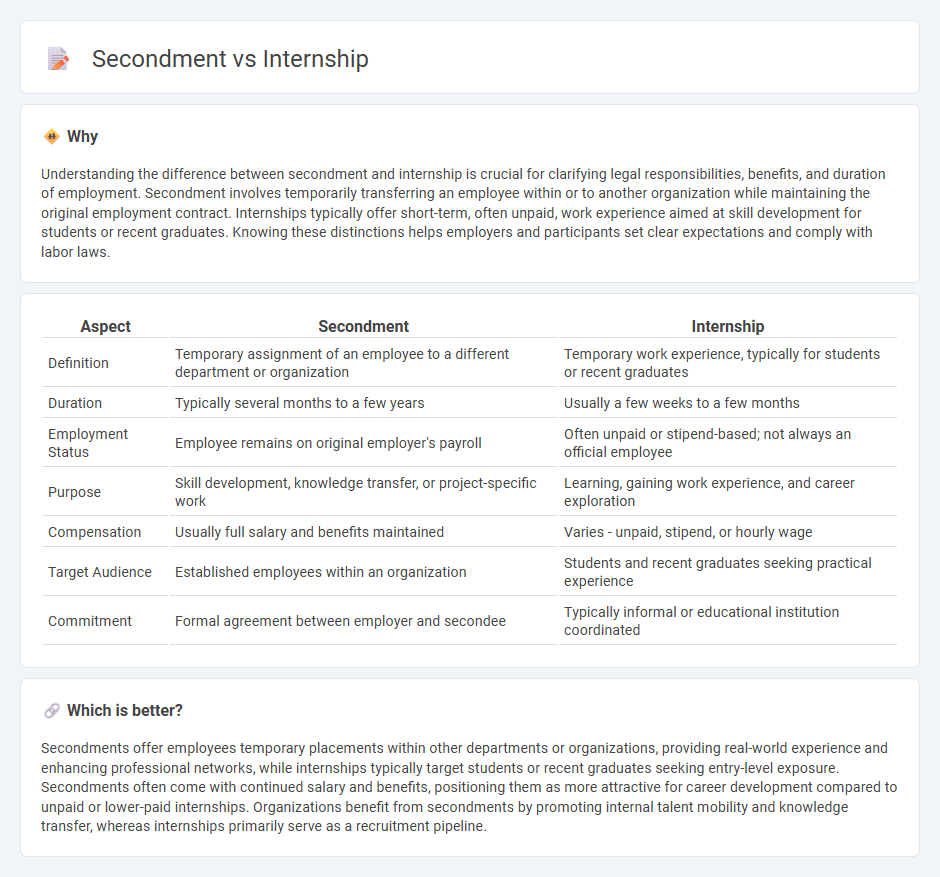
Understanding the difference between secondment and internship is crucial for clarifying legal responsibilities, benefits, and duration of employment. Secondment involves temporarily transferring an employee within or to another organization while maintaining the original employment contract. Internships typically offer short-term, often unpaid, work experience aimed at skill development for students or recent graduates. Knowing these distinctions helps employers and participants set clear expectations and comply with labor laws.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Secondment | Internship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temporary assignment of an employee to a different department or organization | Temporary work experience, typically for students or recent graduates |
| Duration | Typically several months to a few years | Usually a few weeks to a few months |
| Employment Status | Employee remains on original employer's payroll | Often unpaid or stipend-based; not always an official employee |
| Purpose | Skill development, knowledge transfer, or project-specific work | Learning, gaining work experience, and career exploration |
| Compensation | Usually full salary and benefits maintained | Varies - unpaid, stipend, or hourly wage |
| Target Audience | Established employees within an organization | Students and recent graduates seeking practical experience |
| Commitment | Formal agreement between employer and secondee | Typically informal or educational institution coordinated |
Which is better?
Secondments offer employees temporary placements within other departments or organizations, providing real-world experience and enhancing professional networks, while internships typically target students or recent graduates seeking entry-level exposure. Secondments often come with continued salary and benefits, positioning them as more attractive for career development compared to unpaid or lower-paid internships. Organizations benefit from secondments by promoting internal talent mobility and knowledge transfer, whereas internships primarily serve as a recruitment pipeline.
Connection
Secondment and internship both serve as strategic employment tools designed to enhance professional skills and industry exposure. Secondments typically involve temporary transfers of employees to different roles or departments within or outside their organization to gain specialized expertise. Internships provide structured work experiences primarily for students or recent graduates, enabling them to apply academic knowledge in real-world settings and build practical competencies.
Key Terms
Duration
Internships typically last from a few weeks to several months, designed to provide hands-on experience and skill development in a specific field. Secondments generally extend from several months to a few years, involving temporary transfers within or between organizations to fill key roles or develop expertise. Explore the differences further to determine which option suits your career goals best.
Employer Relationship
An internship typically establishes a temporary learning relationship where the intern gains practical experience without long-term obligations from the employer. A secondment involves an employee being temporarily transferred within or between organizations, maintaining their employment contract and benefits with the original employer. Explore further to understand how these arrangements impact workforce management and legal responsibilities.
Purpose
An internship primarily aims to provide practical experience and skill development for students or recent graduates in their chosen field, enhancing employability and industry knowledge. Secondment involves temporarily transferring an employee to another department or organization to fulfill specific business needs or projects while gaining broader organizational insight. Discover more about how these purposes impact career growth and organizational benefits.
Source and External Links
Internship - Wikipedia - An internship is a limited period of work experience offered by organizations to students or graduates to gain relevant skills and build professional networks, often leading to employment opportunities.
What Is an Internship? - UMBC Career Center - Internships are professional learning experiences that offer practical work related to a student's field of study or career interest, usually involving supervised, structured tasks and regular feedback.
Internship Meaning and Definition: A NACE Guide - Internships integrate classroom knowledge with practical application in a professional setting, allowing students to develop skills, explore careers, and build connections, while also serving as a recruiting tool for employers.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com