Gig platforms offer flexible job opportunities by connecting independent contractors with short-term tasks through digital marketplaces, enabling rapid income generation and diverse work experiences. In contrast, co-operatives provide worker-owned and democratically managed employment structures that emphasize collective decision-making, profit sharing, and long-term job stability. Explore how these contrasting models reshape modern employment and empower different types of workers.
Why it is important
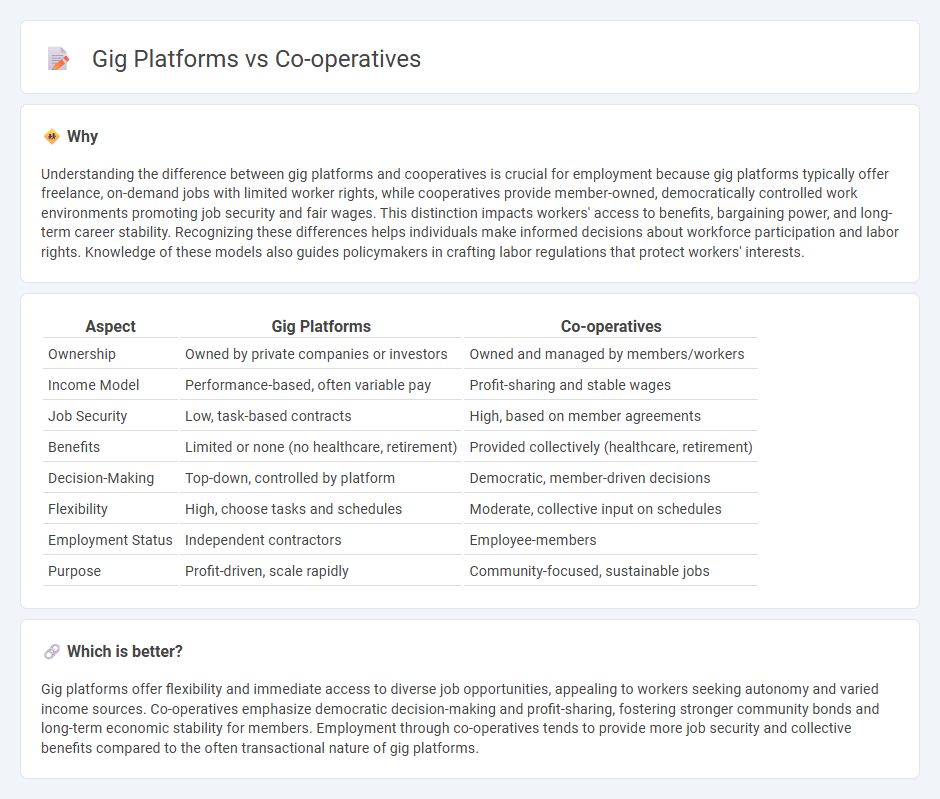
Understanding the difference between gig platforms and cooperatives is crucial for employment because gig platforms typically offer freelance, on-demand jobs with limited worker rights, while cooperatives provide member-owned, democratically controlled work environments promoting job security and fair wages. This distinction impacts workers' access to benefits, bargaining power, and long-term career stability. Recognizing these differences helps individuals make informed decisions about workforce participation and labor rights. Knowledge of these models also guides policymakers in crafting labor regulations that protect workers' interests.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Gig Platforms | Co-operatives |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Owned by private companies or investors | Owned and managed by members/workers |
| Income Model | Performance-based, often variable pay | Profit-sharing and stable wages |
| Job Security | Low, task-based contracts | High, based on member agreements |
| Benefits | Limited or none (no healthcare, retirement) | Provided collectively (healthcare, retirement) |
| Decision-Making | Top-down, controlled by platform | Democratic, member-driven decisions |
| Flexibility | High, choose tasks and schedules | Moderate, collective input on schedules |
| Employment Status | Independent contractors | Employee-members |
| Purpose | Profit-driven, scale rapidly | Community-focused, sustainable jobs |
Which is better?
Gig platforms offer flexibility and immediate access to diverse job opportunities, appealing to workers seeking autonomy and varied income sources. Co-operatives emphasize democratic decision-making and profit-sharing, fostering stronger community bonds and long-term economic stability for members. Employment through co-operatives tends to provide more job security and collective benefits compared to the often transactional nature of gig platforms.
Connection
Gig platforms enable flexible work opportunities by connecting freelancers with clients, while co-operatives empower workers through collective ownership and shared decision-making. Both models address labor market gaps but differ in control and profit distribution, with co-operatives fostering worker autonomy and gig platforms focusing on efficiency and scalability. The intersection emerges as some gig platforms adopt cooperative principles to enhance worker benefits and sustainability in the gig economy.
Key Terms
Worker Ownership
Worker ownership in co-operatives ensures employees have equal shares and governance rights, fostering transparent decision-making and profit distribution. In contrast, gig platforms typically classify workers as independent contractors, limiting their participation in company ownership and control. Explore deeper insights into how these models impact worker autonomy and economic equity.
Job Security
Co-operatives offer enhanced job security by fostering member ownership and collective decision-making, providing workers with stable income and control over their work conditions. Gig platforms, in contrast, often lack employment guarantees, exposing workers to income volatility and limited labor protections. Explore how co-operatives are reshaping job security in the evolving gig economy.
Flexibility
Co-operatives offer workers democratic control and predictable working hours, enhancing stability and long-term flexibility. Gig platforms provide unmatched task variety and on-demand scheduling but often lack consistent income or worker protections. Explore how these models balance flexibility to choose the ideal work arrangement for different needs.
Source and External Links
Cooperative - A cooperative is an autonomous association of persons united voluntarily to meet their common economic, social, and cultural needs, often aiming to create a sustainable, equitable local economy through member ownership and democratic governance.
What are Cooperatives? | Business Enterprise Institute - Cooperatives are member-owned and democratically controlled businesses that serve the interests of their members and operate according to seven principles including voluntary membership, democratic control, and concern for community.
What is a Co-op? - A co-operative is a business model focused on meeting members' needs rather than generating profits for investors, where members have equal voting power and profits are reinvested or shared based on usage, covering diverse sectors globally with nearly a billion members.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com