Job carving focuses on customizing positions by breaking down existing roles into specific tasks tailored to an individual's skills, enhancing productivity and job satisfaction. Job rotation involves systematically shifting employees between different roles to develop versatile skill sets and prevent job monotony. Explore these innovative employment strategies to optimize workforce efficiency and employee engagement.
Why it is important
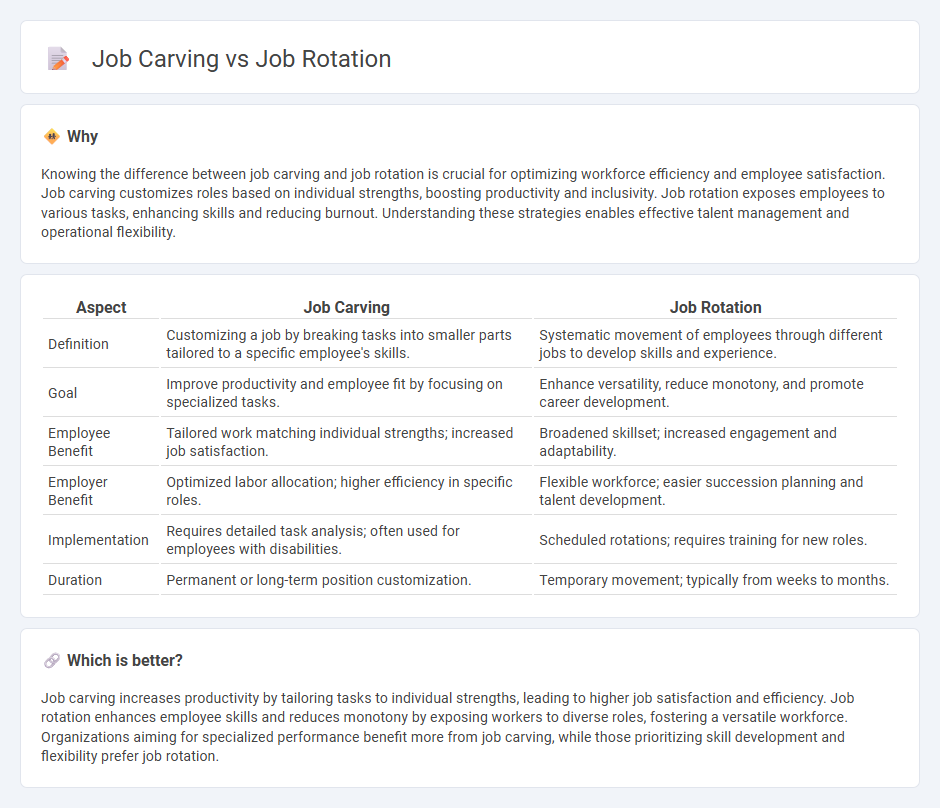
Knowing the difference between job carving and job rotation is crucial for optimizing workforce efficiency and employee satisfaction. Job carving customizes roles based on individual strengths, boosting productivity and inclusivity. Job rotation exposes employees to various tasks, enhancing skills and reducing burnout. Understanding these strategies enables effective talent management and operational flexibility.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Job Carving | Job Rotation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Customizing a job by breaking tasks into smaller parts tailored to a specific employee's skills. | Systematic movement of employees through different jobs to develop skills and experience. |
| Goal | Improve productivity and employee fit by focusing on specialized tasks. | Enhance versatility, reduce monotony, and promote career development. |
| Employee Benefit | Tailored work matching individual strengths; increased job satisfaction. | Broadened skillset; increased engagement and adaptability. |
| Employer Benefit | Optimized labor allocation; higher efficiency in specific roles. | Flexible workforce; easier succession planning and talent development. |
| Implementation | Requires detailed task analysis; often used for employees with disabilities. | Scheduled rotations; requires training for new roles. |
| Duration | Permanent or long-term position customization. | Temporary movement; typically from weeks to months. |
Which is better?
Job carving increases productivity by tailoring tasks to individual strengths, leading to higher job satisfaction and efficiency. Job rotation enhances employee skills and reduces monotony by exposing workers to diverse roles, fostering a versatile workforce. Organizations aiming for specialized performance benefit more from job carving, while those prioritizing skill development and flexibility prefer job rotation.
Connection
Job carving and job rotation are interconnected workforce strategies designed to enhance employee engagement and productivity by matching tasks to individual skills and providing variety in job functions. Job carving customizes roles by extracting specific responsibilities tailored to an employee's strengths, while job rotation systematically moves employees through different roles to develop diverse skills and reduce monotony. Together, these approaches optimize talent utilization and promote adaptability within organizations.
Key Terms
Skill Development
Job rotation enhances skill development by allowing employees to experience diverse roles, fostering adaptability and a broader skill set. Job carving targets specific tasks tailored to an individual's strengths, optimizing productivity while enhancing specialized skills. Explore how strategic implementation of job rotation and carving can maximize workforce potential and career growth.
Task Allocation
Job rotation involves systematically moving employees through a variety of positions to develop diverse skills and increase adaptability, enhancing overall task allocation by exposing workers to multiple functions. Job carving customizes roles by dissecting traditional job descriptions to assign specific tasks that match an individual's strengths, optimizing productivity and employee satisfaction in task allocation. Explore more about how tailored task allocation strategies like job rotation and job carving can improve workforce efficiency and engagement.
Employee Engagement
Job rotation enhances employee engagement by providing diverse experiences and skill development opportunities, fostering motivation and reducing job monotony. Job carving increases engagement by customizing roles to match individual strengths and interests, leading to higher job satisfaction and productivity. Explore these strategies to discover which approach best boosts engagement in your workforce.
Source and External Links
Job rotation - Wikipedia - Job rotation is the lateral transfer of employees between jobs in an organization without a change in hierarchical rank or salary, used to improve staffing, motivation, fatigue management, orientation, and career development through varied rotation periods.
Job rotation | EBSCO Research Starters - Job rotation is a human resources strategy moving employees among jobs or departments to build diverse skills, reduce monotony and burnout, increase satisfaction, and improve productivity and retention.
Job Rotation: A Full Guide with 5 Examples - Job rotation involves temporary lateral moves between jobs, with examples like Heineken's Technologist Program showing how structured rotations enhance skills and flexibility, reduce turnover, and support workforce adaptability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com