Polyworking involves individuals managing multiple jobs or projects simultaneously, enhancing skill diversity and income streams, while outsourcing delegates tasks to external specialists to optimize efficiency and reduce costs. Both strategies aim to address workforce demands dynamically but differ in control, flexibility, and resource allocation. Explore how polyworking and outsourcing can transform your employment approach for maximum productivity.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between polyworking and outsourcing is crucial for optimizing workforce management, as polyworking involves individuals juggling multiple roles internally, while outsourcing delegates tasks to external specialists. This distinction impacts cost efficiency, talent allocation, and project control within businesses. Companies leveraging polyworking can enhance employee versatility and internal knowledge retention, whereas outsourcing enables access to specialized skills and scalability. Knowing these differences assists in strategic planning for productivity and operational agility in dynamic markets.
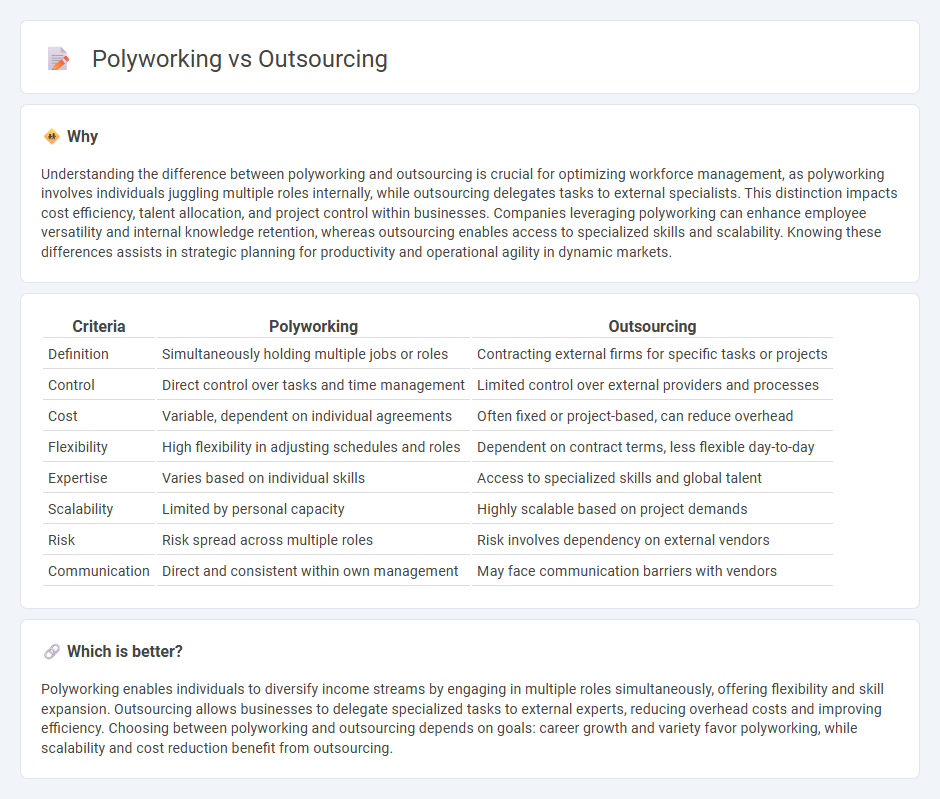
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Polyworking | Outsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Simultaneously holding multiple jobs or roles | Contracting external firms for specific tasks or projects |
| Control | Direct control over tasks and time management | Limited control over external providers and processes |
| Cost | Variable, dependent on individual agreements | Often fixed or project-based, can reduce overhead |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in adjusting schedules and roles | Dependent on contract terms, less flexible day-to-day |
| Expertise | Varies based on individual skills | Access to specialized skills and global talent |
| Scalability | Limited by personal capacity | Highly scalable based on project demands |
| Risk | Risk spread across multiple roles | Risk involves dependency on external vendors |
| Communication | Direct and consistent within own management | May face communication barriers with vendors |
Which is better?
Polyworking enables individuals to diversify income streams by engaging in multiple roles simultaneously, offering flexibility and skill expansion. Outsourcing allows businesses to delegate specialized tasks to external experts, reducing overhead costs and improving efficiency. Choosing between polyworking and outsourcing depends on goals: career growth and variety favor polyworking, while scalability and cost reduction benefit from outsourcing.
Connection
Polyworking allows individuals to diversify their income streams by engaging in multiple job roles, often facilitated through outsourcing platforms that connect freelancers with businesses worldwide. Outsourcing enables companies to delegate specialized tasks to polyworkers who manage various projects simultaneously, increasing efficiency and reducing operational costs. The synergy between polyworking and outsourcing drives flexible labor markets, empowering workers with autonomy while optimizing resource allocation for organizations.
Key Terms
Cost Efficiency
Outsourcing significantly reduces labor and operational costs by leveraging specialized external providers, allowing companies to avoid expenses related to full-time salaries, benefits, and infrastructure. Polyworking optimizes cost efficiency through talent diversification and flexible project-based hiring, minimizing overhead while enhancing innovation and adaptability. Explore more to understand which approach best aligns with your business cost strategies.
Flexibility
Outsourcing offers companies the flexibility to scale operations quickly by delegating tasks to external experts, allowing a focus on core business activities without the constraints of in-house resource limitations. Polyworking, on the other hand, provides individuals with the flexibility to diversify income streams and skill sets by engaging in multiple roles or projects simultaneously, enhancing job satisfaction and adaptability in a dynamic market. Explore more about how these flexible work models can transform business efficiency and career growth.
Workforce Management
Outsourcing involves delegating specific tasks or business processes to external vendors, optimizing workforce management by reducing in-house labor costs and enhancing operational efficiency. Polyworking, or gig economy employment, leverages a flexible pool of multi-skilled workers performing diverse roles simultaneously, enabling businesses to adapt rapidly to changing demands and project needs. Explore the nuances of these workforce strategies to identify the most effective approach for your organization's growth and flexibility.
Source and External Links
What is Outsourcing and How Does it Work? - Outsourcing is a business practice where a company hires a third-party provider to perform tasks or services, often including IT, customer service, manufacturing, and financial functions, either onsite or externally, emphasizing partnership management over just logistics.
What is outsourcing? | Definition and examples - Outsourcing is the strategy of transferring tasks, subareas, or entire business processes to external contractors, often to reduce costs, including outsourcing customer service, marketing, and manufacturing processes to regional or foreign companies.
Outsourcing - Outsourcing involves companies using external providers to perform business processes previously handled internally, including both domestic and foreign contracting, and sometimes involves transferring employees and assets, distinct from but related to offshoring.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com