Digital nomad visas provide remote workers with the flexibility to live and work legally in foreign countries without local employment restrictions, often requiring proof of income and health insurance. Entrepreneur visas target business founders seeking to establish or expand operations abroad, typically demanding a solid business plan, investment capital, and job creation commitments. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which visa suits your employment goals and lifestyle preferences.
Why it is important
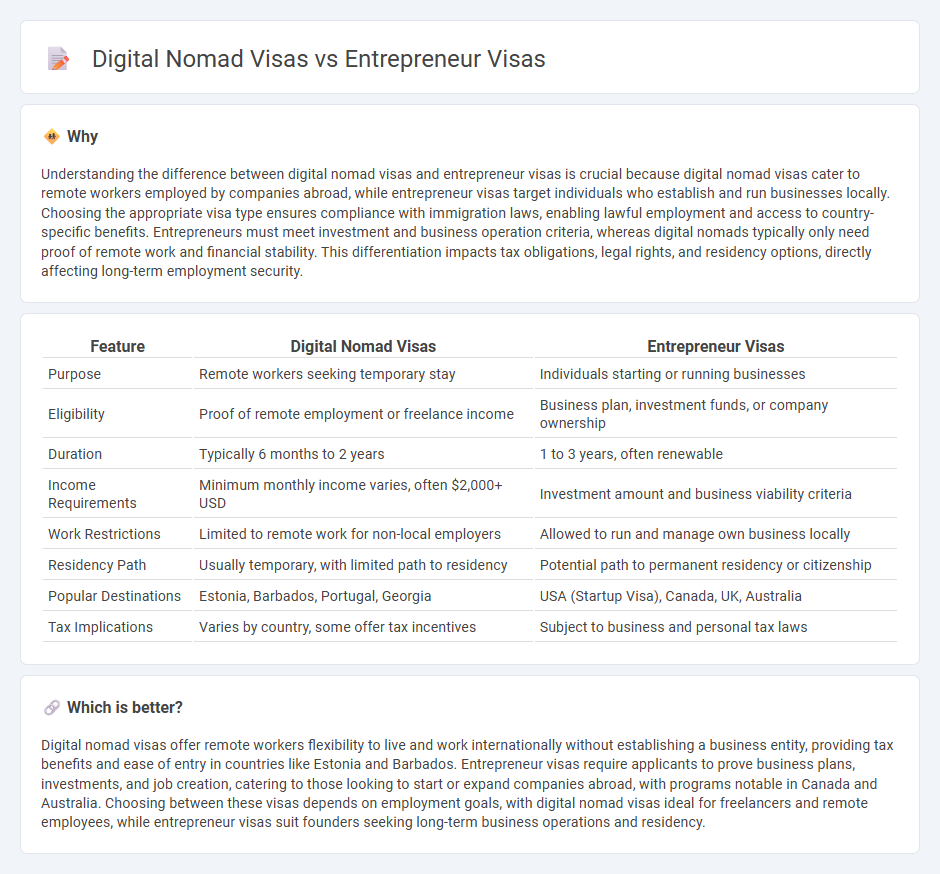
Understanding the difference between digital nomad visas and entrepreneur visas is crucial because digital nomad visas cater to remote workers employed by companies abroad, while entrepreneur visas target individuals who establish and run businesses locally. Choosing the appropriate visa type ensures compliance with immigration laws, enabling lawful employment and access to country-specific benefits. Entrepreneurs must meet investment and business operation criteria, whereas digital nomads typically only need proof of remote work and financial stability. This differentiation impacts tax obligations, legal rights, and residency options, directly affecting long-term employment security.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Nomad Visas | Entrepreneur Visas |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Remote workers seeking temporary stay | Individuals starting or running businesses |
| Eligibility | Proof of remote employment or freelance income | Business plan, investment funds, or company ownership |
| Duration | Typically 6 months to 2 years | 1 to 3 years, often renewable |
| Income Requirements | Minimum monthly income varies, often $2,000+ USD | Investment amount and business viability criteria |
| Work Restrictions | Limited to remote work for non-local employers | Allowed to run and manage own business locally |
| Residency Path | Usually temporary, with limited path to residency | Potential path to permanent residency or citizenship |
| Popular Destinations | Estonia, Barbados, Portugal, Georgia | USA (Startup Visa), Canada, UK, Australia |
| Tax Implications | Varies by country, some offer tax incentives | Subject to business and personal tax laws |
Which is better?
Digital nomad visas offer remote workers flexibility to live and work internationally without establishing a business entity, providing tax benefits and ease of entry in countries like Estonia and Barbados. Entrepreneur visas require applicants to prove business plans, investments, and job creation, catering to those looking to start or expand companies abroad, with programs notable in Canada and Australia. Choosing between these visas depends on employment goals, with digital nomad visas ideal for freelancers and remote employees, while entrepreneur visas suit founders seeking long-term business operations and residency.
Connection
Digital nomad visas and entrepreneur visas both facilitate remote work and business operations by granting legal residency for individuals seeking flexible work environments outside their home countries. These visas support economic growth by attracting skilled professionals and innovators who can contribute to local economies while maintaining international business activities. The connection lies in their shared goal of promoting mobility, ease of doing business, and global talent exchange.
Key Terms
Business Investment Requirements
Entrepreneur visas typically require applicants to demonstrate substantial business investment, often specifying minimum capital thresholds and job creation metrics to qualify. In contrast, digital nomad visas focus more on proof of remote income and financial self-sufficiency without stringent investment mandates. Explore detailed comparisons of these visa types to determine the best fit for your business goals and lifestyle.
Remote Work Eligibility
Entrepreneur visas typically require applicants to establish or invest in a business within the host country, often demanding proof of financial commitment and job creation, while digital nomad visas focus on individuals working remotely for foreign employers without engaging in local employment. Remote work eligibility under entrepreneur visas involves active local business management, whereas digital nomad visas primarily validate continuous remote work from a foreign location, simplifying residency for freelancers and remote professionals. Explore detailed requirements and benefits of each visa type to determine the best fit for your remote work lifestyle.
Local Employment Restrictions
Entrepreneur visas typically impose local employment restrictions requiring visa holders to establish or actively manage a business within the host country, often limiting work to the registered enterprise. Digital nomad visas generally allow remote work for foreign employers or self-employed activities without engaging in local job markets, offering greater employment flexibility but prohibiting local hiring. Explore more differences in employment conditions between these visa types to determine the best option for your professional goals.
Source and External Links
Choose From 5 Entrepreneur Visas to Launch Your U.S. Dream - Explains five key U.S. entrepreneur visas including the popular E-2 Treaty Investor visa, which requires substantial investment and business development in the U.S.
The best countries to get a startup visa in 2025 - Expatica - Provides an overview of startup and entrepreneur visas globally, highlighting that these visas usually require a solid business plan, proof of funds, and may offer residency options.
US Visa Options for Entrepreneurs - Davies & Associates - Details several U.S. visa options for entrepreneurs such as the E-2, O-1, EB-2 National Interest Waiver visa, the latter allowing self-petitioning without a job offer if the business has national importance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com