Boomerang employees bring valuable company-specific knowledge and proven loyalty when they return after a break, often resulting in quicker onboarding and higher retention rates. Gig workers offer flexible, project-based expertise that allows businesses to scale their workforce efficiently without long-term commitments. Explore the unique advantages and challenges of these employment models to optimize your workforce strategy.
Why it is important
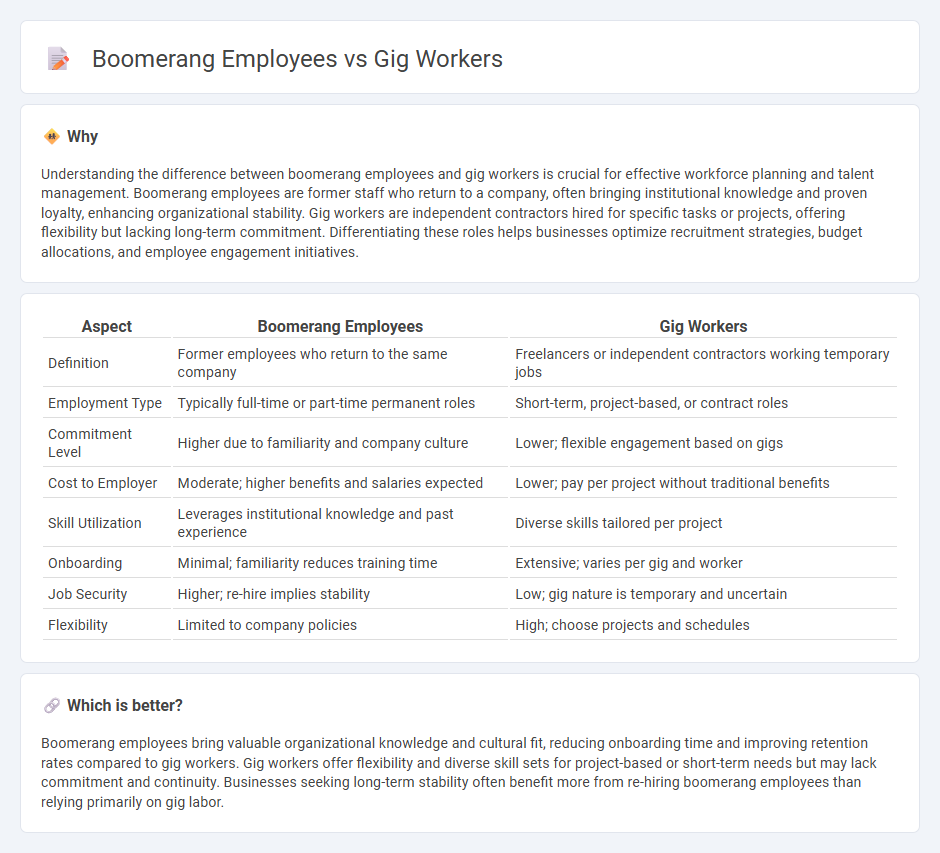
Understanding the difference between boomerang employees and gig workers is crucial for effective workforce planning and talent management. Boomerang employees are former staff who return to a company, often bringing institutional knowledge and proven loyalty, enhancing organizational stability. Gig workers are independent contractors hired for specific tasks or projects, offering flexibility but lacking long-term commitment. Differentiating these roles helps businesses optimize recruitment strategies, budget allocations, and employee engagement initiatives.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Boomerang Employees | Gig Workers |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Former employees who return to the same company | Freelancers or independent contractors working temporary jobs |
| Employment Type | Typically full-time or part-time permanent roles | Short-term, project-based, or contract roles |
| Commitment Level | Higher due to familiarity and company culture | Lower; flexible engagement based on gigs |
| Cost to Employer | Moderate; higher benefits and salaries expected | Lower; pay per project without traditional benefits |
| Skill Utilization | Leverages institutional knowledge and past experience | Diverse skills tailored per project |
| Onboarding | Minimal; familiarity reduces training time | Extensive; varies per gig and worker |
| Job Security | Higher; re-hire implies stability | Low; gig nature is temporary and uncertain |
| Flexibility | Limited to company policies | High; choose projects and schedules |
Which is better?
Boomerang employees bring valuable organizational knowledge and cultural fit, reducing onboarding time and improving retention rates compared to gig workers. Gig workers offer flexibility and diverse skill sets for project-based or short-term needs but may lack commitment and continuity. Businesses seeking long-term stability often benefit more from re-hiring boomerang employees than relying primarily on gig labor.
Connection
Boomerang employees and gig workers share a common emphasis on flexible employment arrangements, adapting to modern workforce dynamics shaped by technological advancements. Both categories contribute to a fluid labor market where companies leverage short-term engagements and rehire proven talent to optimize operational efficiency. This interconnected trend reflects shifts toward project-based roles, remote work, and personalized career paths within the evolving gig economy.
Key Terms
Flexibility
Gig workers prioritize flexibility by choosing when, where, and how much to work, adapting quickly to changing schedules and demands. Boomerang employees value flexibility within established roles, leveraging past company experience to negotiate work arrangements that balance organizational needs with personal preferences. Explore the evolving dynamics of workforce flexibility and how it reshapes employee engagement and productivity.
Rehiring
Gig workers provide companies with flexible, project-based labor without long-term commitments, while boomerang employees are rehired former staff who bring institutional knowledge and proven skills back to the organization. Rehiring boomerang employees can reduce onboarding costs and accelerate productivity due to their familiarity with company culture and processes. Explore the benefits and strategies of rehiring talent to optimize workforce dynamics.
Contractual Work
Gig workers engage in temporary, project-based tasks without long-term commitments, offering businesses flexibility and specialized skills for specific contracts. Boomerang employees, who return to former employers, provide continuity and institutional knowledge while often negotiating new contracts that balance stability and adaptability. Explore how contractual work paradigms evolve by comparing these workforce models in detail.
Source and External Links
Gig worker - Wikipedia - Gig workers are independent contractors, freelancers, and on-demand workers who provide services through temporary or project-based work arrangements, often facilitated by online platforms, and their legal classification varies globally with debates over employee status and benefits.
What Is a Gig Worker? Meaning and How To Find Gig Work - Upwork - A gig worker takes on short-term or project-based jobs for multiple clients rather than holding permanent employment, representing a key part of the emerging gig economy driven by shifting work patterns and technology.
The Pros and Cons of the Gig Economy - WGU - The gig economy enables workers to pursue flexible, freelance, or short-term jobs across various industries, with over 70 million Americans participating, reflecting a substantial shift toward flexible work but also raising questions about job security and benefits.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com