No-collar work encompasses roles in unconventional or emerging industries that do not fit traditional white- or blue-collar categories, often leveraging technology and creativity. Green-collar work focuses on environmentally sustainable jobs in renewable energy, conservation, and eco-friendly practices. Explore the key differences and opportunities between no-collar and green-collar employment sectors.
Why it is important
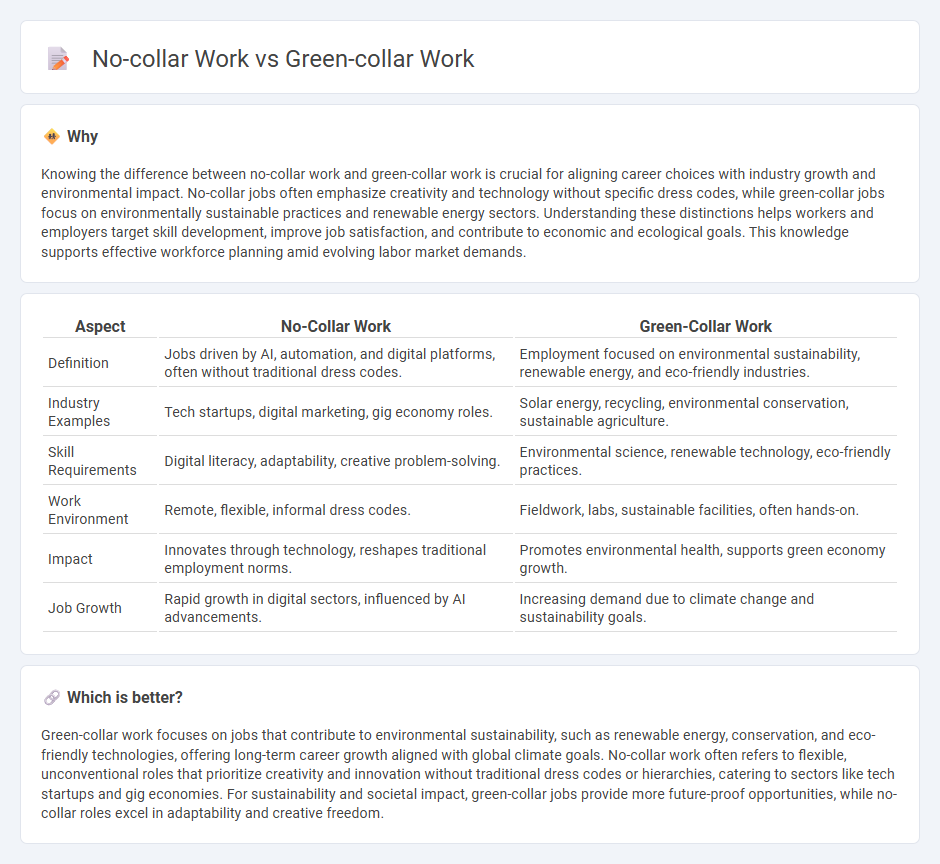
Knowing the difference between no-collar work and green-collar work is crucial for aligning career choices with industry growth and environmental impact. No-collar jobs often emphasize creativity and technology without specific dress codes, while green-collar jobs focus on environmentally sustainable practices and renewable energy sectors. Understanding these distinctions helps workers and employers target skill development, improve job satisfaction, and contribute to economic and ecological goals. This knowledge supports effective workforce planning amid evolving labor market demands.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | No-Collar Work | Green-Collar Work |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Jobs driven by AI, automation, and digital platforms, often without traditional dress codes. | Employment focused on environmental sustainability, renewable energy, and eco-friendly industries. |
| Industry Examples | Tech startups, digital marketing, gig economy roles. | Solar energy, recycling, environmental conservation, sustainable agriculture. |
| Skill Requirements | Digital literacy, adaptability, creative problem-solving. | Environmental science, renewable technology, eco-friendly practices. |
| Work Environment | Remote, flexible, informal dress codes. | Fieldwork, labs, sustainable facilities, often hands-on. |
| Impact | Innovates through technology, reshapes traditional employment norms. | Promotes environmental health, supports green economy growth. |
| Job Growth | Rapid growth in digital sectors, influenced by AI advancements. | Increasing demand due to climate change and sustainability goals. |
Which is better?
Green-collar work focuses on jobs that contribute to environmental sustainability, such as renewable energy, conservation, and eco-friendly technologies, offering long-term career growth aligned with global climate goals. No-collar work often refers to flexible, unconventional roles that prioritize creativity and innovation without traditional dress codes or hierarchies, catering to sectors like tech startups and gig economies. For sustainability and societal impact, green-collar jobs provide more future-proof opportunities, while no-collar roles excel in adaptability and creative freedom.
Connection
No-collar work, characterized by flexible, technology-driven roles, intersects with green-collar work through the shared focus on sustainability and innovation. Both sectors emphasize reducing environmental impact while leveraging digital skills to improve energy efficiency and promote eco-friendly practices. This convergence drives the growth of jobs that merge technological expertise with environmental stewardship in emerging green industries.
Key Terms
Sustainability
Green-collar work centers on employment in sectors dedicated to environmental sustainability, such as renewable energy, conservation, and eco-friendly manufacturing, aiming to reduce carbon footprints and promote clean technologies. No-collar work, often found in creative and tech industries, emphasizes flexibility and innovation but may not directly contribute to sustainability goals. Discover how these job categories influence ecological impact and drive future employment trends by learning more.
Traditional hierarchy
Green-collar work typically involves environmentally focused jobs within traditional hierarchical organizations where defined roles and management structures guide workflow and responsibility. No-collar work, by contrast, often breaks away from conventional hierarchies, favoring flexible roles and collaborative environments that prioritize skills and innovation over rigid titles. Explore how these different structures impact workplace culture and career growth.
Technological innovation
Green-collar work centers on environmentally sustainable jobs that leverage technological innovation to advance renewable energy, waste reduction, and green infrastructure. No-collar work, often characterized by creative and flexible roles in technology-driven industries, emphasizes innovation without strict corporate hierarchy, fostering rapid development in digital solutions and artificial intelligence. Explore how these contrasting employment models shape the future of work and innovation.
Source and External Links
Green-collar worker - A green-collar worker is employed in environmentally focused jobs that promote sustainability, such as conservation, renewable energy installation, green building, and environmental consulting, aiming to improve ecology and energy efficiency through design, policy, and technology.
What Does a "Green-Collar" Employee Do? (And Other ...) - Green-collar jobs are found in fields like conservation, green construction, electric vehicle development, environmental consulting, green energy production, organic farming, and recycling, all focused on reducing environmental impact and supporting sustainability.
What Are Green Collar Workers? - Green-collar workers contribute to environmental sustainability in roles across renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and waste management, playing a vital role in advancing eco-friendly practices for a sustainable future.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com