Neurodiversity hiring leverages individuals' unique cognitive strengths, enhancing innovation and problem-solving within organizations by embracing diverse neurological profiles such as autism and ADHD. Blind recruitment eliminates bias by anonymizing candidate information, promoting fairness and diversity through merit-based selection. Explore the benefits of combining these approaches to create a truly inclusive and dynamic workforce.
Why it is important
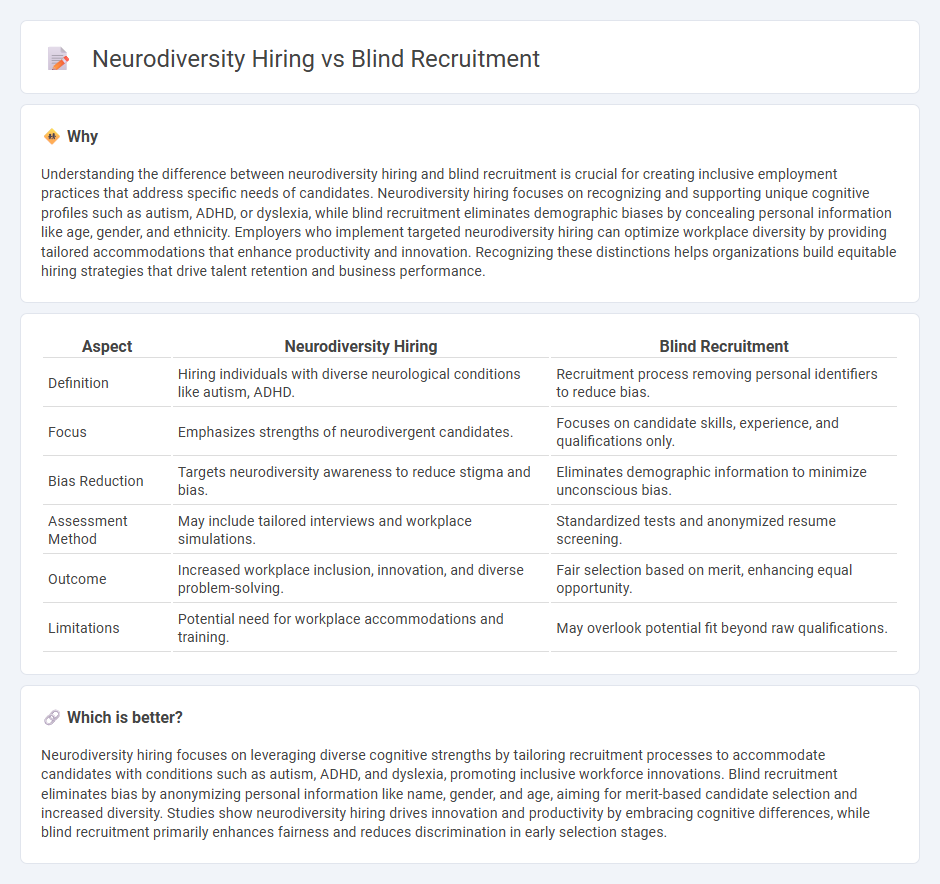
Understanding the difference between neurodiversity hiring and blind recruitment is crucial for creating inclusive employment practices that address specific needs of candidates. Neurodiversity hiring focuses on recognizing and supporting unique cognitive profiles such as autism, ADHD, or dyslexia, while blind recruitment eliminates demographic biases by concealing personal information like age, gender, and ethnicity. Employers who implement targeted neurodiversity hiring can optimize workplace diversity by providing tailored accommodations that enhance productivity and innovation. Recognizing these distinctions helps organizations build equitable hiring strategies that drive talent retention and business performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Neurodiversity Hiring | Blind Recruitment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hiring individuals with diverse neurological conditions like autism, ADHD. | Recruitment process removing personal identifiers to reduce bias. |
| Focus | Emphasizes strengths of neurodivergent candidates. | Focuses on candidate skills, experience, and qualifications only. |
| Bias Reduction | Targets neurodiversity awareness to reduce stigma and bias. | Eliminates demographic information to minimize unconscious bias. |
| Assessment Method | May include tailored interviews and workplace simulations. | Standardized tests and anonymized resume screening. |
| Outcome | Increased workplace inclusion, innovation, and diverse problem-solving. | Fair selection based on merit, enhancing equal opportunity. |
| Limitations | Potential need for workplace accommodations and training. | May overlook potential fit beyond raw qualifications. |
Which is better?
Neurodiversity hiring focuses on leveraging diverse cognitive strengths by tailoring recruitment processes to accommodate candidates with conditions such as autism, ADHD, and dyslexia, promoting inclusive workforce innovations. Blind recruitment eliminates bias by anonymizing personal information like name, gender, and age, aiming for merit-based candidate selection and increased diversity. Studies show neurodiversity hiring drives innovation and productivity by embracing cognitive differences, while blind recruitment primarily enhances fairness and reduces discrimination in early selection stages.
Connection
Neurodiversity hiring emphasizes recognizing diverse cognitive abilities in the workforce, while blind recruitment eliminates biases by removing identifiable candidate information during the hiring process. Both approaches aim to create an inclusive employment environment that focuses on skills and potential rather than traditional criteria like appearance or background. This connection enhances fair hiring practices, increasing opportunities for individuals with neurodiverse traits to access meaningful employment.
Key Terms
Unconscious Bias
Blind recruitment minimizes unconscious bias by removing identifiable candidate information such as names, gender, and ethnicity, promoting fair evaluation based solely on skills and experience. Neurodiversity hiring focuses on creating inclusive processes that recognize diverse cognitive styles and strengths, addressing biases related to neurotypical norms in recruitment. Explore deeper strategies to reduce unconscious bias and enhance diversity in talent acquisition.
Inclusive Assessment
Blind recruitment minimizes unconscious bias by removing identifiable candidate information during the hiring process, fostering fairness and diversity. Neurodiversity hiring emphasizes tailoring assessment methods to accommodate cognitive variations, like autism or ADHD, ensuring candidates are evaluated on skills rather than neurotypical norms. Explore how Inclusive Assessment bridges these strategies to create equitable hiring practices for all talents.
Accessibility Accommodations
Blind recruitment emphasizes anonymizing candidate information to reduce bias, while neurodiversity hiring prioritizes tailored Accessibility Accommodations to support diverse cognitive needs. Employers implementing inclusive technologies and personalized adjustments enhance workplace integration and performance for neurodivergent employees. Explore effective strategies to balance unbiased hiring processes with comprehensive accessibility measures for a truly inclusive workforce.
Source and External Links
Complete Guide to Blind Recruitment, What It Is and How It Works - Blind recruitment is a hiring method that removes personal info like name, gender, and age from applications to evaluate candidates purely on skills and results, aiming to eliminate bias especially at initial selection stages.
Blind Recruitment: Driving Diversity & Inclusion - Allied OneSource - Blind recruitment involves anonymizing applications to remove personal details and using standardized skill-based evaluations to ensure fair, merit-based hiring decisions that reduce unconscious bias.
The Advantages of Blind Recruiting - WorkGenius - Blind recruiting improves workplace diversity and inclusion by preventing bias linked to names or demographics, enabling employers to focus strictly on candidates' abilities and fit for the role.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com