Job stacking involves simultaneously holding multiple part-time jobs to maximize income, whereas the gig economy focuses on freelance or short-term contracts enabled by digital platforms. Both employment models offer flexible work arrangements but differ in job stability, income sources, and time management challenges. Explore the advantages and drawbacks of job stacking versus the gig economy to determine which better suits your career goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between job stacking and the gig economy is crucial for effective career planning and income stability. Job stacking involves holding multiple traditional jobs simultaneously to maximize overall earnings, whereas the gig economy focuses on short-term, freelance, or project-based work driven by digital platforms. Knowing this distinction helps workers optimize time management, tax obligations, and benefits eligibility tailored to their work style. Employers and policymakers also benefit by creating more accurate labor regulations and support systems aligned with these employment models.
Comparison Table
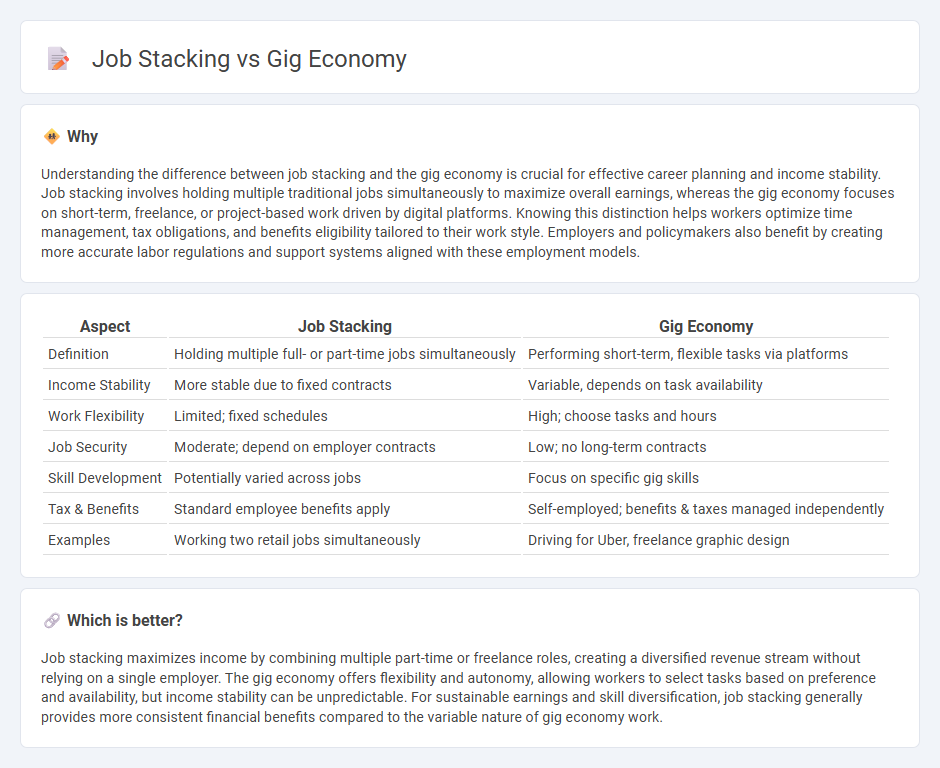
| Aspect | Job Stacking | Gig Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Holding multiple full- or part-time jobs simultaneously | Performing short-term, flexible tasks via platforms |
| Income Stability | More stable due to fixed contracts | Variable, depends on task availability |
| Work Flexibility | Limited; fixed schedules | High; choose tasks and hours |
| Job Security | Moderate; depend on employer contracts | Low; no long-term contracts |
| Skill Development | Potentially varied across jobs | Focus on specific gig skills |
| Tax & Benefits | Standard employee benefits apply | Self-employed; benefits & taxes managed independently |
| Examples | Working two retail jobs simultaneously | Driving for Uber, freelance graphic design |
Which is better?
Job stacking maximizes income by combining multiple part-time or freelance roles, creating a diversified revenue stream without relying on a single employer. The gig economy offers flexibility and autonomy, allowing workers to select tasks based on preference and availability, but income stability can be unpredictable. For sustainable earnings and skill diversification, job stacking generally provides more consistent financial benefits compared to the variable nature of gig economy work.
Connection
Job stacking involves holding multiple part-time or freelance positions simultaneously, a practice that thrives within the gig economy's flexible work environment. The gig economy offers diverse opportunities through digital platforms, enabling workers to combine various income streams efficiently. This synergy allows individuals to maximize earnings while maintaining autonomy over their work schedules.
Key Terms
Flexibility
The gig economy offers unparalleled flexibility by allowing workers to choose projects and set their own schedules, fostering autonomy in managing work-life balance. Job stacking involves simultaneously holding multiple part-time roles or gigs, maximizing income potential while maintaining adaptable working hours. Explore how these flexible work strategies can optimize your earnings and lifestyle.
Income sources
Gig economy work involves taking on short-term, flexible jobs through platforms like Uber or Fiverr, providing diverse income sources but often with unpredictable earnings. Job stacking refers to simultaneously managing multiple part-time or gig roles to maximize overall income, leveraging different skill sets and schedules to create a more stable financial foundation. Explore deeper insights into optimizing income through these strategies to boost your financial resilience.
Employment structure
The gig economy features short-term, flexible jobs often mediated through digital platforms, allowing workers to engage in various independent tasks without traditional employment contracts. Job stacking involves simultaneously managing multiple gig or part-time roles to maximize income and job security while maintaining autonomy. Explore how these evolving employment structures impact worker flexibility and financial stability.
Source and External Links
Gig Economy - Overview, Advantages, Disadvantages - The gig economy is a flexible labor market system where individuals work as independent contractors or freelancers via digital platforms, providing temporary services without traditional full-time employment, allowing businesses to reduce costs and offer consumers fast, varied services.
The Pros and Cons of the Gig Economy - The gig economy enables people to work on short-term projects or "gigs" with flexibility and autonomy, reshaping the workforce and business models, with over 70 million Americans participating and significant market growth projected through the next decade.
What is the Gig Economy?| Definition from TechTarget - It is a free market system where temporary jobs are common and digital platforms connect customers with gig workers like freelancers and contractors worldwide, decoupling jobs from locations and enabling more flexible, project-based work.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com