Fractional work involves professionals offering part-time expertise to multiple clients, focusing on specialized, high-value tasks within a structured timeframe. Gig work typically consists of short-term, task-oriented jobs completed on demand, often through digital platforms connecting freelancers with clients. Explore how understanding these models can optimize your employment strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between fractional work and gig work is crucial for managing expectations regarding job stability, benefits, and income consistency. Fractional work typically involves part-time roles with a longer commitment and potential access to benefits, whereas gig work consists of short-term, task-based assignments with more flexibility but less security. Knowing these distinctions helps workers make informed career decisions and navigate employment rights effectively. Employers also benefit by aligning recruitment strategies with the appropriate employment model to optimize workforce management.
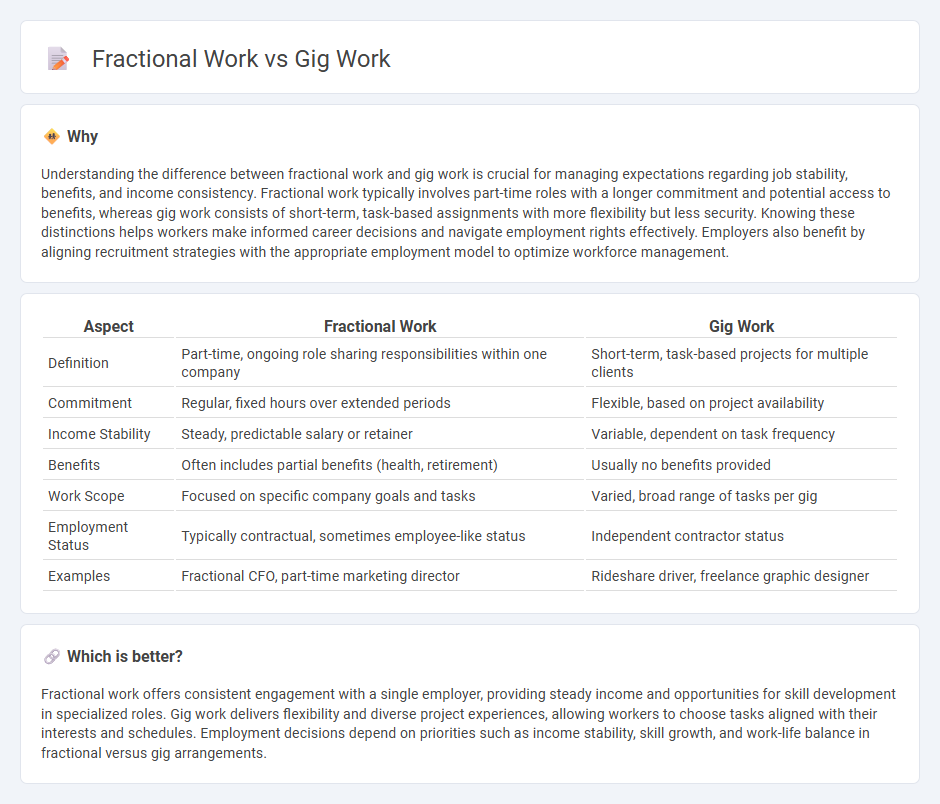
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Fractional Work | Gig Work |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Part-time, ongoing role sharing responsibilities within one company | Short-term, task-based projects for multiple clients |
| Commitment | Regular, fixed hours over extended periods | Flexible, based on project availability |
| Income Stability | Steady, predictable salary or retainer | Variable, dependent on task frequency |
| Benefits | Often includes partial benefits (health, retirement) | Usually no benefits provided |
| Work Scope | Focused on specific company goals and tasks | Varied, broad range of tasks per gig |
| Employment Status | Typically contractual, sometimes employee-like status | Independent contractor status |
| Examples | Fractional CFO, part-time marketing director | Rideshare driver, freelance graphic designer |
Which is better?
Fractional work offers consistent engagement with a single employer, providing steady income and opportunities for skill development in specialized roles. Gig work delivers flexibility and diverse project experiences, allowing workers to choose tasks aligned with their interests and schedules. Employment decisions depend on priorities such as income stability, skill growth, and work-life balance in fractional versus gig arrangements.
Connection
Fractional work and gig work both represent flexible employment models that allow individuals to engage in multiple short-term or project-based roles rather than traditional full-time positions. These forms of employment leverage digital platforms and remote opportunities to match workers with specific tasks or time-bound projects, emphasizing autonomy and diverse income streams. The rise of the gig economy has significantly contributed to the growth of fractional work by normalizing freelance engagements and on-demand services.
Key Terms
Flexibility
Gig work offers maximum flexibility by allowing individuals to choose tasks and schedules independently, ideal for short-term, varied projects. Fractional work provides flexibility through longer-term commitments with part-time involvement, granting experts the ability to manage workloads while delivering specialized skills. Explore more about how these work models adapt to different professional needs and lifestyles.
Duration
Gig work typically involves short-term, task-based projects that last from a few hours to several days, often providing immediate, flexible income. Fractional work spans longer durations, usually several months, where professionals contribute specialized skills part-time to multiple companies simultaneously. Explore the differences in work duration and benefits to determine which model suits your career goals.
Commitment
Gig work often involves short-term, task-based assignments with minimal commitment, allowing flexibility but less stability. Fractional work requires dedicated time and expertise over an extended period, offering deeper engagement and consistent contribution to business goals. Explore the differences in commitment levels to determine which work model suits your professional needs.
Source and External Links
35 Gigs Jobs To Explore (With Benefits and Tips) | Indeed.com - Gig work offers flexible, contract-based or on-demand jobs across industries such as transportation, delivery, and personal services including ride-share driver, food delivery, dog walking, and telehealth provider.
How To Find and Get Gig Work Fast | Indeed.com - To quickly find gig work, you can network with gig contractors, join on-demand apps like Uber Eats or DoorDash, and look for flexible, location-based gigs that allow you to work as your own boss.
Manage taxes for your gig work | Internal Revenue Service - Gig work includes self-employed activities done through digital platforms like driving, renting property, running errands, or providing freelance services, and requires filing taxes if net earnings exceed $400.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com